Tolerancing Basics Calculating A Fit Between And Cylinder And A Hole

Tolerancing Basics Calculating A Fit Between And Cylinder And A Hole Nominal size ( 0.01) located on side of cylinder but means Ø when the hole is at it's smallest size that is when we are going to have the most trouble making the cylinder fit, so it will fit best at lmc mmc = .99 0.01=.98 Ø nomial size Ø = .98 0.01 = .97 Ø lmc= .97 .01= .96Ø. Autocad videos from technical drawing 101 with autocad by smith, ramirez and schmidt, sdc publications. order book from: sdcpublications text.

Tolerancing Basics Calculating A Fit Between And Cylinder And A Hole Engineering fits. fit types. fit charts. technical drawings often include notations such as “50 g6” or “17.5 h11 g8” to specify tolerances. however, determining the final limits can be time consuming and involve navigating complex charts. our online calculator streamlines this process and provides a detailed final result immediately. Fits and tolerance calculator for shaft and hole tolerance calculation according to iso 286 1 and ansi b4.2 metric standards . the schematic representation of the fit is also drawn by tolerance calculator. the tolerances defined in iso 286 1 are applicable to size range from 0 mm to 3150 mm but there are exceptional cases defined in the. Ansi limits and fits calculator works in line with ansi b4.1 standard which is based on inch units. according to nominal size and fit type selection among running and sliding [rc], locational clearance [lc], locational transition [lt], locational interference [ln], force and shrink [fn] fits, size limits for hole shaft are calculated with. (the hole chosen as a basis for the hole basis system of fit) 22. fit (fit is the relationship that exists between two mating parts, a hole and shaft with respect to their dimensional difference ) 23. basic size of a fit (common value of the basic size of the two parts of a fit) chapter one : fits and tolerances.

Tolerancing Basics Calculating A Fit Between And Cylinder And A Hole Ansi limits and fits calculator works in line with ansi b4.1 standard which is based on inch units. according to nominal size and fit type selection among running and sliding [rc], locational clearance [lc], locational transition [lt], locational interference [ln], force and shrink [fn] fits, size limits for hole shaft are calculated with. (the hole chosen as a basis for the hole basis system of fit) 22. fit (fit is the relationship that exists between two mating parts, a hole and shaft with respect to their dimensional difference ) 23. basic size of a fit (common value of the basic size of the two parts of a fit) chapter one : fits and tolerances. Ansi standard b4.1 specifies a series of standard fits between cylindrical parts, based on the basic hole system. the different fit classes are as follows: running and sliding fit (rc) – the loosest of the fit classes, when a shaft must move freely inside a bearing or hole, and the positioning of the shaft is not critical. Bonus tolerance explained: as the size of the pin departs from mmc toward lmc, a bonus tolerance is added equal to the amount of that departure. bonus tolerance equals the difference between the actual feature size and the mmc of the feature. in this case, bonus tolerance = mmc lmc=25 15=10. clearance for assembly increases if the actual sizes.

Tolerance Chart For Holes And Shafts Ansi standard b4.1 specifies a series of standard fits between cylindrical parts, based on the basic hole system. the different fit classes are as follows: running and sliding fit (rc) – the loosest of the fit classes, when a shaft must move freely inside a bearing or hole, and the positioning of the shaft is not critical. Bonus tolerance explained: as the size of the pin departs from mmc toward lmc, a bonus tolerance is added equal to the amount of that departure. bonus tolerance equals the difference between the actual feature size and the mmc of the feature. in this case, bonus tolerance = mmc lmc=25 15=10. clearance for assembly increases if the actual sizes.
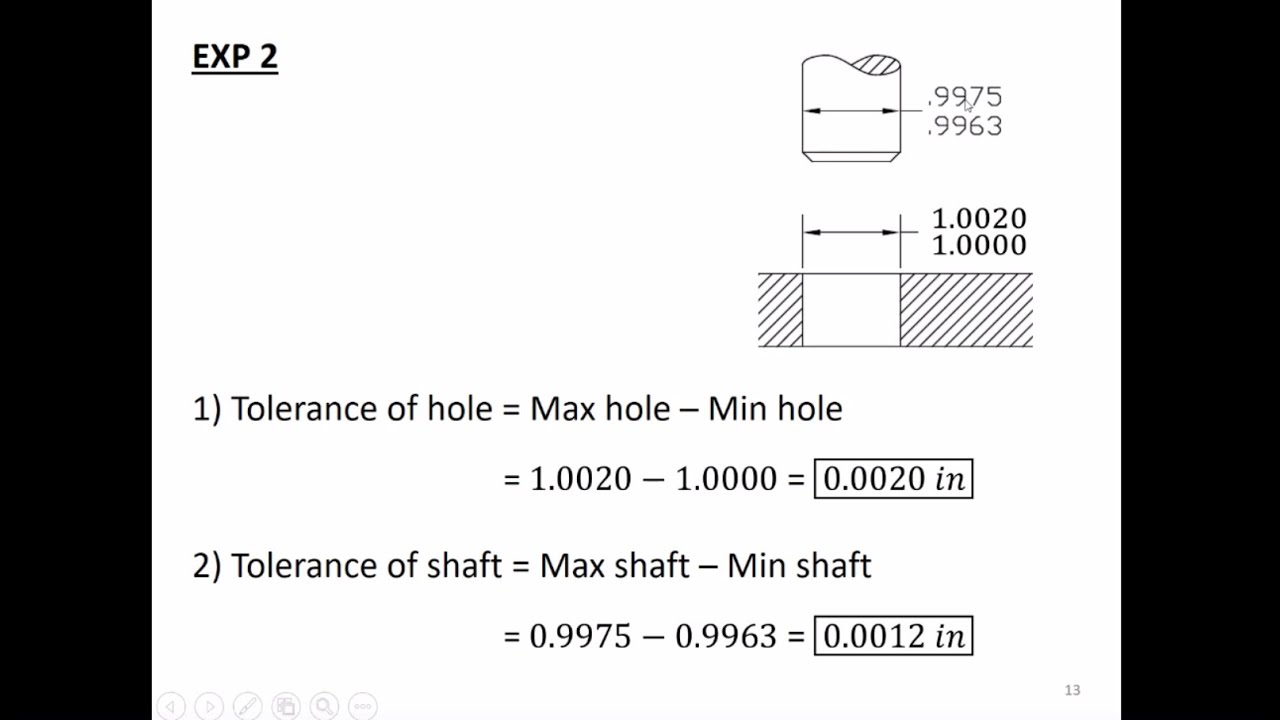
Tolerance Fits Hole And Shaft Mates Clearance Interference Fit

Comments are closed.