What Are The 4 Different Macromolecules
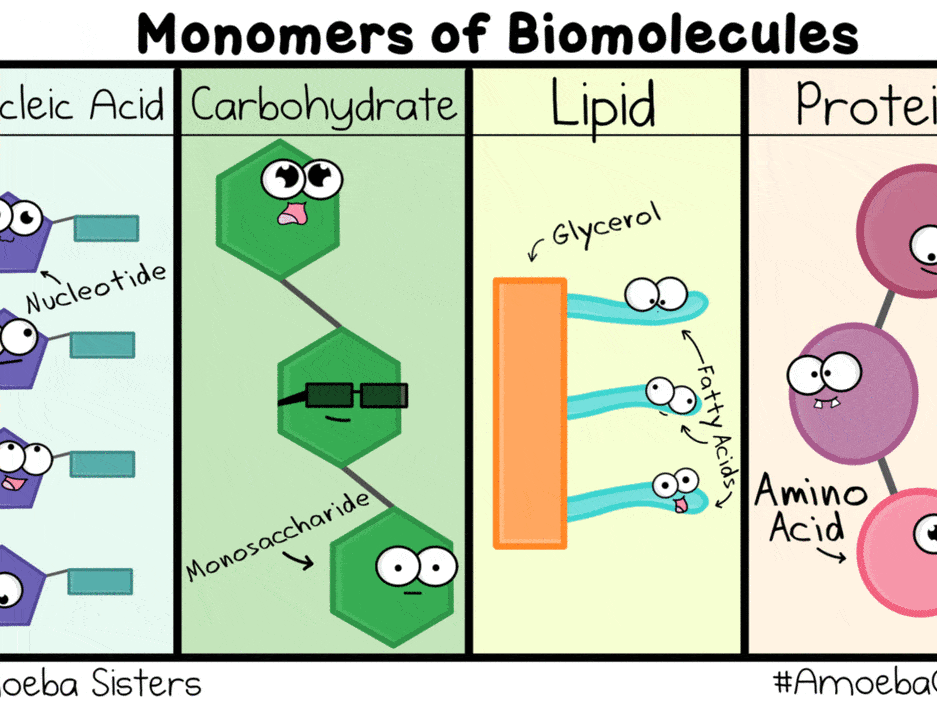
What Are The 4 Different Macromolecules The four types of macromolecules are proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. macromolecules are large, complex molecules that are fundamental to both biological and chemical processes. they play a crucial role in the structure, function, and regulation of living organisms and have diverse applications in various scientific fields. Biology – or informally, life itself – is characterized by elegant macromolecules that have evolved over hundreds of millions of years to serve a range of critical functions. these are often categorized into four basic types: carbohydrates (or polysaccharides), lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. if you have any background in nutrition, you.

What Are The 4 Types Of Macromolecules In summary: different types of biological macromolecules. proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to. 5.14: different types of biological macromolecules. now that we’ve discussed the four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), let’s talk about macromolecules as a whole. each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules: carbohydrates. lipids. proteins. nucleic acids. each of these types of macromolecules performs a wide array of important functions within the cell; a cell cannot perform its role within the body without many different types of these crucial molecules. Lipids are a class of macromolecules that are nonpolar and hydrophobic in nature. major types include fats and oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. fats and oils are a stored form of energy and can include triglycerides. fats and oils are usually made up of fatty acids and glycerol. proteins are a class of macromolecules that can perform a.

Five Simplified Diagrams Of Biological Molecules There are four major classes of biological macromolecules: carbohydrates. lipids. proteins. nucleic acids. each of these types of macromolecules performs a wide array of important functions within the cell; a cell cannot perform its role within the body without many different types of these crucial molecules. Lipids are a class of macromolecules that are nonpolar and hydrophobic in nature. major types include fats and oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. fats and oils are a stored form of energy and can include triglycerides. fats and oils are usually made up of fatty acids and glycerol. proteins are a class of macromolecules that can perform a. 4.1 biological molecules. the large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules are called biological macromolecules. there are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions. Concept 5.1 most macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers. three of the four classes of macromolecules—carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids—form chainlike molecules called polymers. a polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds.
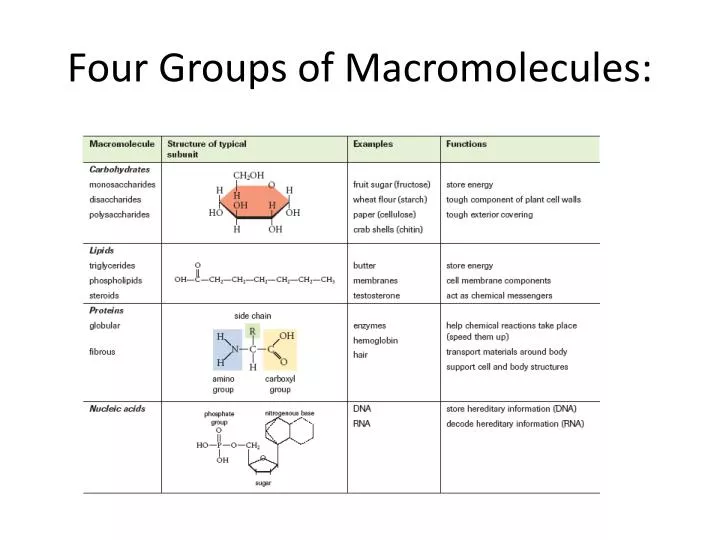
Ppt Four Groups Of Macromolecules Powerpoint Presentation Free 4.1 biological molecules. the large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules are called biological macromolecules. there are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions. Concept 5.1 most macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers. three of the four classes of macromolecules—carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids—form chainlike molecules called polymers. a polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds.

Types Of Biological Macromolecules Introduction To Chemistry

Comments are closed.