Yeast Lab Cellular Respiration

Yeast Cellular Respiration Lab Youtube Part 2: aerobic respiration in yeast. optional activity or demonstration. this part of the lab investigates aerobic cellular respiration by saccharomyces cerevisiae, also referred to as “baker’s yeast” and “brewer’s yeast.” yeast is a unicellular fungus that can convert glucose into carbon dioxide and atp when oxygen is present. Yeast can metabolize glucose through two different pathways: aerobic respiration and anaerobic fermentation. in aerobic respiration, yeast utilize oxygen to break down glucose molecules completely, resulting in the production of carbon dioxide (co 2) and water (h 2 o) as byproducts. this process is highly efficient and yields a larger amount of.
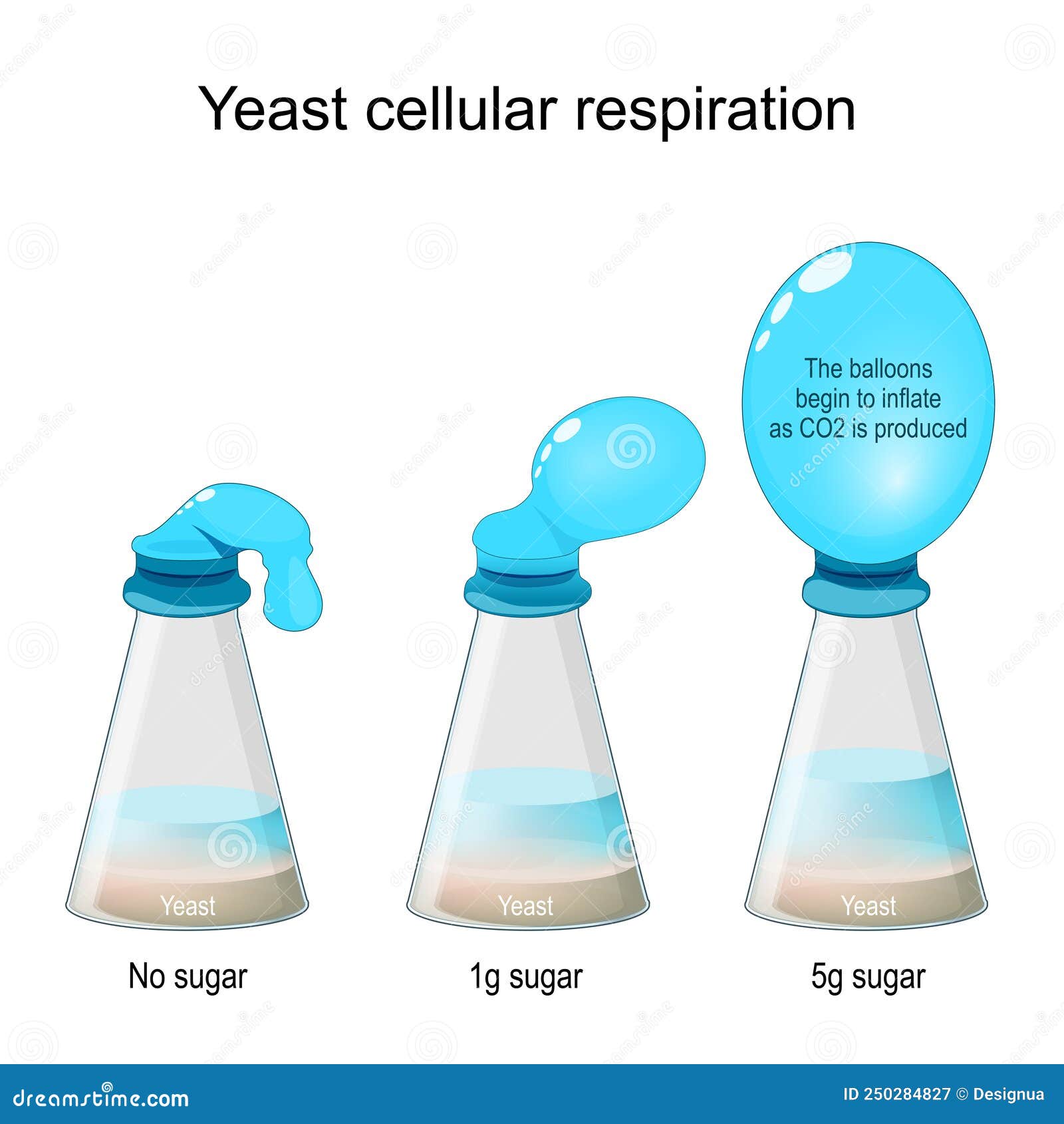
Yeast Cellular Respiration Lab Bottle Balloon Experiment Stock Vector This lab explores the concepts of cellular respiration and fermentation in yeast. yeast do alcoholic fermentation and one of the byproducts is carbon dioxide. when you bake bread with yeast, carbon dioxide is produced, which forms bubbles in the dough, causing the dough to rise. the heat kills the yeast and the bubble pockets lighten the bread. This experiment uses a living organism to investigate the conditions under which life grows the best.(part 8 of 10)playlist link pla. To atp that the organism can use for its cellular. espiration is below: c6h12o6 6 o2 6 h2o 6 co2 atpin this lab. we will observe yeast cells perf. ming cellular respiration. yeast are facultative anaerobes. this means. at if oxygen is present, they will use cellular respiration. however, if there is no oxygen present i. Ethanol (alcohol) and carbon dioxide. alcoholic fermentation is. anaerobic process in which cells convert pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol; carried out by many bacteria and fungi such as yeasts. alcoholic fermentation equation. pyruvic acid nadh > alcohol co2 nad .
Cellular Respiration In Yeast Lab By Rachel Taylor Tpt To atp that the organism can use for its cellular. espiration is below: c6h12o6 6 o2 6 h2o 6 co2 atpin this lab. we will observe yeast cells perf. ming cellular respiration. yeast are facultative anaerobes. this means. at if oxygen is present, they will use cellular respiration. however, if there is no oxygen present i. Ethanol (alcohol) and carbon dioxide. alcoholic fermentation is. anaerobic process in which cells convert pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol; carried out by many bacteria and fungi such as yeasts. alcoholic fermentation equation. pyruvic acid nadh > alcohol co2 nad . We will investigate fermentation by measuring the amount of carbon dioxide produced by yeast. the rate of cellular respiration is proportional to the amount of co 2 produced (see the equation for fermentation above). in this experiment, we will measure the rate of cellular respiration using either distilled water or one of four different food. Produce cellular energy. here is the chemical reaction of fermentation, which produces ethanol and carbon dioxide as metabolic waste products. objective: in this lab, students will use the respiration powers of yeast to blow balloons. this activity will reinforce the basic principles of respiration as a fundamental metabolic process for.

Cellular Respiration Lab Yeast Sugar Balloon Activity Middle School We will investigate fermentation by measuring the amount of carbon dioxide produced by yeast. the rate of cellular respiration is proportional to the amount of co 2 produced (see the equation for fermentation above). in this experiment, we will measure the rate of cellular respiration using either distilled water or one of four different food. Produce cellular energy. here is the chemical reaction of fermentation, which produces ethanol and carbon dioxide as metabolic waste products. objective: in this lab, students will use the respiration powers of yeast to blow balloons. this activity will reinforce the basic principles of respiration as a fundamental metabolic process for.

Comments are closed.