The Microbiota Gut Brain Axis In Inflammatory Bowel Disease Ibdcoach

The Microbiota Gut Brain Axis In Inflammatory Bowel Disease Ibdcoach Abstract. the gut–brain axis is a bidirectional communication system driven by neural, hormonal, metabolic, immunological, and microbial signals. signaling events from the gut can modulate brain function and recent evidence suggests that the gut–brain axis may play a pivotal role in linking gastrointestinal and neurological diseases. The microbiome gut brain axis is one of the most central functional systems connecting the human body to the diverse ecosystems around us. the complex connections between the human gut microbiome, inflammatory bowel disease, our brain, and our health are key drivers of ibd pathogenesis that may be harnessed to promote healing from ibd.
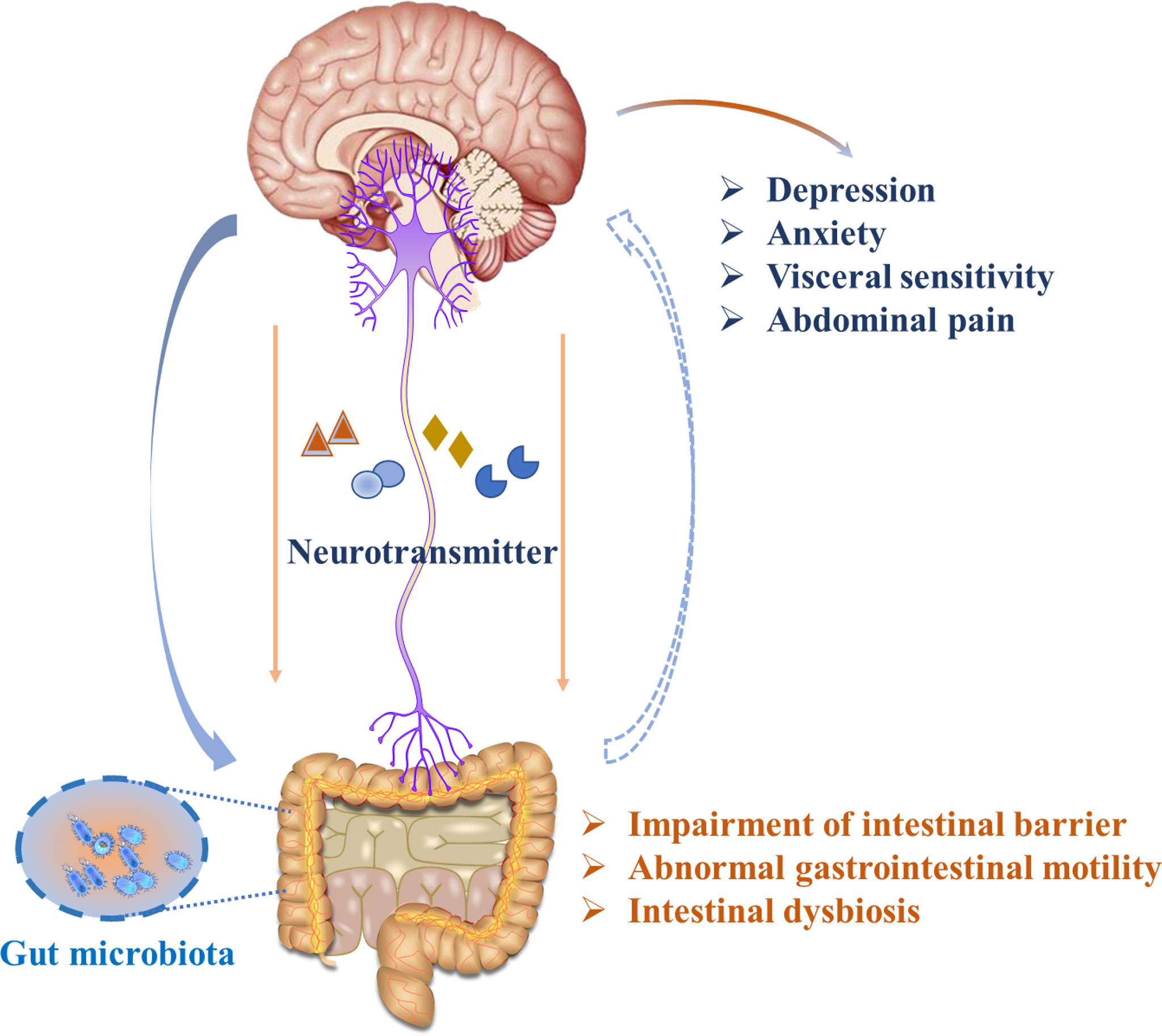
Frontiers Neurotransmitter And Intestinal Interactions Focus On The Core tip: the complex interplay between gut microbiota and the brain, and vice versa, has recently become not only the focus of neuroscience, but also the start point for research regarding many diseases such as inflammatory bowel diseases (ibd) and irritable bowel syndrome. the bi directional interaction between gut microbiota and the brain is. Inflammatory bowel disease (ibd) is a chronic immune mediated disease [5]. based on the analysis of numerous animal models, alteration or an aberrant immune response occurs in the microbiome, which may lead to intestinal inflammation [6]. when pro inflammatory bacteria or microbiota are transferred from mice with ibd to healthy mice. The microbiota–gut–brain axis represents an important regulator of glial functions, making it an actionable target to ameliorate the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases. Despite the bi directional interaction between gut microbiota and the brain not being fully understood, there is increasing evidence arising from animal and human studies that show how this intricate relationship may facilitate inflammatory bowel disease (ibd) pathogenesis, with consequent important implications on the possibility to improve.
