Vein Of Galen Aneurysmal Malformation Neupsy Key
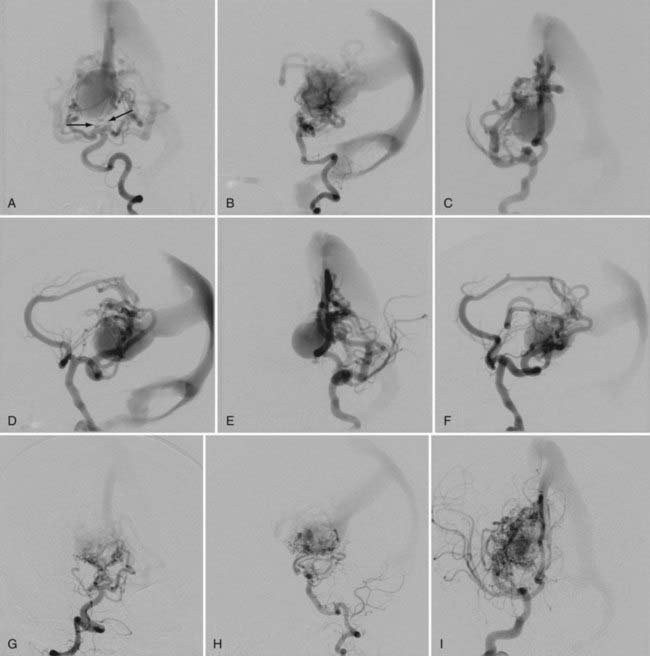
Vein Of Galen Aneurysmal Malformation Neupsy Key Pial arteriovenous malformation with vein of galen aneurysmal dilation. this type of vgad is a pial or parenchymal avm that drains into the dilated vein of galen or its tributary (figs. 208 4 and 208 5). dilation of the vein of galen is secondary to obstruction of outflow. The vein of galen is formed by the confluence of the internal cerebral veins and the basal vein of rosenthal. the median prosencephalic vein of markowski usually regresses during the 11th week of gestation, and by 3 months of gestation, the posterior part of it joins the internal cerebral veins and basal veins to form the vein of galen.
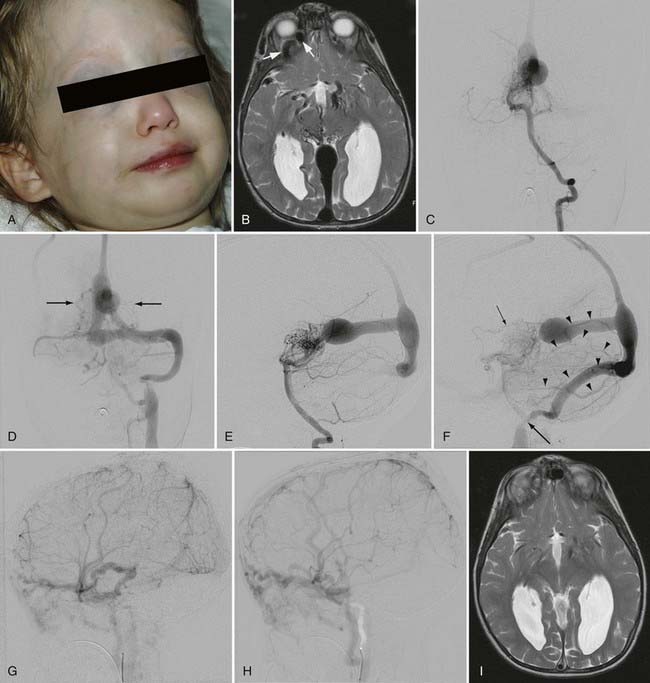
Vein Of Galen Aneurysmal Malformation Neupsy Key The first description of a vein of galen malformation aneurysm dates to 1937 . fortunately, these are extremely rare lesions, and it has been estimated that a neurosciences center serving a population of 3 million will see a patient with this diagnosis less than once per year . this group of lesions is characterized by the midline presence of. The vein of galen aneurysmal malformation (vgam) is a rare arteriovenous malformation of the embryonic choroid plexus. they represent about 30% of all paediatric neurovascular disorders[ 2 , 3 ]. the vgam is constituted by a midline dilated venous structure that receives blood from abnormal macroscopic or microscopic arteriovenous shunting vessels[ 4 ]. Termed vein of galen aneurysmal dilatations, these lesions are characterized by drainage of an arteriovenous malformation or dural fistula into the true vein of galen. the dilated vein in these cases drains brain parenchyma in addition to the malformation, as opposed to the persistent embryonic vein in the true vgam that drains only the malformation ( 4 ). Vein of galen aneurysmal malformation (vgam), a rare congenital intracranial arteriovenous (av) malformation (avm) of the cerebral vasculature, represents about 30% of all prenatally diagnosed.

Vein Of Galen Aneurysmal Malformation Neupsy Key Termed vein of galen aneurysmal dilatations, these lesions are characterized by drainage of an arteriovenous malformation or dural fistula into the true vein of galen. the dilated vein in these cases drains brain parenchyma in addition to the malformation, as opposed to the persistent embryonic vein in the true vgam that drains only the malformation ( 4 ). Vein of galen aneurysmal malformation (vgam), a rare congenital intracranial arteriovenous (av) malformation (avm) of the cerebral vasculature, represents about 30% of all prenatally diagnosed. Ing “vein of galen malformation,”“vein of galen aneurysmal formation,”“arteriovenous aneurysms of the vein of galen,” and“aneurysmsoftheveinofgalen.”however,thesemedical terms are misnomers because the malformation is actually caused by mprosv, rather than the vein of galen. the true vgam wasreported by boldreyandmiller in 1949. The mpv fails to regress and becomes aneurysmal. it drains via the straight sinus (present only in 50%) or a persistent falcine sinus, and the vein of galen does not form. haemodynamically cerebral arteriovenous fistula involving vein of galen can be subdivided into two groups: true vgams. vein of galen dilatation secondary to high flow.

Comments are closed.