Unit Circle Definitions Of Trig Functions Pg 23
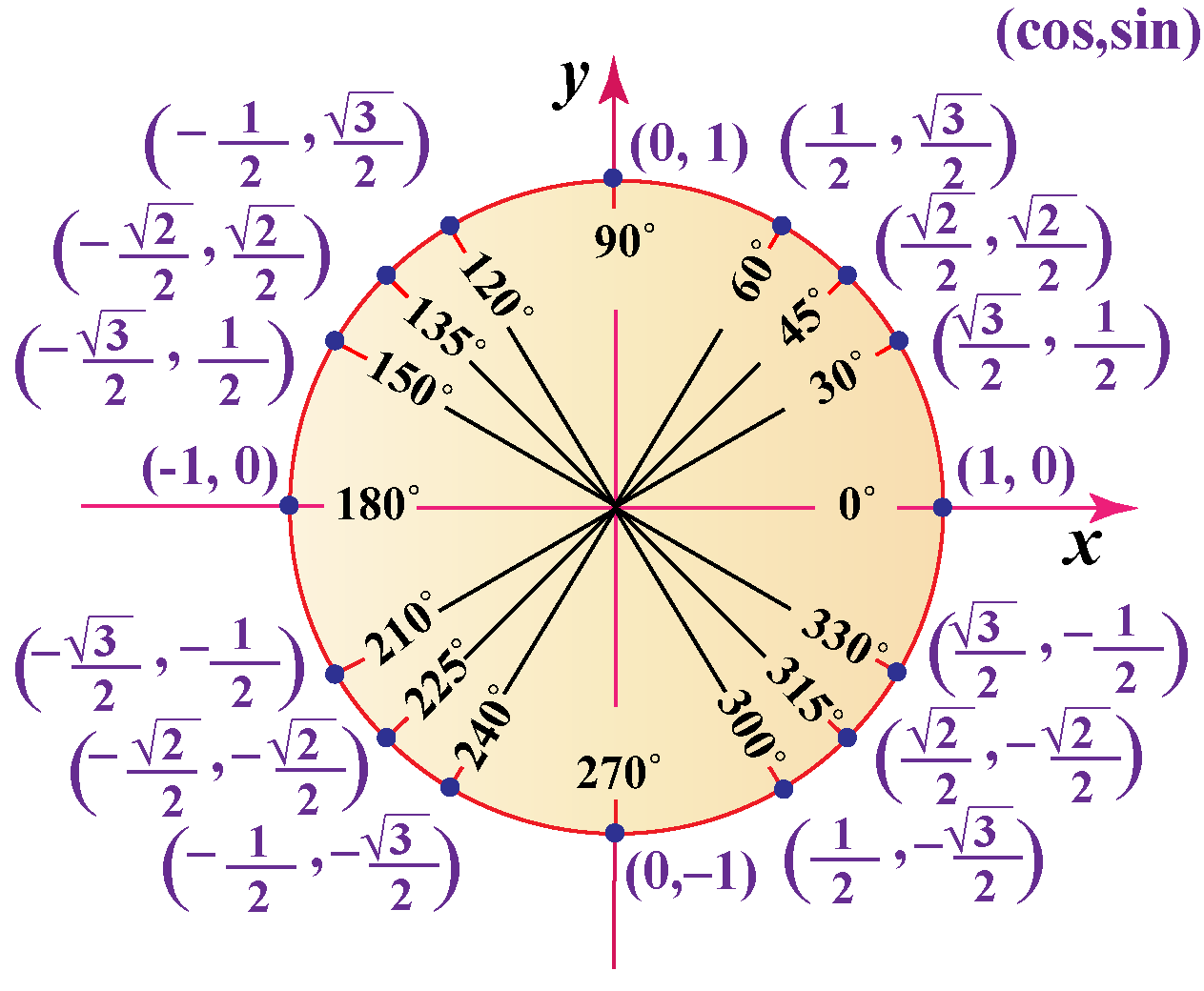
Trigonometry Unit Circle Chart Ma notes 02 page 23find the notes: turksmathstuff math analysis notes topics: the pythagorean triples you should memorize; equation of th. Let p(x, y) be a point on the unit circle, and let t be the arc length from the point (1, 0) to p along the circumference of the unit circle. the trigonometric functions of the real number t are defined as follows: function ratio function ratio sin(t) = y csc(t) = 1 y cos(t) = x sec(t) = 1 x tan(t) = y x cot(t) = x y.

