Vectors And Vector Geometry Exploring Vector Operations And

Introduction To Vectors And Basic Vector Operations Youtube 8604. 11.1: vectors in the plane. some quantities, such as or force, are defined in terms of both size (also called magnitude) and direction. a quantity that has magnitude and direction is called a vector. 11.1e: exercises for vectors in the plane. 11.2: vectors in space. vectors are useful tools for solving two dimensional problems. Structures and analytical geometry of curves and surfaces is covered in detail. the second unit discusses algebra of operators and their types. it explains the equivalence between the algebra of vector operators and the algebra of matrices. formulation of eigenvectors and eigenvalues of a linear vector operator are discussed using vector algebra.

Vectors And Vector Geometry Exploring Vector Operations And 4 vector geometry 4.1 vectors and lines. in this chapter we study the geometry of 3 dimensional space. we view a point in 3 space as an arrow from the origin to that point. doing so provides a “picture” of the point that is truly worth a thousand words. vectors in . introduce a coordinate system in 3 dimensional space in the usual way. The second key operation is vector addition, adding one vector to another. here's how this is defined: if we have two vectors →v and →w in rn, 2 draw →v (with its tail anywhere), and then draw →w with its tail at the head of →v. then, →v →w is defined to be the vector that goes from the tail of →v to the head of →w. Figure 10.22: illustrating how to add vectors using the head to tail rule and parallelogram law. analytically, it is easy to see that →u →v = →v →u. figure 10.22 also gives a graphical representation of this, using gray vectors. note that the vectors →u and →v, when arranged as in the figure, form a parallelogram. Explore vectors in 1d or 2d, and discover how vectors add together. specify vectors in cartesian or polar coordinates, and see the magnitude, angle, and components of each vector. experiment with vector equations and compare vector sums and differences.

Vectors In Linear Algebra Geometric Algebraic Operations With Figure 10.22: illustrating how to add vectors using the head to tail rule and parallelogram law. analytically, it is easy to see that →u →v = →v →u. figure 10.22 also gives a graphical representation of this, using gray vectors. note that the vectors →u and →v, when arranged as in the figure, form a parallelogram. Explore vectors in 1d or 2d, and discover how vectors add together. specify vectors in cartesian or polar coordinates, and see the magnitude, angle, and components of each vector. experiment with vector equations and compare vector sums and differences. Perform basic vector operations (scalar multiplication, addition, subtraction). express a vector in component form. explain the formula for the magnitude of a vector. express a vector in terms of unit vectors. give two examples of vector quantities. In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set whose elements, often called vectors, can be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called scalars. the operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication must satisfy certain requirements, called vector axioms.
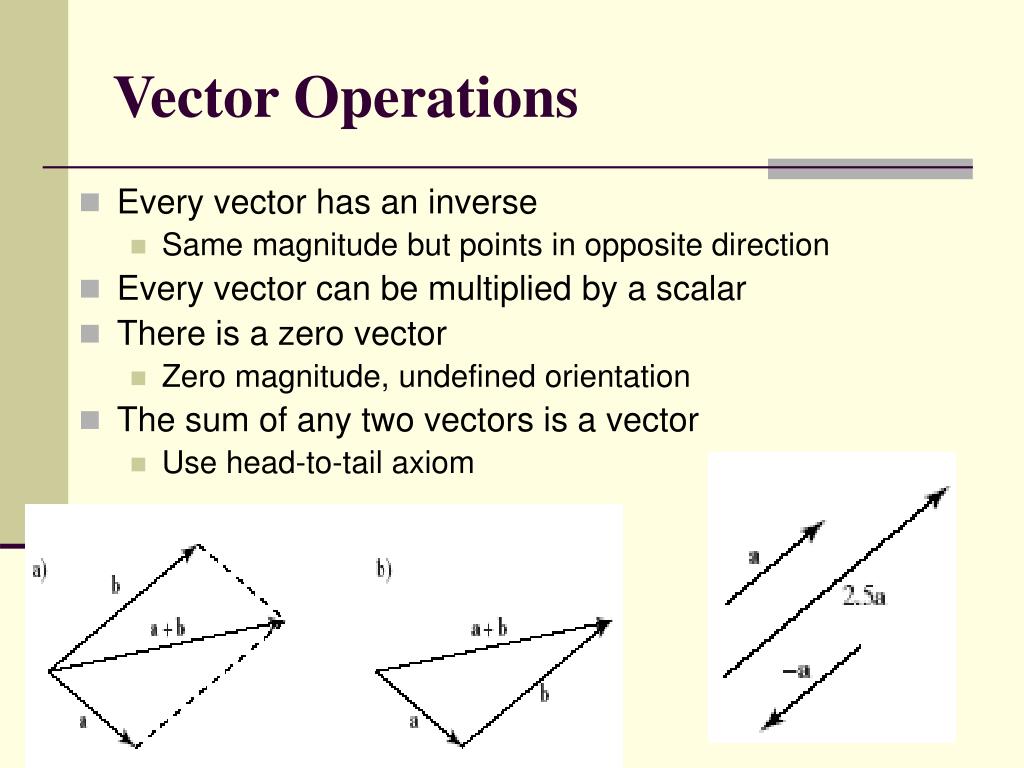
Ppt Vectors Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4696604 Perform basic vector operations (scalar multiplication, addition, subtraction). express a vector in component form. explain the formula for the magnitude of a vector. express a vector in terms of unit vectors. give two examples of vector quantities. In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set whose elements, often called vectors, can be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called scalars. the operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication must satisfy certain requirements, called vector axioms.

Comments are closed.