X Ray Diffraction Xrd Principle And Use
Xrd вђ X Ray Diffraction вђ About Tribology X ray diffraction is a common technique that determine a sample's composition or crystalline structure. for larger crystals such as macromolecules and inorganic compounds, it can be used to determine the structure of atoms within the sample. if the crystal size is too small, it can determine sample composition, crystallinity, and phase purity. X ray diffraction (xrd) is a non destructive technique for analyzing the structure of materials, primarily at the atomic or molecular level. it works best for materials that are crystalline or partially crystalline (i.e., that have periodic structural order) but is also used to study non crystalline materials.
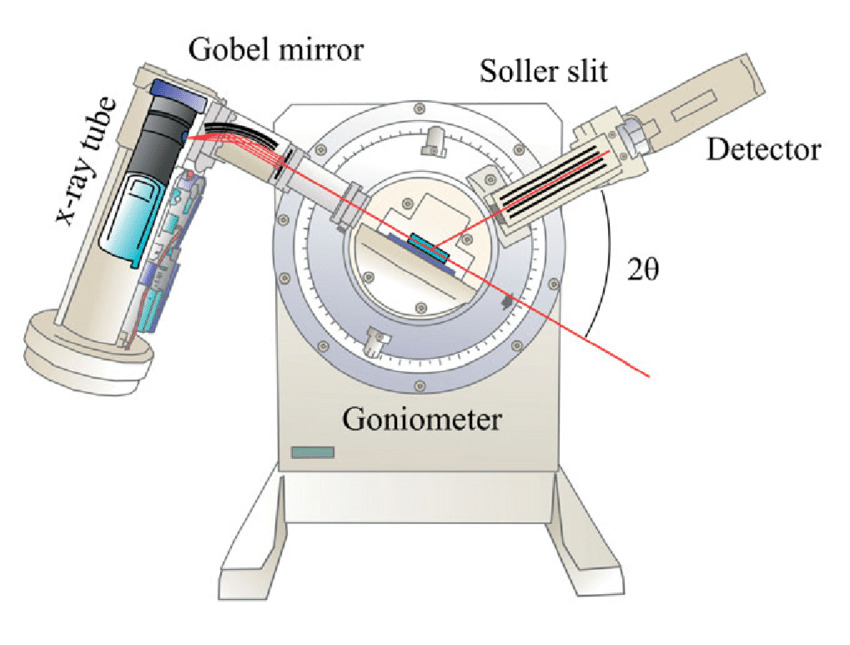
X Ray Diffraction Xrd Principle And Use Debye scherrer camera. 2q = 0°. a sample of some hundreds of crystals (i.e. a powdered sample) show that the diffracted beams form continuous cones. a circle of film is used to record the diffraction pattern as shown. each cone intersects the film giving diffraction lines. the lines are seen as arcs on the film. An x ray diffractometer is the instrument we use to produce monochromatic x rays, focus the beam on a sample, scan through a range of 2θ, and then detect the reflected x rays and their intensity. monochromatic x rays are generated in a cathode ray tube. a filament of tungsten is heated to produce electrons which are then accelerated towards an. X ray diffraction is extensively used in chemistry for the characterization of organic and inorganic compounds that are made for pharmaceutical companies or making batteries of the cell phones. xrd finds the geometry or shape of a molecule using x rays. this technique is based on the elastic scattering of x rays from structures that have long. X ray powder diffraction (xrd) is a rapid analytical technique primarily used for phase identification of a crystalline material and can provide information on unit cell dimensions. the analyzed material is finely ground, homogenized, and average bulk composition is determined.

