Unit Circle Trigonometric Functions Using Unit Circle Unit Circleођ
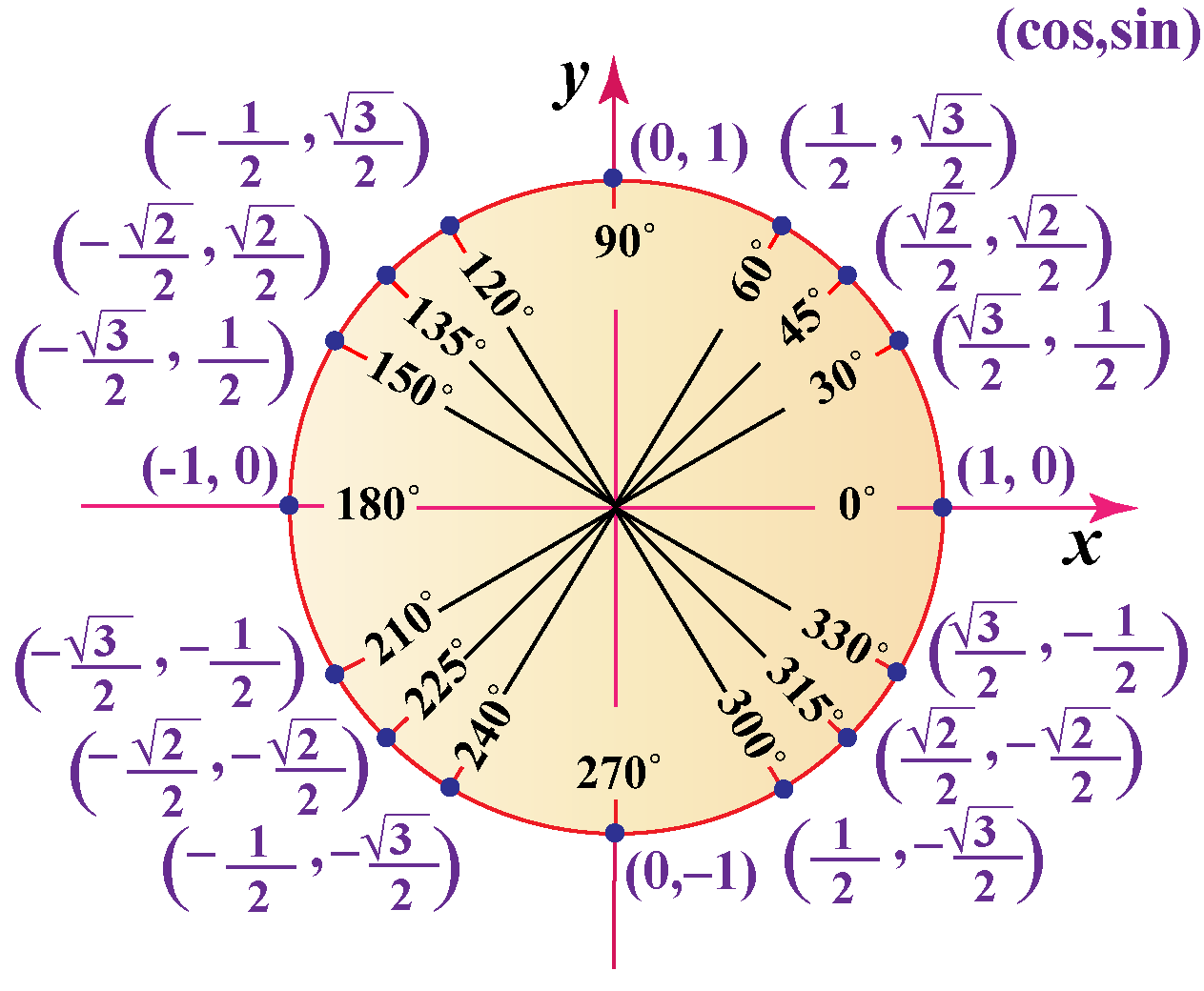
Trigonometry Unit Circle Chart To define our trigonometric functions, we begin by drawing a unit circle, a circle centered at the origin with radius 1, as shown in figure 2.2.2. the angle (in radians) that t intercepts forms an arc of length s. using the formula s = rt, and knowing that r = 1, we see that for a unit circle, s = t. The trigonometric functions for the angles in the unit circle can be memorized and recalled using a set of rules. the sign on a trigonometric function depends on the quadrant that the angle falls in, and the mnemonic phrase “a smart trig class” is used to identify which functions are positive in which quadrant.
