The Science Behind How Your Brain Makes Decisions Psychology Facts

Decision Making Process What Happens To The Brain When We Make Decision making is an encaptivating process that involves various complex interactions within the brain. at its core, decision making encompasses a multitude of cognitive functions, including perception, memory, attention, reasoning, and emotions. neuroscientists have been unraveling the intricate mechanisms underlying decision making for. When you reach a fork in the road and need to make the right decision for your long term health and well being, using the brain science behind decision making is a useful tool.

Your Brain Makes Decisions For You Before You Even At a glance: research reveals how neurons in the brain are wired to help a mouse make decisions. the findings suggest that different sets of neurons work together to solidify choices. the study establishes how specific connections between neurons in the brain support decision making. scientists have gained new insights into how neurons in the. Stanford neuroscientists and engineers used neural implants to track decision making in the brain, in real time. (image credit: gil costa) these scientists and engineers developed a system that. The neuron is a key player in the brain – these are tiny cells that send and receive signals and messages so they can communicate with each other. your brain has somewhere between 80 billion and 100 billion neurons. neurons tend to group together to form neural tracts, which would be like the streets and highways in the city analogy. The neuroscience of decision making. published 1 aug 2011. reviewed 1 aug 2011. source the kavli foundation. daeyeol lee, department of neurobiology and kavli institute for neuroscience, yale university school of medicine. yale university. research is revealing how neurons code the value of different options when people make decisions.

Didyouknow Your Brain Makes Seemingly Conscious Decisions 7 Seconds The neuron is a key player in the brain – these are tiny cells that send and receive signals and messages so they can communicate with each other. your brain has somewhere between 80 billion and 100 billion neurons. neurons tend to group together to form neural tracts, which would be like the streets and highways in the city analogy. The neuroscience of decision making. published 1 aug 2011. reviewed 1 aug 2011. source the kavli foundation. daeyeol lee, department of neurobiology and kavli institute for neuroscience, yale university school of medicine. yale university. research is revealing how neurons code the value of different options when people make decisions. Cognitive psychology grew into prominence between the 1950s and 1970s. prior to this time, behaviorism was the dominant perspective in psychology. this theory holds that we learn all our behaviors from interacting with our environment. it focuses strictly on observable behavior, not thought and emotion. then, researchers became more interested. When making a decision, we form opinions and choose actions via mental processes which are influenced by biases, reason, emotions, and memories. the simple act of deciding supports the notion that.
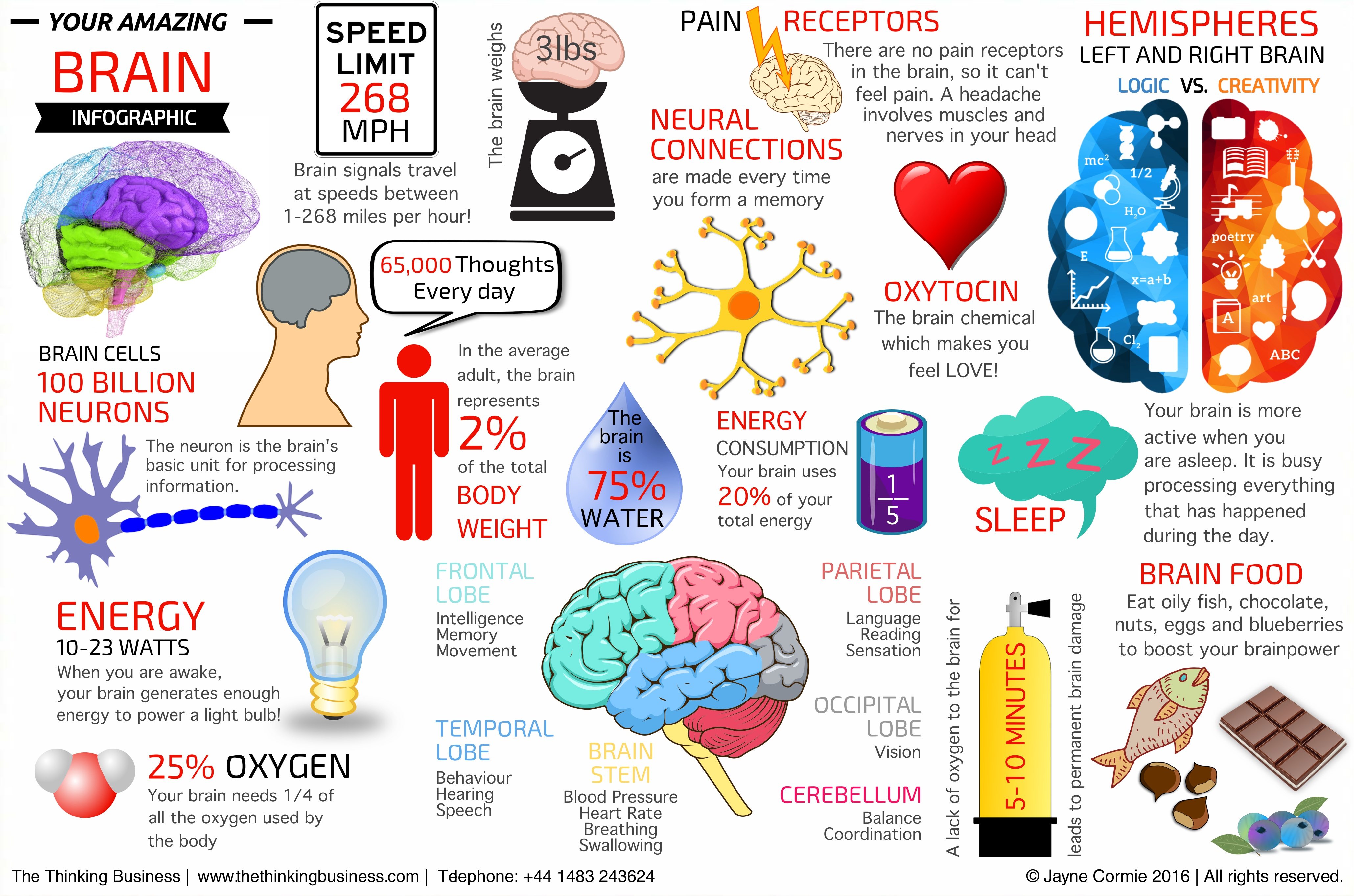
Brain Facts The Thinking Business The Thinking Business Cognitive psychology grew into prominence between the 1950s and 1970s. prior to this time, behaviorism was the dominant perspective in psychology. this theory holds that we learn all our behaviors from interacting with our environment. it focuses strictly on observable behavior, not thought and emotion. then, researchers became more interested. When making a decision, we form opinions and choose actions via mental processes which are influenced by biases, reason, emotions, and memories. the simple act of deciding supports the notion that.

Comments are closed.