Unit Circle Sine Cosine

Unit Circle Sine Cosine Finding the function values for the sine and cosine begins with drawing a unit circle, which is centered at the origin and has a radius of 1 unit. using the unit circle, the sine of an angle \(t\) equals the \(y\) value of the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of length \(t\) whereas the cosine of an angle \(t\) equals the \(x\) value of. Sine, cosine and tangent. sine, cosine and tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: for a given angle θ each ratio stays the same. no matter how big or small the triangle is. trigonometry index unit circle.

Unit Circle Quick Lesson Printable Pdf Chart в Matter Of Math Because angles smaller than 0 and angles larger than 2 π 2 π can still be graphed on the unit circle and have real values of x, y, x, y, and r, r, there is no lower or upper limit to the angles that can be inputs to the sine and cosine functions. 7.0: introduction to the unit circle sine and cosine functions. a function that repeats its values in regular intervals is known as a periodic function. the graphs of such functions show a general shape reflective of a pattern that keeps repeating. this means the graph of the function has the same output at exactly the same place in every cycle. A corollary of the pythagorean theorem stating that the square of the cosine of a given angle plus the square of the sine of that angle equals 1. sine function. the y value of the point on a unit circle corresponding to a given angle. unit circle. a circle with a center at [latex]\left (0,0\right) [ latex] and radius. Pythagoras' theorem says that for a right angled triangle, the square of the long side equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides: x 2 y 2 = 1 2. but 1 2 is just 1, so: x2 y2 = 1. equation of the unit circle. also, since x=cos and y=sin, we get: (cos (θ))2 (sin (θ))2 = 1. a useful "identity".
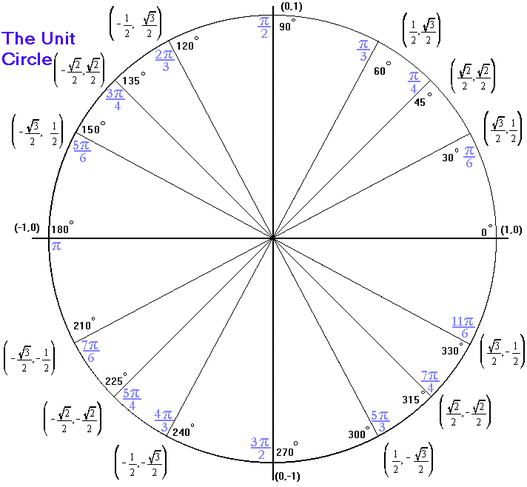
Unit Circle Graphs Of Sine And Cosine A corollary of the pythagorean theorem stating that the square of the cosine of a given angle plus the square of the sine of that angle equals 1. sine function. the y value of the point on a unit circle corresponding to a given angle. unit circle. a circle with a center at [latex]\left (0,0\right) [ latex] and radius. Pythagoras' theorem says that for a right angled triangle, the square of the long side equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides: x 2 y 2 = 1 2. but 1 2 is just 1, so: x2 y2 = 1. equation of the unit circle. also, since x=cos and y=sin, we get: (cos (θ))2 (sin (θ))2 = 1. a useful "identity". Defining sine and cosine functions from the unit circle. the sine function relates a real number t t to the y coordinate of the point where the corresponding angle intercepts the unit circle. more precisely, the sine of an angle t t equals the y value of the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of length t. t. in figure 2, the sine is equal to. A corollary of the pythagorean theorem stating that the square of the cosine of a given angle plus the square of the sine of that angle equals 1. sine function. the y value of the point on a unit circle corresponding to a given angle. unit circle. a circle with a center at. (0, 0) \left (0,0\right) (0,0) and radius.
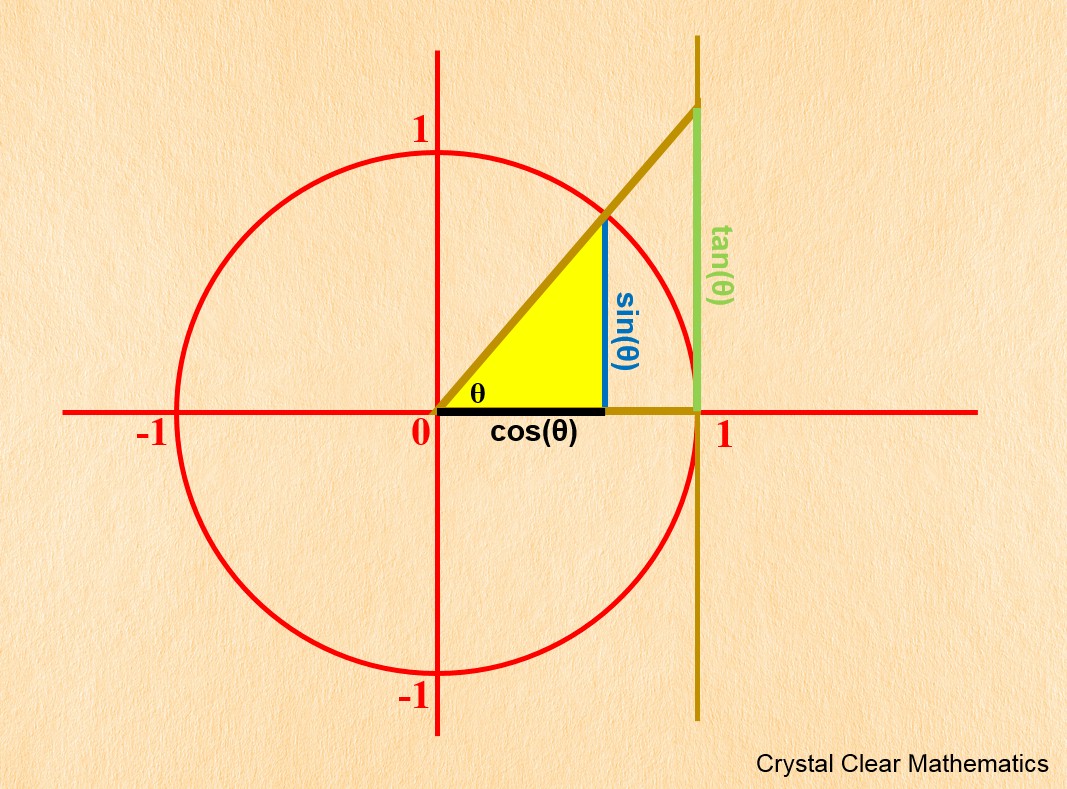
The Unit Circle And Trigonometric Identities Crystal Clear Mathematics Defining sine and cosine functions from the unit circle. the sine function relates a real number t t to the y coordinate of the point where the corresponding angle intercepts the unit circle. more precisely, the sine of an angle t t equals the y value of the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of length t. t. in figure 2, the sine is equal to. A corollary of the pythagorean theorem stating that the square of the cosine of a given angle plus the square of the sine of that angle equals 1. sine function. the y value of the point on a unit circle corresponding to a given angle. unit circle. a circle with a center at. (0, 0) \left (0,0\right) (0,0) and radius.

Comments are closed.