Yeast Fermentation In Bread

Easy Slow Fermented Bread Colorful Foodie Here a portion of the flour is matured with water and a small amount of yeast. yeast fermentation matures the flour to produce a prefermented dough. after 12 18 hours (typically) it is added to the main dough. when the preferment is ready to use it will have bubbles throughout, and on the surface. To prevent stalls in fermentation, following proper bread baking techniques is essential. first and foremost, ensure that the dough is at the right temperature – around 75 80°f (24 27°c) – before adding the yeast. it’s also crucial to use fresh yeast and provide a nutrient rich environment by adding sugar or honey to the dough.

Yeast Fermentation In Bread Carbon dioxide helps bread rise. carbon dioxide is one of the major gases responsible for leavening in baking. in cakes, it comes from the reaction of sodium bicarbonate under acidic conditions. in bread making (or special yeasted cakes), the yeast organisms expel carbon dioxide as they feed off of sugars. as the dough rises and proofs, carbon. Introduction to yeast. yeast, a type of fungus, is a living organism that converts sugars into carbon dioxide, gas, and alcohol through fermentation. this carbon dioxide gas causes the dough to rise and gives the bread its fluffy and light texture. in bread making, bakers commonly use active dry yeast or instant yeast. 2.2.1. bread fermentation . the fermentation of the dough made by the yeasts is the most critical phase in the making of bread. the fermentative yield of yeast cells during this fermentation is crucial and determines the final quality of the bread. July 22, 2019. 122. bulk fermentation (also called the first rise or primary fermentation) is one of the most important steps of yeast bread baking. it begins right when mixing ends and lasts until the dough is divided and preshaped. the name signifies exactly what it is: the step when the dough is fermenting in a large, single mass.

Fermented Bread With Spikes Of Wheat Flour And Yeast Traditional 2.2.1. bread fermentation . the fermentation of the dough made by the yeasts is the most critical phase in the making of bread. the fermentative yield of yeast cells during this fermentation is crucial and determines the final quality of the bread. July 22, 2019. 122. bulk fermentation (also called the first rise or primary fermentation) is one of the most important steps of yeast bread baking. it begins right when mixing ends and lasts until the dough is divided and preshaped. the name signifies exactly what it is: the step when the dough is fermenting in a large, single mass. Fermentation in bread is a process that involves the breakdown of sugars in the dough by yeast, resulting in the production of carbon dioxide and alcohol. this process is crucial in creating the light, airy texture that we associate with good bread. the yeast feeds on the sugars in the dough, producing carbon dioxide as a byproduct, which. This is the most common type of fermentation and generally lasts between 2 and 5 hours. bulk fermentation at warmer temperatures encourages strong yeast and bacterial fermentation that results in an active and flavorful bread dough. temperature: 74 to 78°f (23 to 25°c) typical duration: 2 to 5 hours.

Yeast Fermentation In Bread How Does It Work Lesaffre Au Fermentation in bread is a process that involves the breakdown of sugars in the dough by yeast, resulting in the production of carbon dioxide and alcohol. this process is crucial in creating the light, airy texture that we associate with good bread. the yeast feeds on the sugars in the dough, producing carbon dioxide as a byproduct, which. This is the most common type of fermentation and generally lasts between 2 and 5 hours. bulk fermentation at warmer temperatures encourages strong yeast and bacterial fermentation that results in an active and flavorful bread dough. temperature: 74 to 78°f (23 to 25°c) typical duration: 2 to 5 hours.
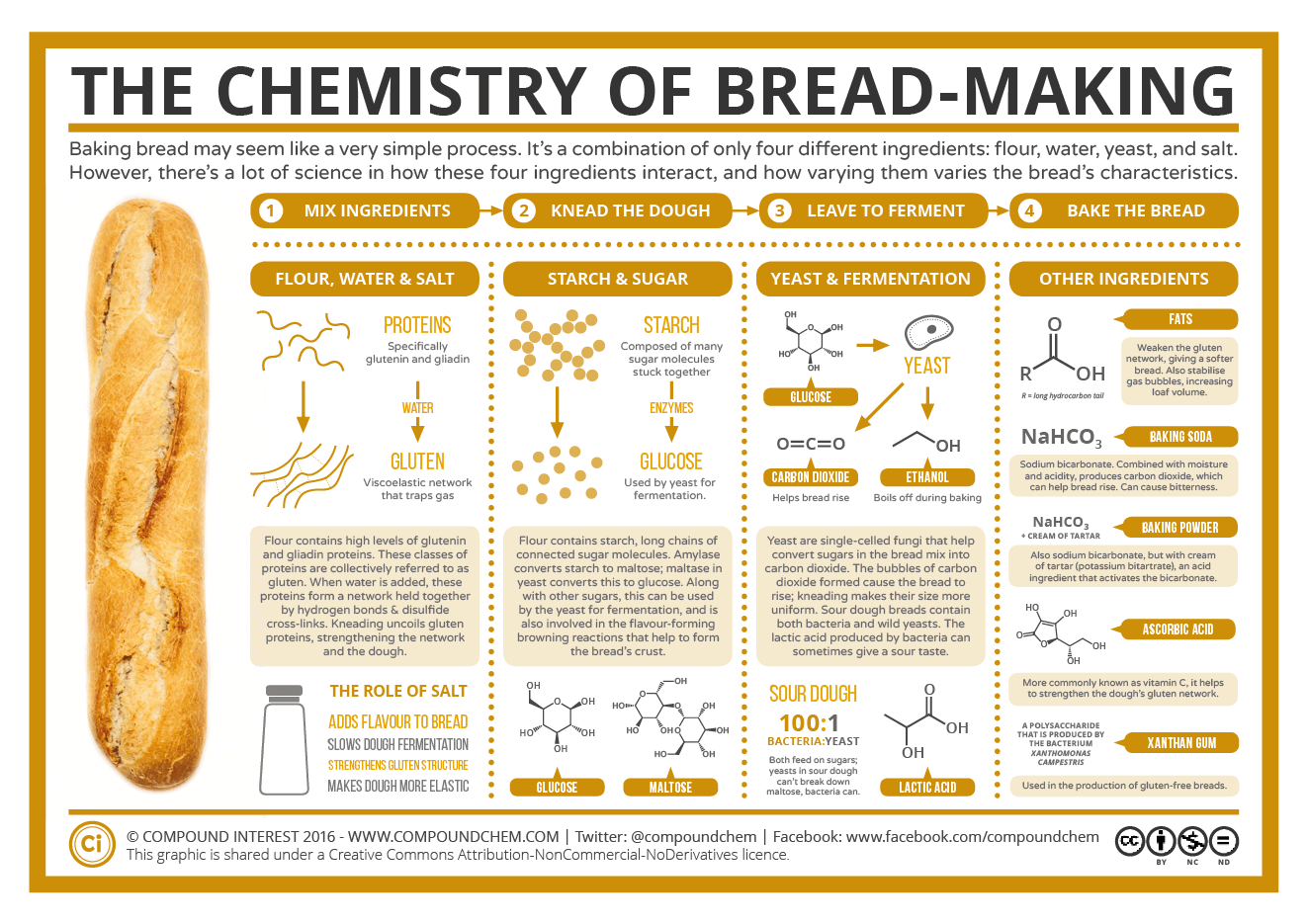
Baking Bread The Chemistry Of Bread Making Compound Interest

Comments are closed.