Unit Circle Reference Triangle
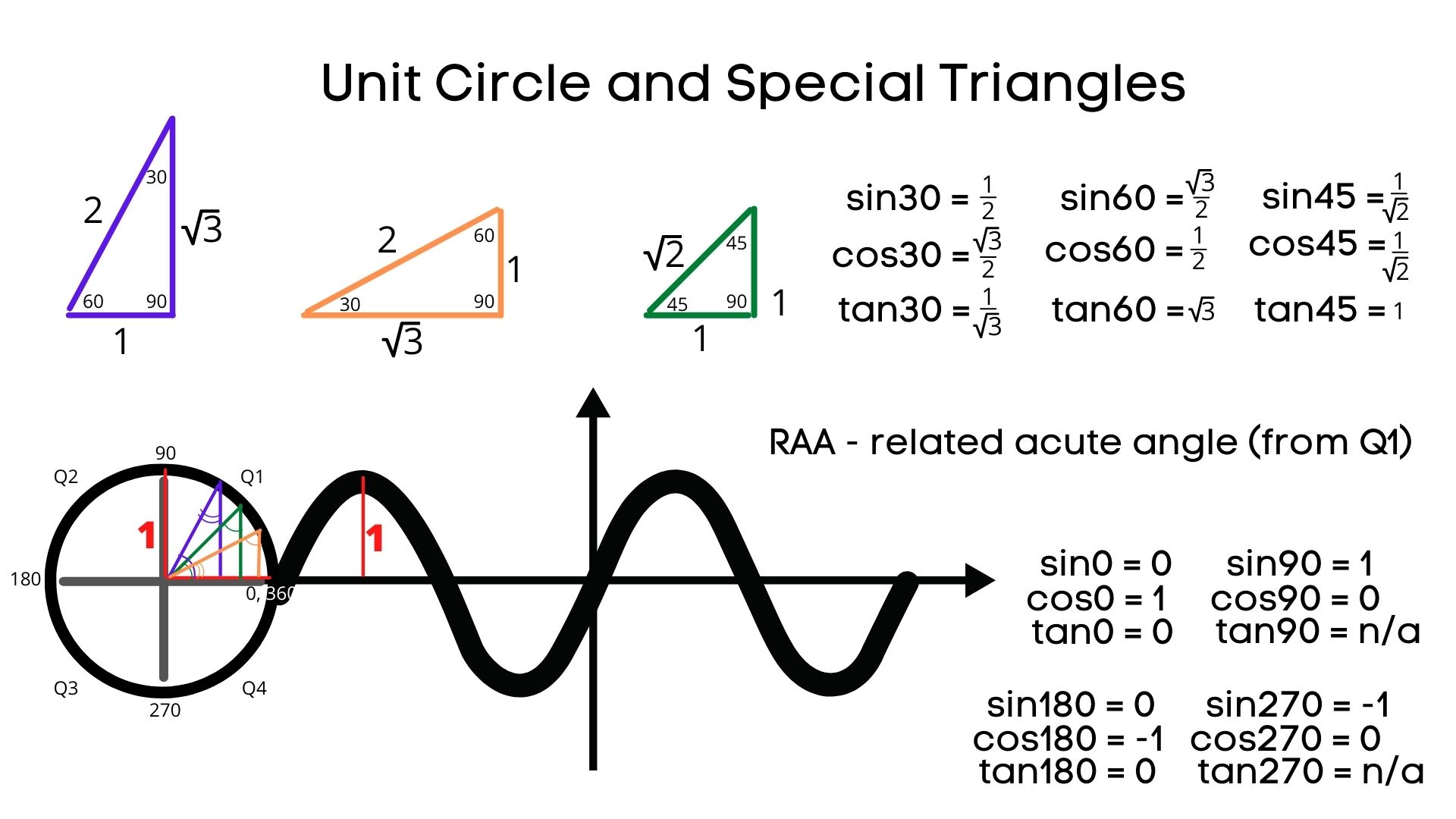
Unit Circle Trigonometry Degrees Intomath A unit circle has a center at (0, 0) and radius 1. the length of the intercepted arc is equal to the radian measure of the central angle t. let (x, y) be the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of arc length s. the (x, y) coordinates of this point can be described as functions of the angle. Unit circle with reference triangles. 1. click on the circles at the left. what patterns do you see? 2. 30 degree reference triangles: 3. π 6 or 30 degrees. 4 (5π.
