Why It Matters Rocks And The Rock Cycle Geology

Rock Cycle Explanation And Diagram Pdf The rock cycle also gives scientists and engineers an idea on where energy sources (mainly fossil fuels, which are found only in sedimentary rock) and building materials such as marble or granite may be located. we will see throughout the course how this cycle plays into just about every aspect of geology. here’s a visual representation of. We need soil to survive—imagine trying to grow vegetables without it. this is an immediate connection to the food chain. the rock cycle also gives scientists and engineers an idea on where energy sources (mainly fossil fuels, which are found only in sedimentary rock) and building materials such as marble or granite may be located.

Why It Matters Rocks And The Rock Cycle Geology Noun. rock formed from fragments of other rocks or the remains of plants or animals. weathering. noun. the breaking down or dissolving of the earth's surface rocks and minerals. the rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in earth’s crust. The rock cycle is the natural, continuous process that forms, breaks down, and reforms rock through geological, chemical, and physical processes. through the cycle, rocks convert between igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary forms. it is a dynamic system that recycles earth’s materials in different forms, from molten magma deep below the. Rock cycle. the rock cycle describes the processes through which the three main rock types (igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary) transform from one type into another. the formation, movement and transformation of rocks results from earth’s internal heat, pressure from tectonic processes, and the effects of water, wind, gravity, and. The rock cycle highlights the dynamic nature of earth’s geology and the interconnectedness of its processes. it explains how rocks of different types can be related and how geological forces such as plate tectonics, volcanic activity, erosion, and sedimentation play roles in shaping the earth’s surface and changing its rock composition over.
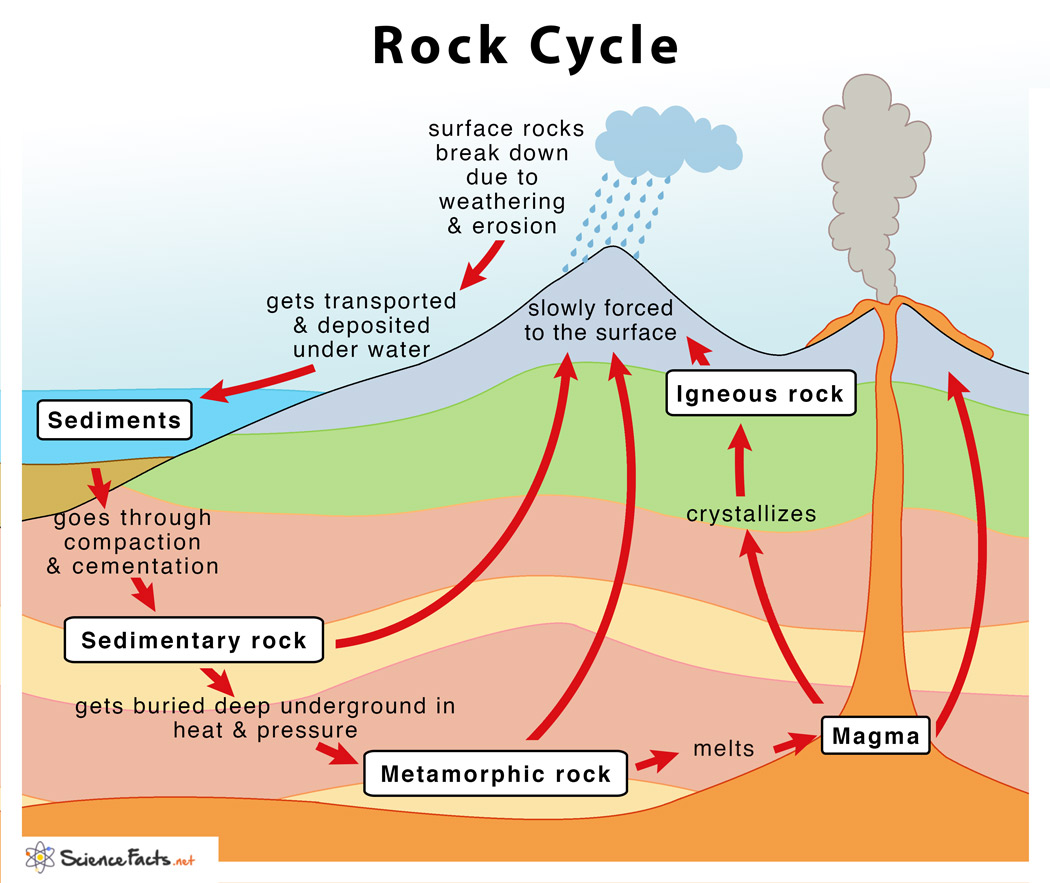