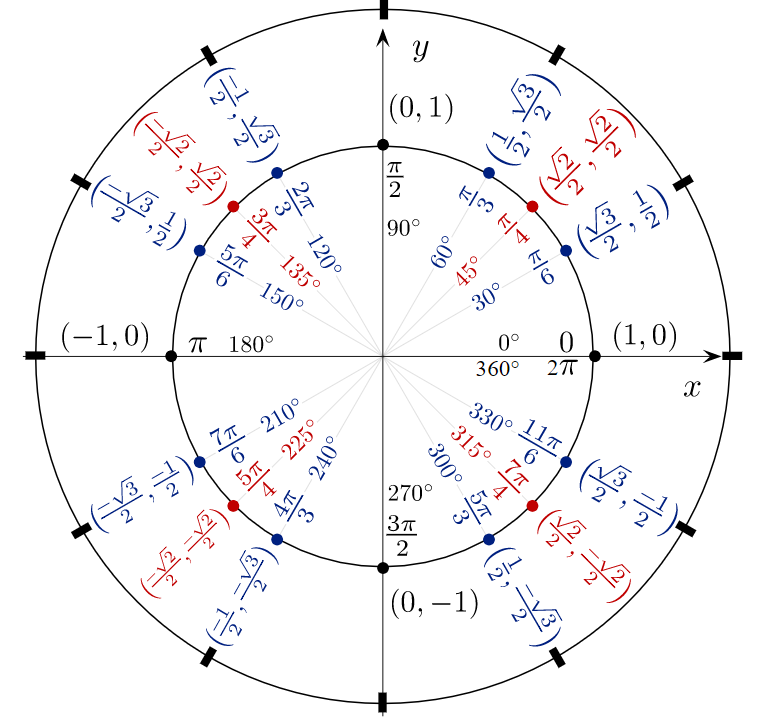
Trigonometric Function Circular Function Statistics How To Let p(x, y) be a point on the unit circle, and let t be the arc length from the point (1, 0) to p along the circumference of the unit circle. the trigonometric functions of the real number t are defined as follows: function ratio function ratio sin(t) = y csc(t) = 1 y cos(t) = x sec(t) = 1 x tan(t) = y x cot(t) = x y. Defining sine and cosine functions from the unit circle. the sine function relates a real number t t to the y coordinate of the point where the corresponding angle intercepts the unit circle. more precisely, the sine of an angle t t equals the y value of the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of length t. t. in figure 2, the sine is equal to. In trigonometry, the unit circle is a circle with of radius 1 that is centered at the origin of the cartesian coordinate plane. the unit circle helps us generalize trigonometric functions, making it easier for us to work with them since it lets us find sine and cosine values given a point on the unit circle. we can then use sine and cosine to. Sine, cosine and tangent. sine, cosine and tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: for a given angle θ each ratio stays the same. no matter how big or small the triangle is. trigonometry index unit circle.
Unit Circle Labeled With Special Angles And Values Clipart Etc In trigonometry, the unit circle is a circle with of radius 1 that is centered at the origin of the cartesian coordinate plane. the unit circle helps us generalize trigonometric functions, making it easier for us to work with them since it lets us find sine and cosine values given a point on the unit circle. we can then use sine and cosine to. Sine, cosine and tangent. sine, cosine and tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: for a given angle θ each ratio stays the same. no matter how big or small the triangle is. trigonometry index unit circle. To define our trigonometric functions, we begin by drawing a unit circle, a circle centered at the origin with radius 1, as shown in figure 2. the angle (in radians) that t t intercepts forms an arc of length s. s. using the formula s = r t, s = r t, and knowing that r = 1, r = 1, we see that for a unit circle, s = t. s = t. The trigonometric functions cosine and sine of angle θ may be defined on the unit circle as follows: if (x, y) is a point on the unit circle, and if the ray from the origin (0, 0) to (x, y) makes an angle θ from the positive x axis, (where counterclockwise turning is positive), then = =.

Comments are closed.