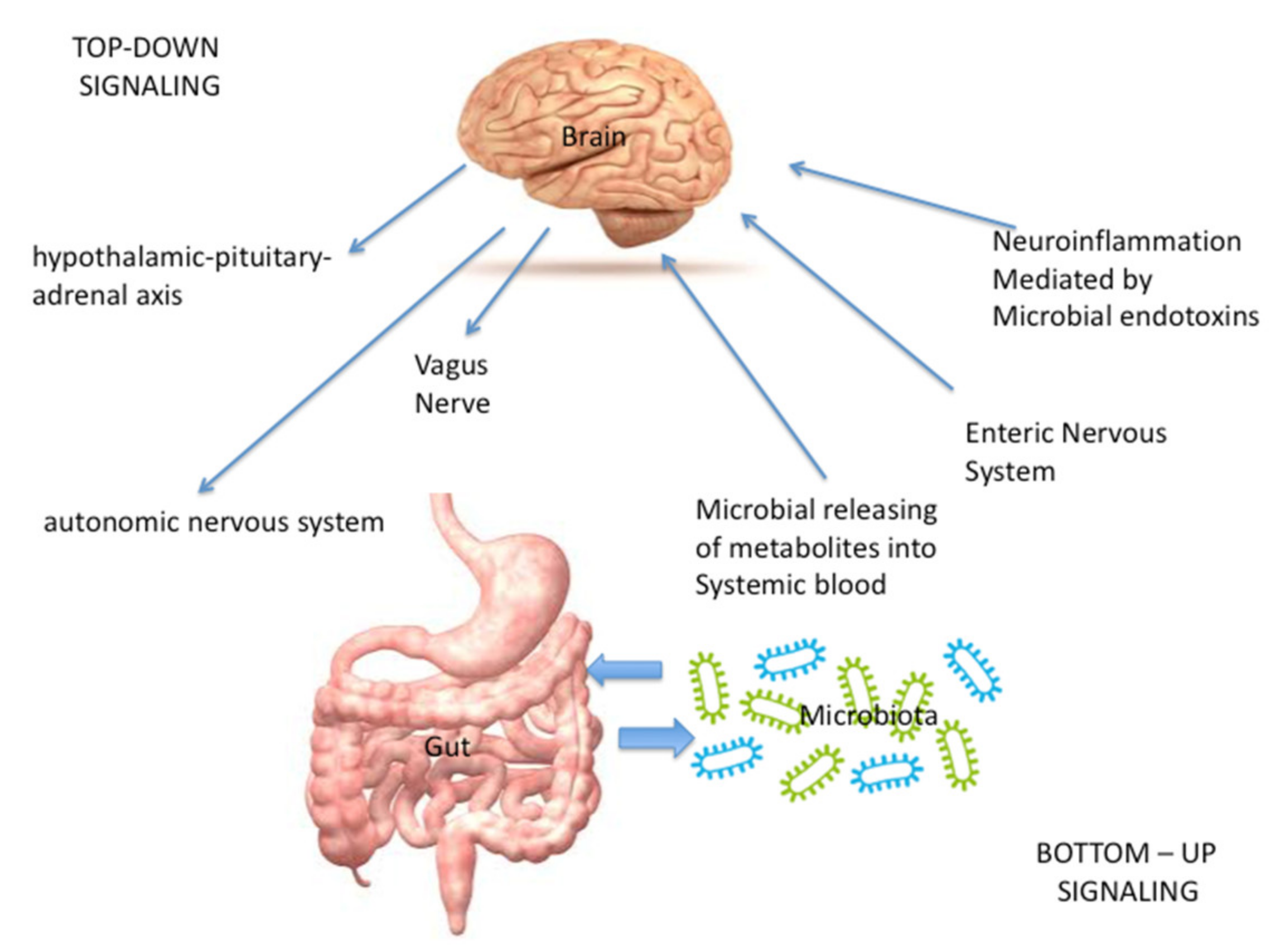
Life Free Full Text Microbiota Gutвђ Brain Axis In Ischemic Stroke A The microbiota–gut–brain axis represents an important regulator of glial functions, making it an actionable target to ameliorate the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases. Despite the bi directional interaction between gut microbiota and the brain not being fully understood, there is increasing evidence arising from animal and human studies that show how this intricate relationship may facilitate inflammatory bowel disease (ibd) pathogenesis, with consequent important implications on the possibility to improve. Emerging evidence suggests that gut brain microbiota axis (gbmax) may play a pivotal role linking gastrointestinal and neuronal disease. in this review, we summarize the latest advances in studies of gbmax in inflammatory bowel disease (ibd) and ischemic stroke. a more thorough understanding of the gbmax could advance our knowledge about the pathophysiology of ibd and ischemic stroke and help. The complex bidirectional communication system existing between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain initially termed the “gut–brain axis” and renamed the “microbiota–gut–brain axis”, considering the pivotal role of gut microbiota in sustaining local and systemic homeostasis, has a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (ibd). the integration of.