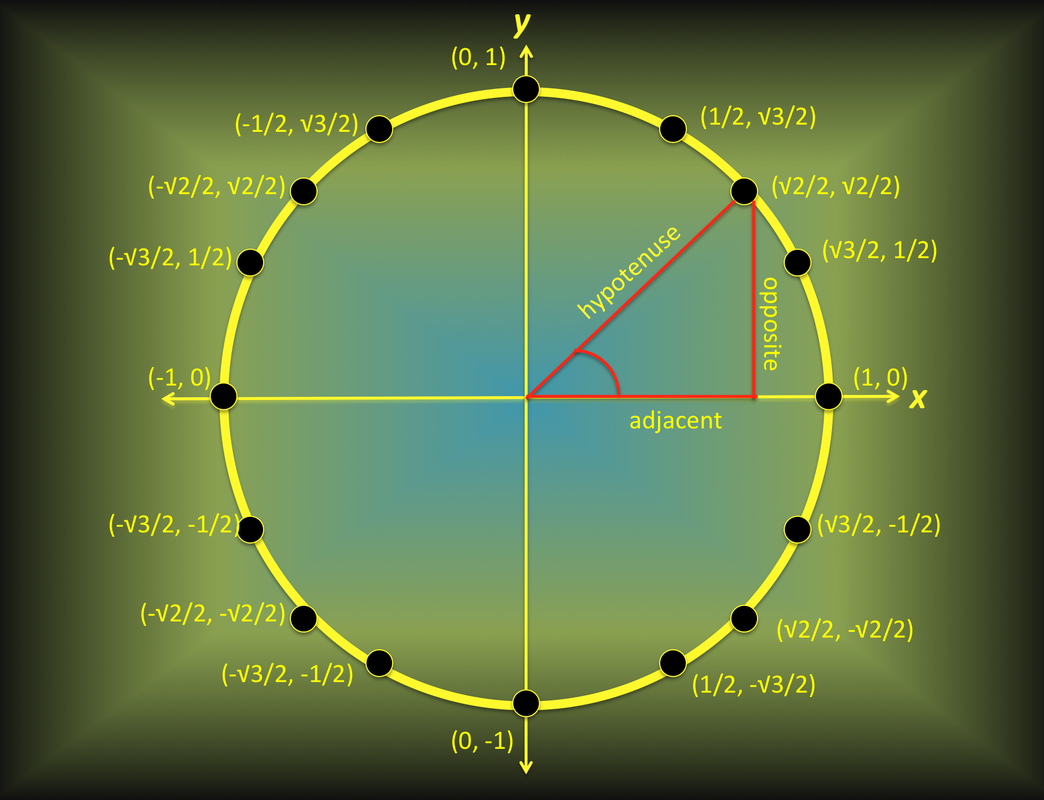
Unit Circle Reference Triangle Unit circle. a unit circle has a center at (0, 0) and radius 1. form the angle with measure t with initial side coincident with the x axis. let (x, y) be point where the terminal side of the angle and unit circle meet. then (x, y) = (cost, sint). further, tant = sint cost. Sine, cosine and tangent. sine, cosine and tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: for a given angle θ each ratio stays the same. no matter how big or small the triangle is. trigonometry index unit circle. 1. find the ordered pair for 240 ∘ and use it to find the value of sin240 ∘. sin240 ∘ = − √3 2. as we found in part b under the question above, the reference angle for 240 ∘ is 60 ∘. the figure below shows 60 ∘ and the three other angles in the unit circle that have 60 ∘ as a reference angle. figure 2.3.7.6. So each leg on the unit circle triangle is: 1 √2 = 1 √2 ⋅ √2 √2 = √2 2. look at the x and y coordinates of the point on the unit circle, then use the triangle to find cos45 ∘ and sin45 ∘. from the coordinates on the unit circle: x = √2 2. from the triangle: cos45 ∘ = adjacent hypotenuse = 1 √2 = √2 2.
Unit Circle Labeled With Special Angles And Values Clipart Etc 1. find the ordered pair for 240 ∘ and use it to find the value of sin240 ∘. sin240 ∘ = − √3 2. as we found in part b under the question above, the reference angle for 240 ∘ is 60 ∘. the figure below shows 60 ∘ and the three other angles in the unit circle that have 60 ∘ as a reference angle. figure 2.3.7.6. So each leg on the unit circle triangle is: 1 √2 = 1 √2 ⋅ √2 √2 = √2 2. look at the x and y coordinates of the point on the unit circle, then use the triangle to find cos45 ∘ and sin45 ∘. from the coordinates on the unit circle: x = √2 2. from the triangle: cos45 ∘ = adjacent hypotenuse = 1 √2 = √2 2. Defining sine and cosine functions from the unit circle. the sine function relates a real number t t to the y coordinate of the point where the corresponding angle intercepts the unit circle. more precisely, the sine of an angle t t equals the y value of the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of length t. t. in figure 2, the sine is equal to. Unit circle. a unit circle has a center at (0, 0) and radius 1. in a unit circle, the length of the intercepted arc is equal to the radian measure of the central angle t. let (x, y) be the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of arc lengths. the (x, y) coordinates of this point can be described as functions of the angle.