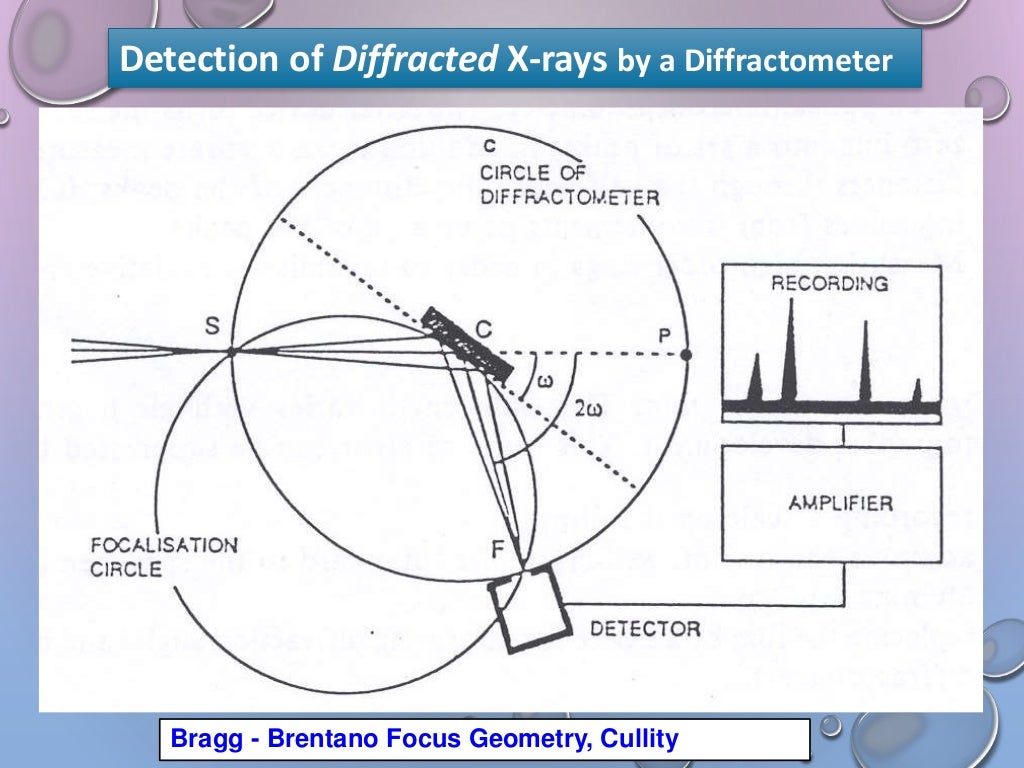
X Ray Diffraction Analysis Principle Instrument And Applications I X ray diffraction is extensively used in chemistry for the characterization of organic and inorganic compounds that are made for pharmaceutical companies or making batteries of the cell phones. xrd finds the geometry or shape of a molecule using x rays. this technique is based on the elastic scattering of x rays from structures that have long. X ray powder diffraction (xrd) is a rapid analytical technique primarily used for phase identification of a crystalline material and can provide information on unit cell dimensions. the analyzed material is finely ground, homogenized, and average bulk composition is determined. We can use grinded bulk sample into fine powders, which are typical under 10 µm, 2 as samples in powder x ray diffraction (xrd). unlike single crystal x ray diffraction (x ray crystallography) technique, the sample will distribute evenly at every possible orientation and powder xrd collects one dimensional information, which is a diagram of. Bragg’s description. the incident beam will be scattered at all scattering centres, which lay on lattice planes. the beam scattered at different lattice planes must be scattered coherent, to give an maximum in intensity. the angle between incident beam and the lattice planes is called θ. the angle between incident and scattered beam is 2θ .

Principle Of The X Ray Diffraction Download Scientific Diagram We can use grinded bulk sample into fine powders, which are typical under 10 µm, 2 as samples in powder x ray diffraction (xrd). unlike single crystal x ray diffraction (x ray crystallography) technique, the sample will distribute evenly at every possible orientation and powder xrd collects one dimensional information, which is a diagram of. Bragg’s description. the incident beam will be scattered at all scattering centres, which lay on lattice planes. the beam scattered at different lattice planes must be scattered coherent, to give an maximum in intensity. the angle between incident beam and the lattice planes is called θ. the angle between incident and scattered beam is 2θ .

Comments are closed.