Unit Circle Trigonometry Sin Cos Tan Radians Degrees
Trigonometry Unit Circle Chart Sine, cosine and tangent. sine, cosine and tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: for a given angle θ each ratio stays the same. no matter how big or small the triangle is. trigonometry index unit circle. This trigonometry tutorial video explains the unit circle and the basics of how to memorize it. it provides the angles in radians and degrees and shows you.

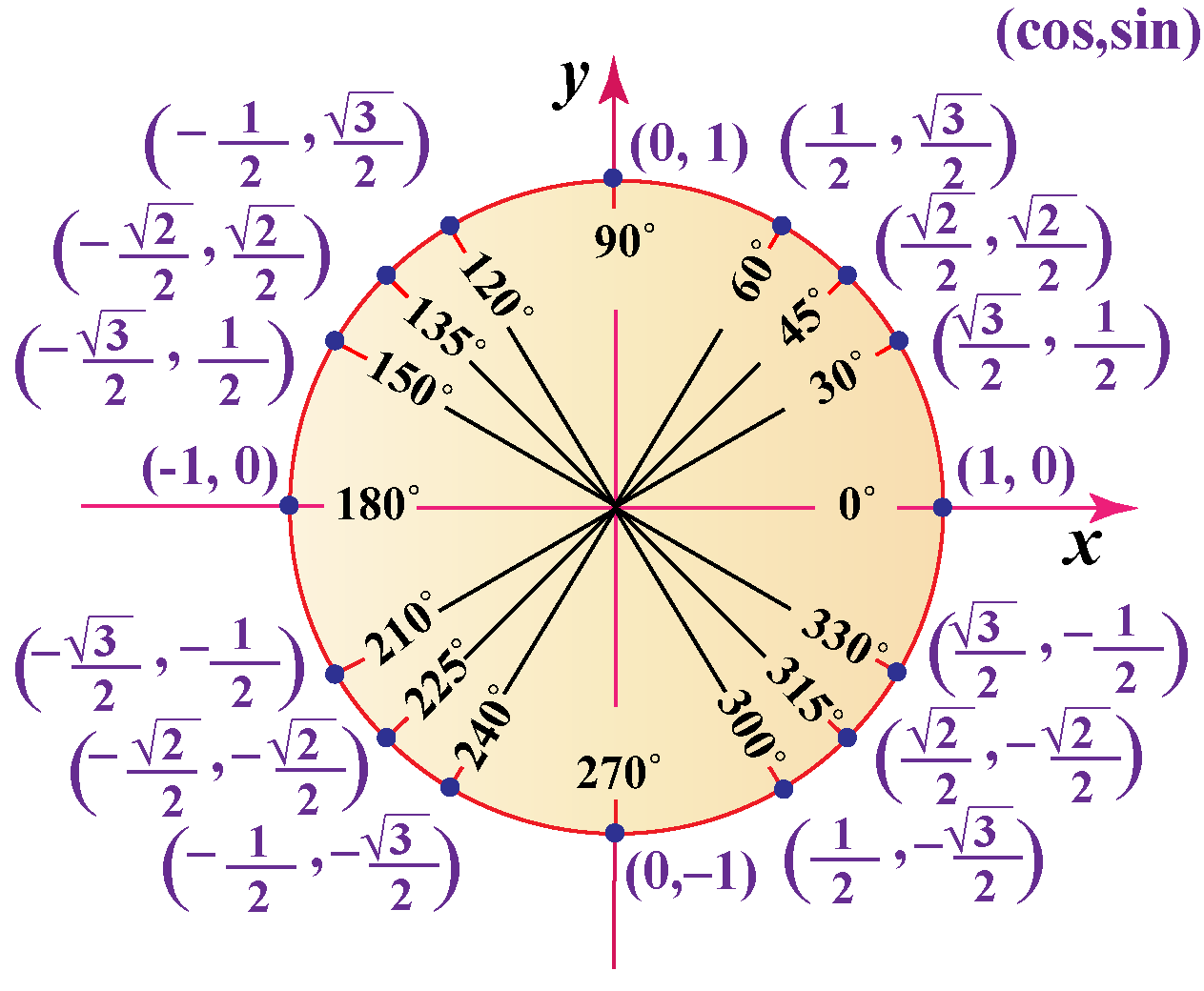
Unit Circle Quick Lesson Printable Pdf Chart в Matter Of Math Conversion of the unit circle's radians to degrees shouldn't be a problem anymore! 💪. the other part – remembering the whole unit circle chart, with sine and cosine values – is a slightly longer process. we won't describe it here, but feel free to check out 3 essential tips on how to remember the unit circle or this wikihow page. if you. Pythagoras. pythagoras' theorem says that for a right angled triangle, the square of the long side equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides: x 2 y 2 = 1 2. but 1 2 is just 1, so: x2 y2 = 1. equation of the unit circle. also, since x=cos and y=sin, we get: (cos (θ))2 (sin (θ))2 = 1. a useful "identity". The measurements of sin, cos, and tan become clear when you see them on a graph. take a moment to soak in what they mean. sin, cos, tan at 0° so, what are the sin, cos, and tan of an angle of 0°? sin, cos, tan at 90° and what about 90°? special angles: 30°, 45°, and 60° a unit circle shows trig functions clearly because the radius is 1. The value of θ can be expressed in both degree and in radians. it is important to remember the values of sin, cos, and tan for some specific angles. these angles are called reference angles. in the unit circle, we have cosine as the x coordinate and sin as the y coordinate. let us find their values for θ = 0° and θ = 90°.
Unit Circle Labeled In 30в Increments With Values Clipart Etc The measurements of sin, cos, and tan become clear when you see them on a graph. take a moment to soak in what they mean. sin, cos, tan at 0° so, what are the sin, cos, and tan of an angle of 0°? sin, cos, tan at 90° and what about 90°? special angles: 30°, 45°, and 60° a unit circle shows trig functions clearly because the radius is 1. The value of θ can be expressed in both degree and in radians. it is important to remember the values of sin, cos, and tan for some specific angles. these angles are called reference angles. in the unit circle, we have cosine as the x coordinate and sin as the y coordinate. let us find their values for θ = 0° and θ = 90°. To define our trigonometric functions, we begin by drawing a unit circle, a circle centered at the origin with radius 1, as shown in figure 2.2.2. the angle (in radians) that t intercepts forms an arc of length s. using the formula s = rt, and knowing that r = 1, we see that for a unit circle, s = t. Defining sine and cosine functions from the unit circle. the sine function relates a real number t t to the y coordinate of the point where the corresponding angle intercepts the unit circle. more precisely, the sine of an angle t t equals the y value of the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of length t. t. in figure 2, the sine is equal to.

Comments are closed.