Rock Cycle вђ Definition Steps Importance Diagram Rock cycle. the rock cycle describes the processes through which the three main rock types (igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary) transform from one type into another. the formation, movement and transformation of rocks results from earth’s internal heat, pressure from tectonic processes, and the effects of water, wind, gravity, and. The rock cycle highlights the dynamic nature of earth’s geology and the interconnectedness of its processes. it explains how rocks of different types can be related and how geological forces such as plate tectonics, volcanic activity, erosion, and sedimentation play roles in shaping the earth’s surface and changing its rock composition over. This is how soil forms, through the breakdown of rocks. we need soil to survive—imagine trying to grow vegetables without it. this is an immediate connection to the food chain. the rock cycle also gives scientists and engineers an idea on where energy sources (mainly fossil fuels, which are found only in sedimentary rock) and building. 3.1: why it matters. identify and compare common rock forming minerals, interpret and understand mineral structures, mineral properties. in this section we will learn about the rock cycle. please watch this short video for an introduction: as you can see, the rock cycle is never ending. the video explained how rocks change from one rock type to.
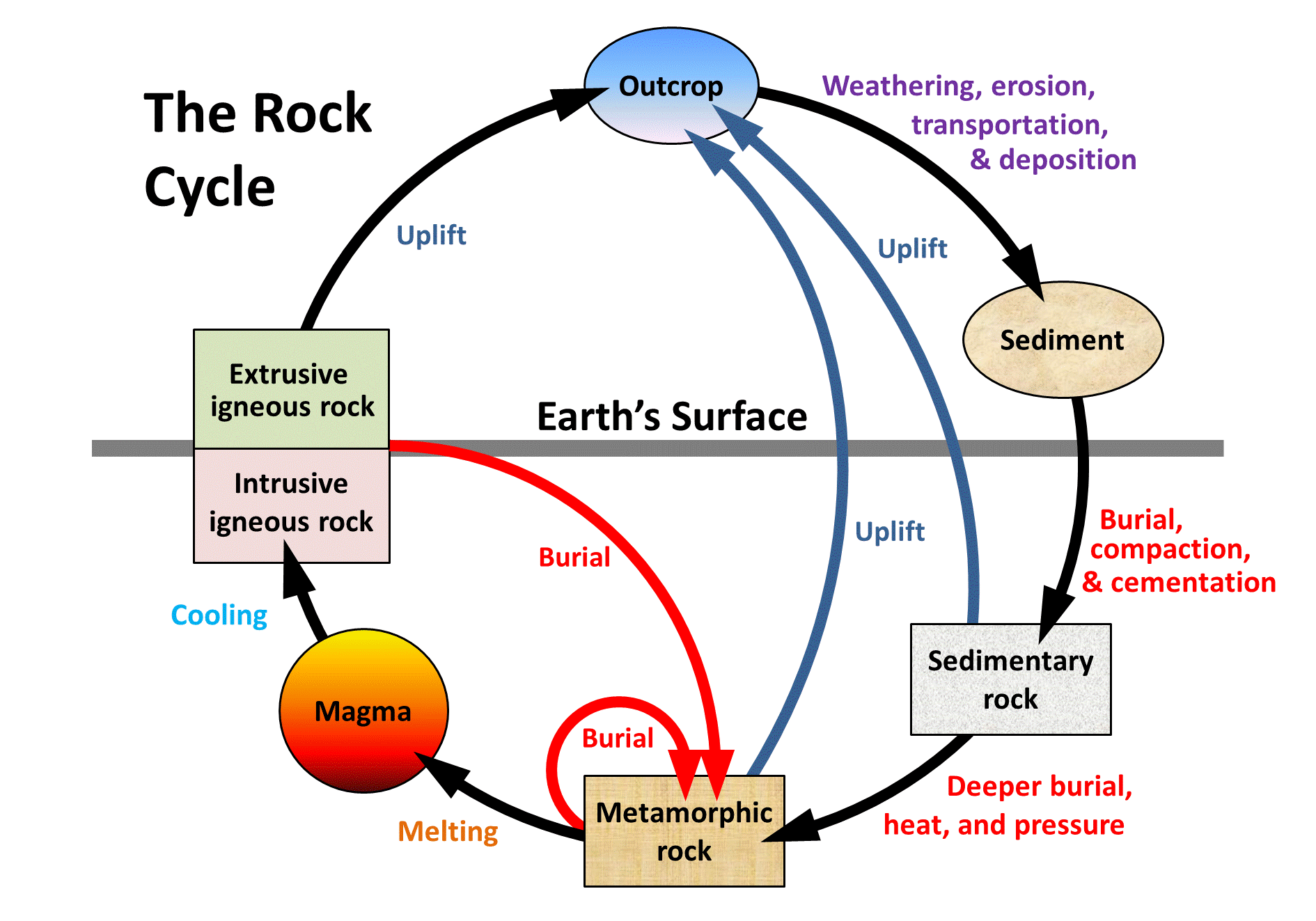
The Rock Cycle Describes Geologic Processes In Which This is how soil forms, through the breakdown of rocks. we need soil to survive—imagine trying to grow vegetables without it. this is an immediate connection to the food chain. the rock cycle also gives scientists and engineers an idea on where energy sources (mainly fossil fuels, which are found only in sedimentary rock) and building. 3.1: why it matters. identify and compare common rock forming minerals, interpret and understand mineral structures, mineral properties. in this section we will learn about the rock cycle. please watch this short video for an introduction: as you can see, the rock cycle is never ending. the video explained how rocks change from one rock type to.

Comments are closed.