Which Layer Of The Tcp Ip Stack Combines The Osi Model Physical And
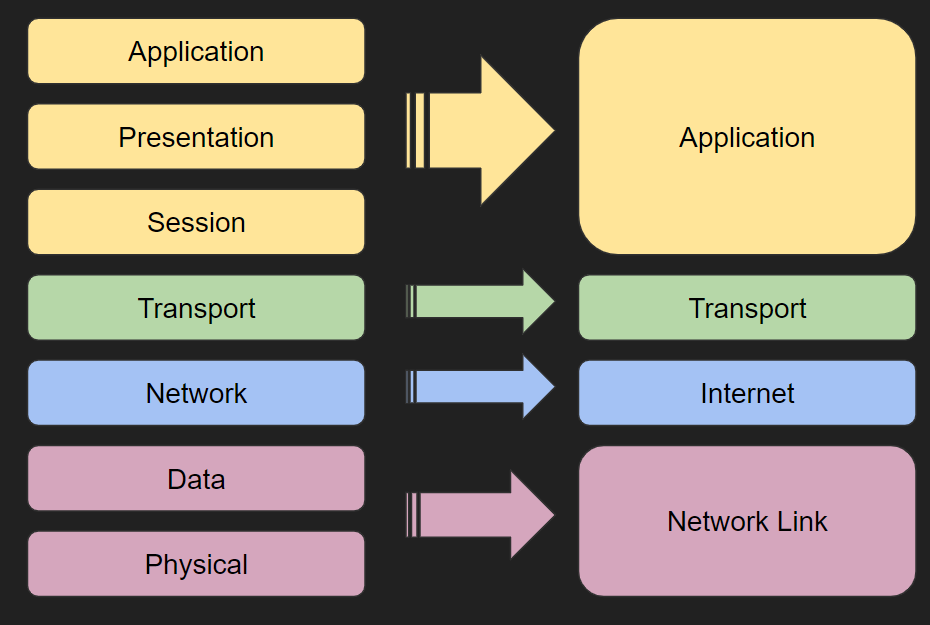
Tcp Ip Model A Level Computer Science The tcp ip model is a fundamental framework for computer networking. it stands for transmission control protocol internet protocol, which are the core protocols of the internet. this model defines how data is transmitted over networks, ensuring reliable communication between devices. it consists of four layers: the link layer, the internet. Tcp ip has four layers. osi model, the transport layer is only connection oriented. a layer of the tcp ip model is both connection oriented and connectionless. in the osi model, the data link layer and physical are separate layers. in tcp, physical and data link are both combined as a single host to network layer.

Osi Model Vs Tcp Ip Model Route Xp In tcp ip, this provides users with the physical standards, transport functions, network interface, and internetworking functions that correspond with the first three layers of the osi model. in other words, in the tcp ip model, these services are all done in the application layer. here is a breakdown of what each layer in the tcp ip model does:. Definition. tcp ip stands for transmission control protocol internet protocol. osi stands for open systems interconnection. developed by. it is developed by dod (department of defence) project agency. osi model is developed by iso (international standard organization). technology platform. it comprises of a set of standard protocols which. The layers described by rfc 1122 and rfc 1123 each encapsulate protocols that satisfy the layer’s functionality. let’s look at each of these communications layers and see how tcp and ip stack up in this model of the internet layer cake. link layer protocols. the link layer is the most basic, or lowest level, classification of communication. Differences between tcp ip vs osi models. the tcp ip model is older than osi model (it was created much earlier). the 2 models differ in how they split the various networking functions. the osi model provides 7 layers while the tcp ip uses only 4 layers to define its stack. figure 3 below shows clearly the difference between the 2 stacks:.
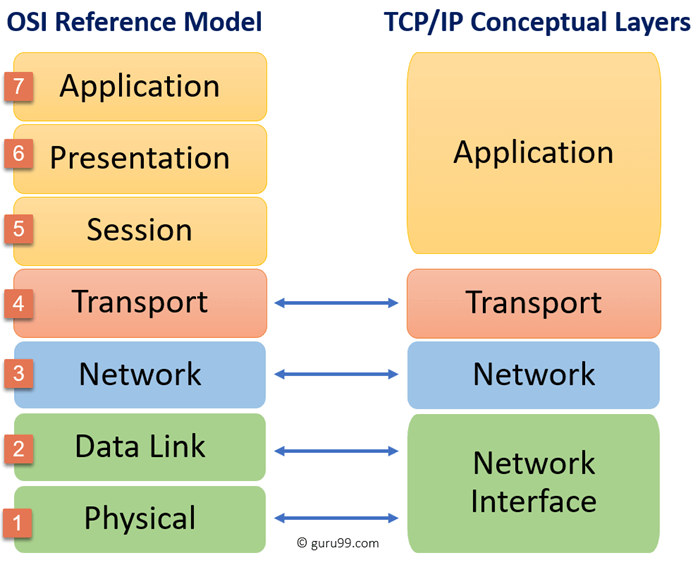
How Each Of The Network Protocol Layers Work Behind The Scene Sudeep The layers described by rfc 1122 and rfc 1123 each encapsulate protocols that satisfy the layer’s functionality. let’s look at each of these communications layers and see how tcp and ip stack up in this model of the internet layer cake. link layer protocols. the link layer is the most basic, or lowest level, classification of communication. Differences between tcp ip vs osi models. the tcp ip model is older than osi model (it was created much earlier). the 2 models differ in how they split the various networking functions. the osi model provides 7 layers while the tcp ip uses only 4 layers to define its stack. figure 3 below shows clearly the difference between the 2 stacks:. Internet or network layer. in the original tcp ip model, this layer is defined as the internet layer. in the updated version, it is renamed to the network layer. the main functions of this layer are addressing and routing. for these functions, it uses ip protocol. The tcp ip architectural model has four layers that approximately match six of the seven layers in the osi reference model. the tcp ip model does not address the physical layer, which is where hardware devices reside. the next three layers— network interface, internet and (host to host) transport —correspond to layers 2, 3 and 4 of the osi.

Introduction Internet or network layer. in the original tcp ip model, this layer is defined as the internet layer. in the updated version, it is renamed to the network layer. the main functions of this layer are addressing and routing. for these functions, it uses ip protocol. The tcp ip architectural model has four layers that approximately match six of the seven layers in the osi reference model. the tcp ip model does not address the physical layer, which is where hardware devices reside. the next three layers— network interface, internet and (host to host) transport —correspond to layers 2, 3 and 4 of the osi.

Comments are closed.