The Life Cycle Of Biofilm Formation Provides Different Intervention
The Life Cycle Of Biofilm Formation Provides Different Intervention An additional key regulator of the biofilm developmental life cycle is the ubiquitous bacterial second messenger c di gmp, with high c di gmp levels favoring the biofilm mode of growth, while low levels have been associated with planktonic and dispersed cells (68–70). c di gmp is required to mediate surface sensing, repress motility upon surface attachment, and increase biosynthesis of. An additional key regulator of the biofilm developmental life cycle is the ubiquitous bacterial second messenger cyclic diguanylate (c di gmp), with high c di gmp levels favouring the biofilm mode.
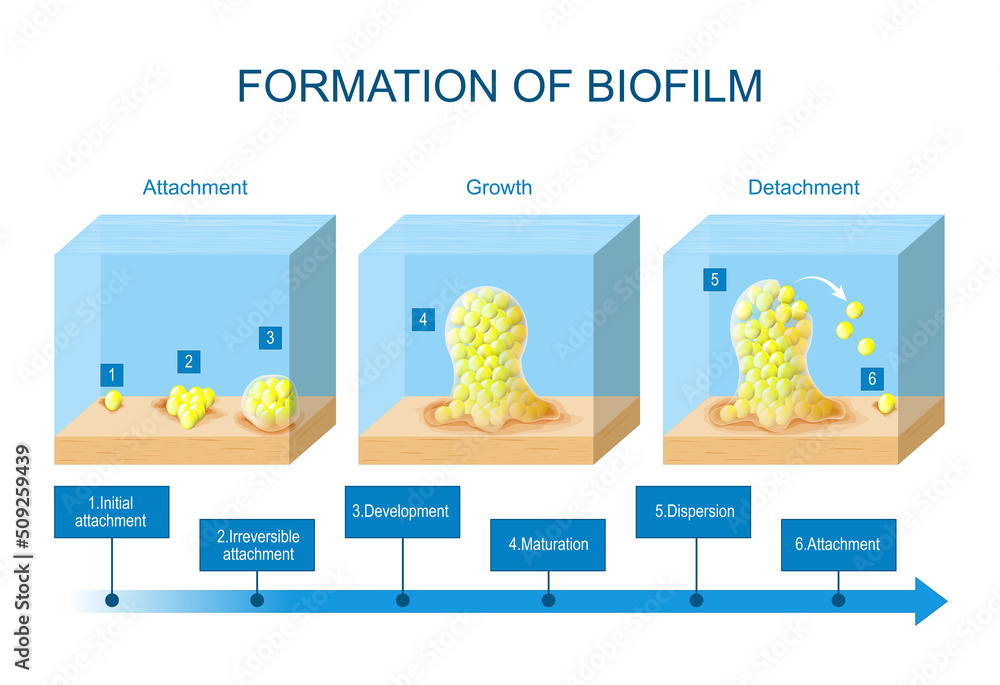
Biofilm Formation Stages Of Biofilm Development Life Cycle Of Different points can be targeted for biofilm inhibition and eradication at different stages of biofilm formation (figure 3). these combating strategies include inhibition of planktonic cells. We aim to present a simplistic developmental model for biofilm formation that is flexible enough to include all the diverse scenarios and microenvironments where biofilms are formed. with this new expanded, inclusive model, we hereby introduce a common platform for developing an understanding of biofilms and anti biofilm strategies that can be. Biofilm formation, growth, and proliferation are key parts of the biofilm life cycle , and gi biofilms occur as (1) mucosal biofilms with a mucin rich matrix, (2) biofilm clusters around mucin aggregates, (3) biofilms adherent to food particles, or (4) intermingled versions of these forms (figure 2, figure 3). 2, 3, 32. The original model of bio film formation is based on key publications investigating pseudomonas aeruginosa. the model proposed that the formation of biofilms is a cyclic process that occurs in a.

What Are Biofilms And How Do They Form Biofilm formation, growth, and proliferation are key parts of the biofilm life cycle , and gi biofilms occur as (1) mucosal biofilms with a mucin rich matrix, (2) biofilm clusters around mucin aggregates, (3) biofilms adherent to food particles, or (4) intermingled versions of these forms (figure 2, figure 3). 2, 3, 32. The original model of bio film formation is based on key publications investigating pseudomonas aeruginosa. the model proposed that the formation of biofilms is a cyclic process that occurs in a. Biofilm formation proceeds as a developmental process with distinct stages: 'initial adhesion', in which microorganisms adhere to a host or attach to medical device surfaces through cell surface. In this review, bjarnsholt and colleagues propose a revised conceptual model of the biofilm life cycle that encompasses the three major steps of biofilm formation — aggregation, growth and disaggregation — independently of surfaces, and initiation from single cell planktonic bacteria, and thus represents a broader range of biofilm systems.

The Biofilm Life Cycle Different Stages Of Bacterial Biofilm Biofilm formation proceeds as a developmental process with distinct stages: 'initial adhesion', in which microorganisms adhere to a host or attach to medical device surfaces through cell surface. In this review, bjarnsholt and colleagues propose a revised conceptual model of the biofilm life cycle that encompasses the three major steps of biofilm formation — aggregation, growth and disaggregation — independently of surfaces, and initiation from single cell planktonic bacteria, and thus represents a broader range of biofilm systems.

Comments are closed.