What Is The Biogenic Carbon Cycle Inside Renewable Fuels
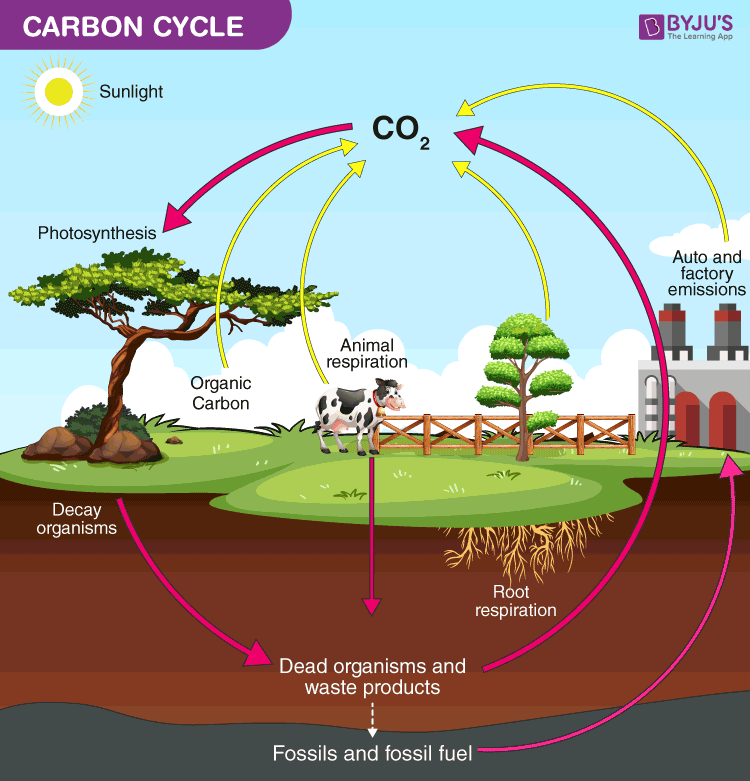
Carbon Cycle Definition Process Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Biogenic carbons refer to all those which are stored in, sequestered by and emitted through organic matter. the most common biogenic feedstocks include trees, plants and soil, which absorb carbon as a natural part of their life cycle. this process occurs during photosynthesis, when organic flora removes carbon from the atmosphere and deposits. Biogenic carbon vs non biogenic carbon. on the one hand, biogenic carbon is absorbed and stored by the flora on our planet as a natural consequence of its life cycle. through the process of photosynthesis, carbon is taken from the air and distributed among the leaves, stems and roots of the plant in question, or else sequestered in the soil.