Trigonometric Ratios On The Unit Circle Ck 12 Foundation Defining sine and cosine functions from the unit circle. the sine function relates a real number t t to the y coordinate of the point where the corresponding angle intercepts the unit circle. more precisely, the sine of an angle t t equals the y value of the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of length t. t. in figure 2, the sine is equal to. Unit circle. a unit circle has a center at (0, 0) and radius 1. in a unit circle, the length of the intercepted arc is equal to the radian measure of the central angle t. let (x, y) be the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of arc lengths. the (x, y) coordinates of this point can be described as functions of the angle.
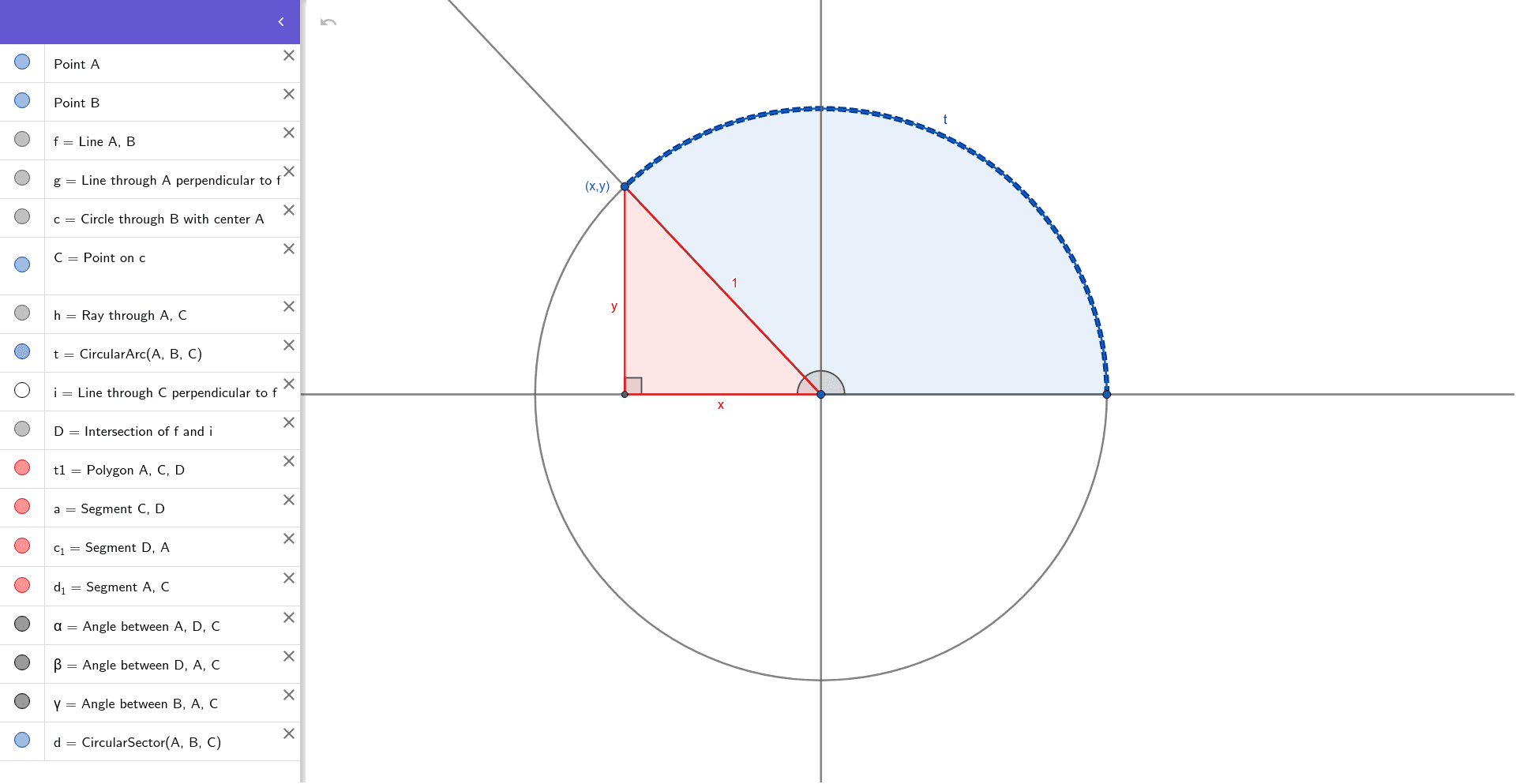
Unit Circle Reference Triangle

Comments are closed.