Unit Circle Ck 12 Foundation To define our trigonometric functions, we begin by drawing a unit circle, a circle centered at the origin with radius 1, as shown in figure 2.2.2. the angle (in radians) that t intercepts forms an arc of length s. using the formula s = rt, and knowing that r = 1, we see that for a unit circle, s = t. The radian is the standard unit used to measure angles in mathematics. one radian is the measure of a central angle of a circle that intercepts an arc equal in length to the radius of that circle. one radian: the angle [latex]t [ latex] sweeps out a measure of one radian. note that the length of the intercepted arc is the same as the length of. Definition: circular functions. suppose θ is an angle plotted in standard position and p(x, y) is the point on the terminal side of θ which lies on the unit circle. the cosine of θ, denoted cos(θ), is defined by cos(θ) = x. the sine of θ, denoted sin(θ), is defined by sin(θ) = y. the secant of θ, denoted sec(θ), is defined by sec(θ. More precisely, the sine of an angle t t equals the y value of the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of length t. t. in figure 2, the sine is equal to y. y. like all functions, the sine function has an input and an output. its input is the measure of the angle; its output is the y coordinate of the corresponding point on the unit circle.
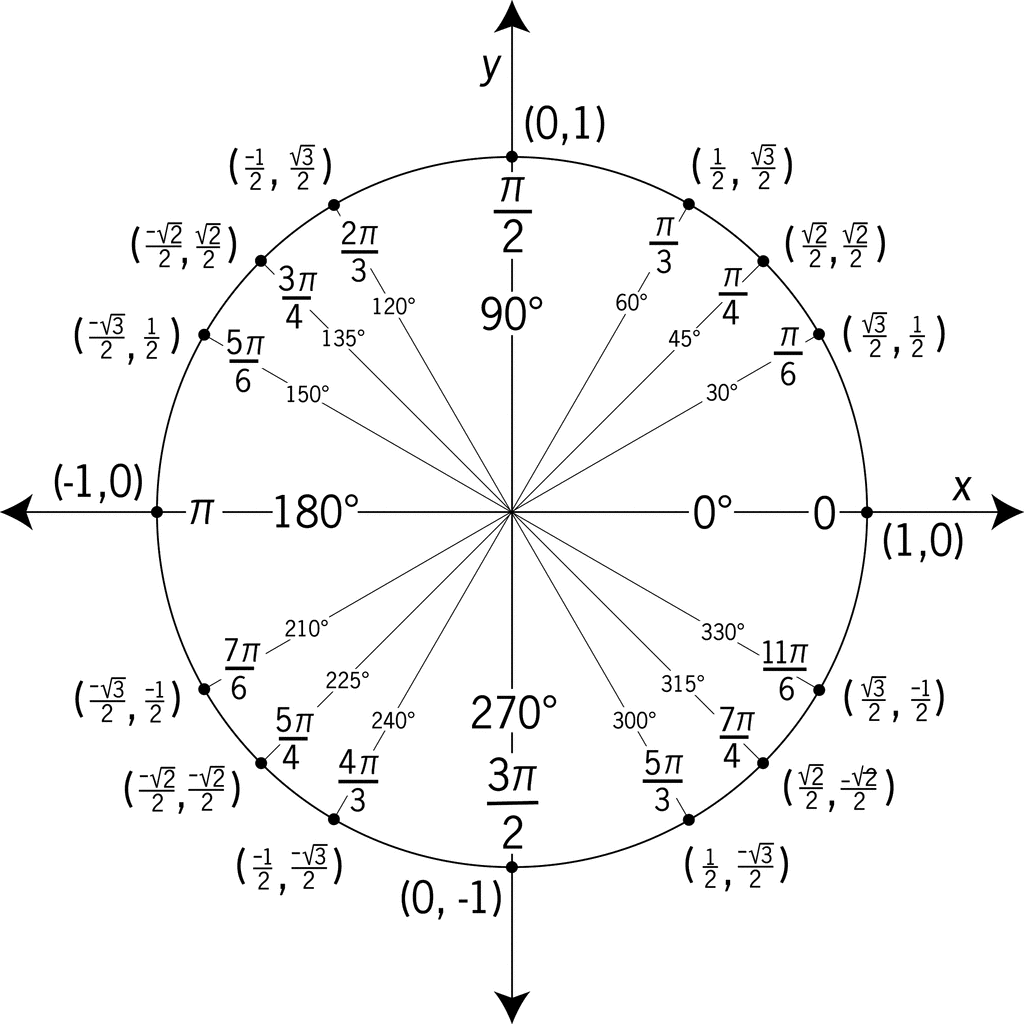
Unit Circle Definition: circular functions. suppose θ is an angle plotted in standard position and p(x, y) is the point on the terminal side of θ which lies on the unit circle. the cosine of θ, denoted cos(θ), is defined by cos(θ) = x. the sine of θ, denoted sin(θ), is defined by sin(θ) = y. the secant of θ, denoted sec(θ), is defined by sec(θ. More precisely, the sine of an angle t t equals the y value of the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of length t. t. in figure 2, the sine is equal to y. y. like all functions, the sine function has an input and an output. its input is the measure of the angle; its output is the y coordinate of the corresponding point on the unit circle. Thus, the definition is y = sine and x = cosine. the following diagram shows the unit circle definition of the trig functions: sin, cos, and tan. scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on the unit circle and trigonometry. unit circle definition of trig functions using the unit circle to define the sine, cosine, and tangent functions. Interactive element. determine exact values of trig ratios for common radian measures. the unit circle is a circle of radius one, centered at the origin, that summarizes all the 30 60 90 and 45 45 90 triangle relationships that exist. when memorized, it is extremely useful for evaluating expressions like cos(135∘) or sin(−5π 3).