Systems Thinking And The Carbon Cycle вђ An Interactive Introduction To Carbon used for e fuels should be based primarily on biogenic co2, while fossil co2 should be kept underground. it is important that it is not the other way around because storing biogenic co2 will reduce the availability of a key component of e fuels, which will drive up prices and slow down the decarbonization of hard to abate sectors. In other words, fossil fuel use increases the total amount of carbon in the biosphere atmosphere system while bioenergy systems operates within this system; biomass combustion simply returns to the atmosphere the carbon that was absorbed as the plants grew.*. the net greenhouse gas (ghg) outcome of using biomass for energy cannot be determined. To be qualified as renewable energy for cellulosic fuels, the life cycle ghg emissions should be 60% less than the life cycle ghg emissions of the 2005 baseline average gasoline or diesel fuel (92. In contrast to fossil fuels, carbon dioxide (co 2) emissions from the combustion of biomass or biomass derived fuels are biogenic, meaning that carbon in the fuel comes from atmospheric co 2.
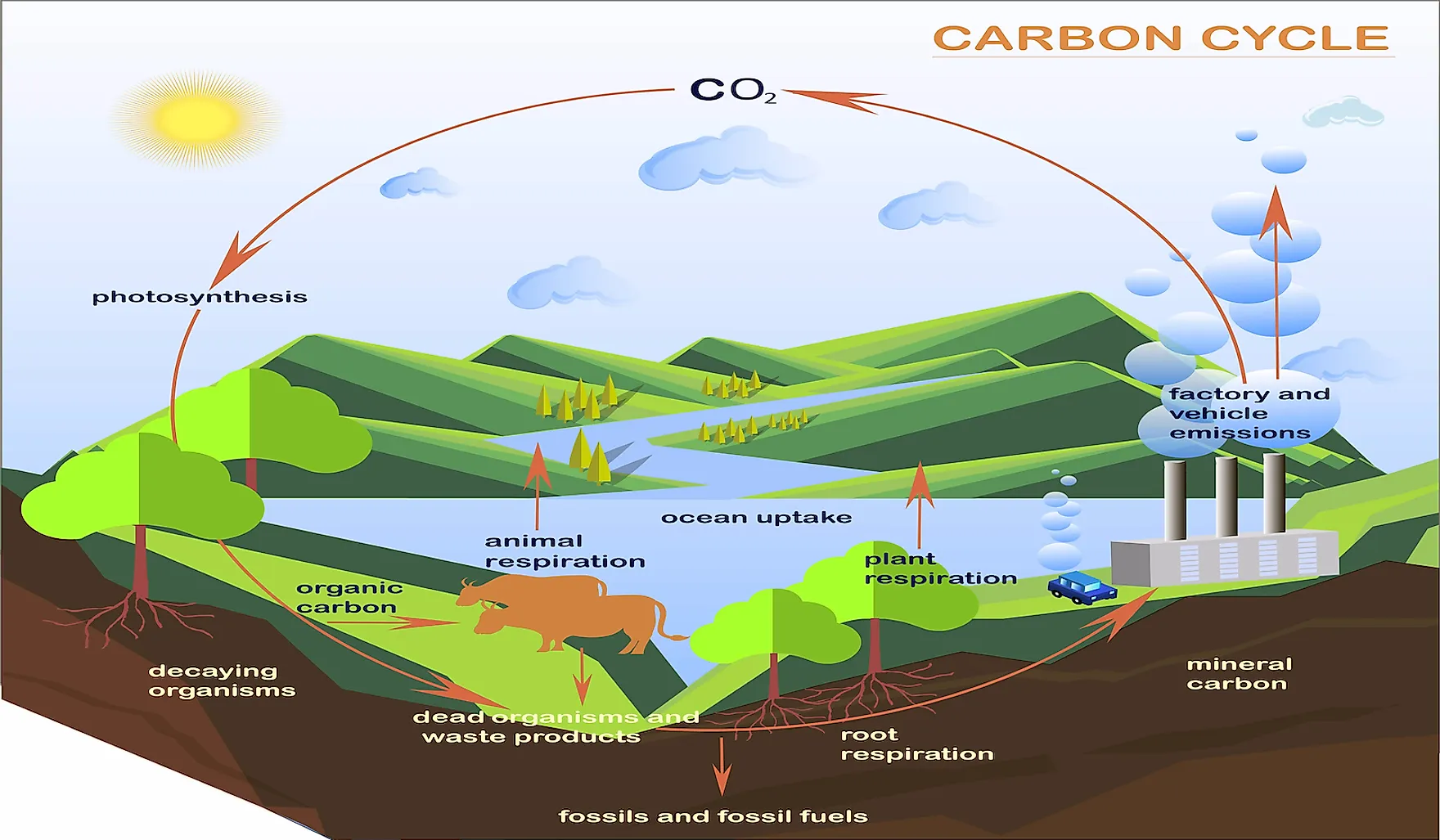
What Is The Carbon Cycle Worldatlas To be qualified as renewable energy for cellulosic fuels, the life cycle ghg emissions should be 60% less than the life cycle ghg emissions of the 2005 baseline average gasoline or diesel fuel (92. In contrast to fossil fuels, carbon dioxide (co 2) emissions from the combustion of biomass or biomass derived fuels are biogenic, meaning that carbon in the fuel comes from atmospheric co 2. A climate impact assessment, such as life cycle assessment or carbon footprint, is crucial for a science based policy recommendation. however, those assessments can often be incomplete, especially since many of those adopt an assumption that biogenic co 2 emissions cause no harm to the climate and do not need to be accounted. The term “biogenic carbon” refers to the carbon which is sequestered by and stored in organic matter, such as plants, trees, grasses and soil. these organisms naturally absorb carbon as part of their life cycle, converting it into cellulose which helps them to grow and develop. in return, they release oxygen into the atmosphere, which is.

Quiz 3 Carbon Cycle Diagram Quizlet A climate impact assessment, such as life cycle assessment or carbon footprint, is crucial for a science based policy recommendation. however, those assessments can often be incomplete, especially since many of those adopt an assumption that biogenic co 2 emissions cause no harm to the climate and do not need to be accounted. The term “biogenic carbon” refers to the carbon which is sequestered by and stored in organic matter, such as plants, trees, grasses and soil. these organisms naturally absorb carbon as part of their life cycle, converting it into cellulose which helps them to grow and develop. in return, they release oxygen into the atmosphere, which is.

Comments are closed.