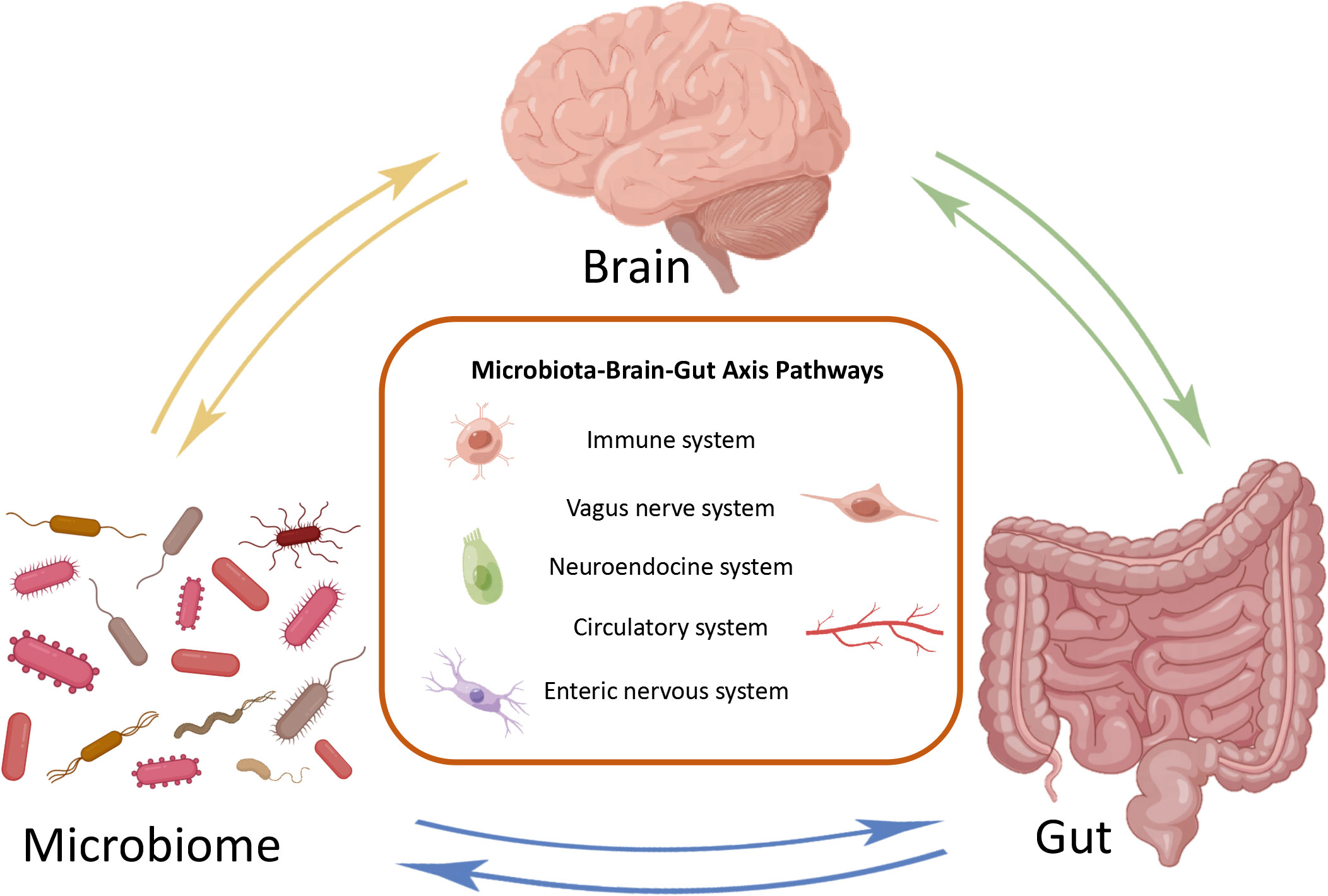
Frontiers Review Of Microbiota Gut Brain Axis And Innate Immunity In Emerging evidence suggests that gut brain microbiota axis (gbmax) may play a pivotal role linking gastrointestinal and neuronal disease. in this review, we summarize the latest advances in studies of gbmax in inflammatory bowel disease (ibd) and ischemic stroke. a more thorough understanding of the gbmax could advance our knowledge about the pathophysiology of ibd and ischemic stroke and help. The complex bidirectional communication system existing between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain initially termed the “gut–brain axis” and renamed the “microbiota–gut–brain axis”, considering the pivotal role of gut microbiota in sustaining local and systemic homeostasis, has a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (ibd). the integration of.

Comments are closed.