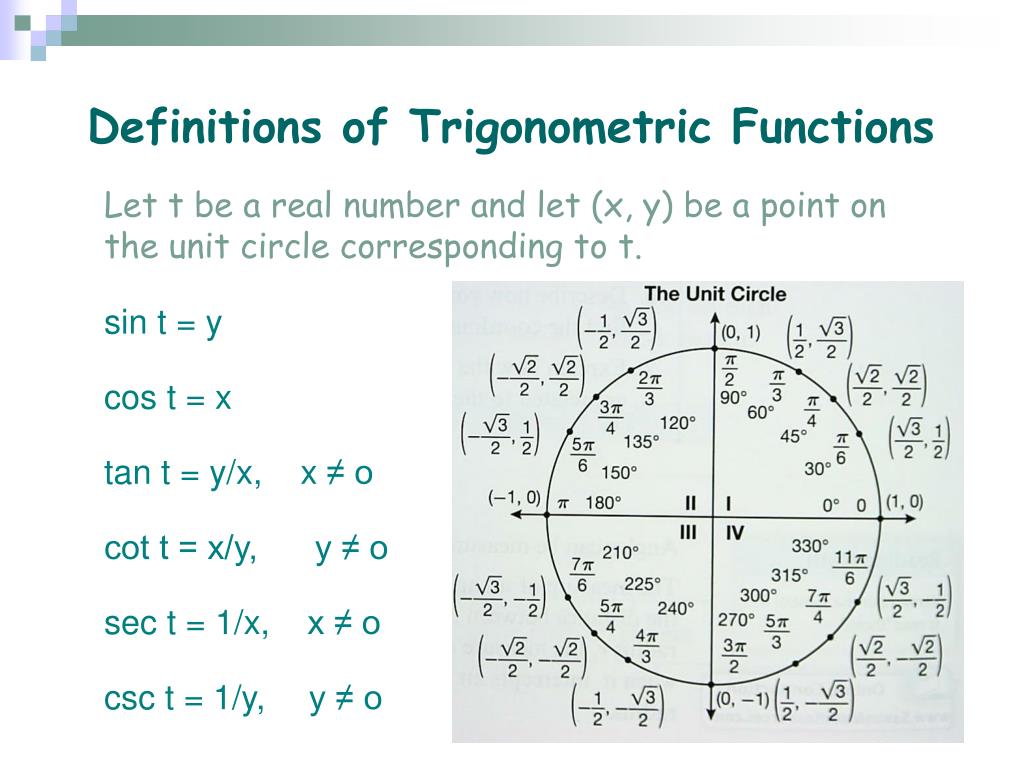
Ppt Trigonometric Functions The Unit Circle Powerpoint Presentation 4f1 Thus, the definition is y = sine and x = cosine. the following diagram shows the unit circle definition of the trig functions: sin, cos, and tan. scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on the unit circle and trigonometry. unit circle definition of trig functions using the unit circle to define the sine, cosine, and tangent functions. Interactive element. determine exact values of trig ratios for common radian measures. the unit circle is a circle of radius one, centered at the origin, that summarizes all the 30 60 90 and 45 45 90 triangle relationships that exist. when memorized, it is extremely useful for evaluating expressions like cos(135∘) or sin(−5π 3).
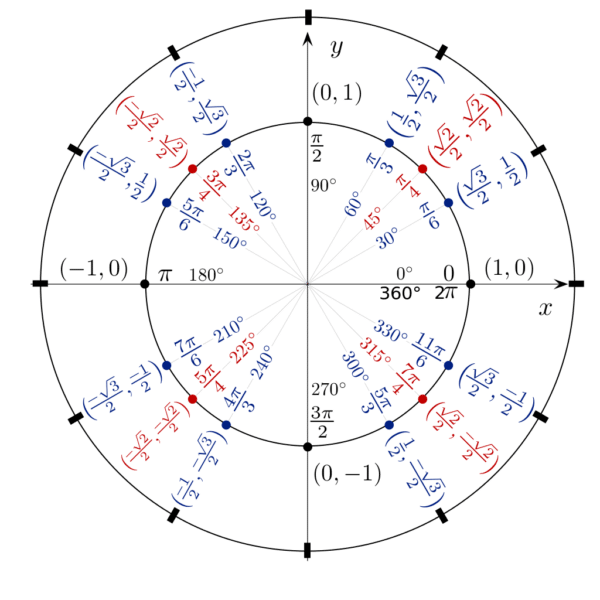
Unit Circle Trig Practice

Comments are closed.