The Gut Microbiota Modulates The Intestinal Immune Response The Gut

The Gut Microbiota Modulates The Intestinal Immune Response The Gut The gut microbiota modulates the intestinal barrier and affects thrombotic risk. f. j. the aryl hydrocarbon receptor: an environmental sensor integrating immune responses in health and disease. The gut microbiota influences development 1,2,3 and homeostasis 4,5,6,7 of the mammalian immune system, and is associated with human inflammatory 8 and immune diseases 9,10 as well as responses to.

The Gut Microbiota Modulates The Inflammatory Response And Cognitive The gut microbiota modulates immune processes both locally and systemically. this includes whether and how the immune system reacts to emerging tumours, whether antitumour immune responses are. Dynamic interactions between gut microbiota and a host’s innate and adaptive immune systems play key roles in maintaining intestinal homeostasis and inhibiting inflammation. the gut microbiota metabolizes proteins and complex carbohydrates, synthesize vitamins, and produce an enormous number of metabolic products that can mediate cross talk. The gut microbiota encompasses a diverse community of bacteria that carry out various functions influencing the overall health of the host. these comprise nutrient metabolism, immune system regulation and natural defence against infection. the presence of certain bacteria is associated with inflammatory molecules that may bring about. This intense communication between epithelial cells, immune cells and microbiome will shape specific immune responses to antigens, balancing tolerance and effector immune functions. recent studies indicate that composition of the gut microbiome affects immune system development and modulates immune mediators, which in turn affect the intestinal.
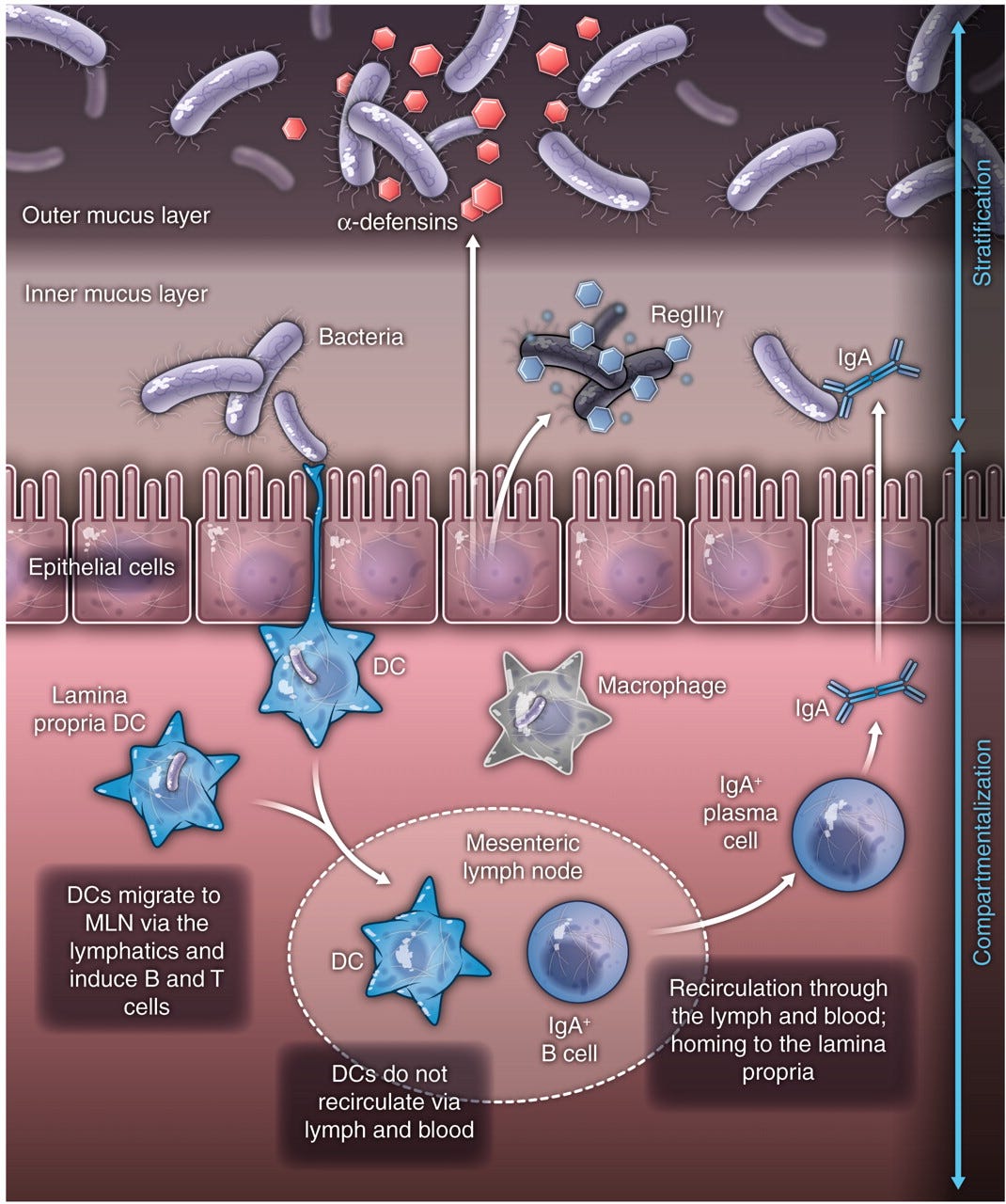
The Gut Microbiota And The Immune System Thryve Medium The gut microbiota encompasses a diverse community of bacteria that carry out various functions influencing the overall health of the host. these comprise nutrient metabolism, immune system regulation and natural defence against infection. the presence of certain bacteria is associated with inflammatory molecules that may bring about. This intense communication between epithelial cells, immune cells and microbiome will shape specific immune responses to antigens, balancing tolerance and effector immune functions. recent studies indicate that composition of the gut microbiome affects immune system development and modulates immune mediators, which in turn affect the intestinal. The intestine exhibits distinct characteristics along its length, with a substantial immune cell reservoir and diverse microbiota crucial for maintaining health. this study investigates how anatomical location and regional microbiota influence intestinal immune cell abundance. using conventionally colonized and germ free mice, segment specific. Abstract. diet modulates the gut microbiome, which in turn can impact the immune system. here, we determined how two microbiota targeted dietary interventions, plant based fiber and fermented foods, influence the human microbiome and immune system in healthy adults. using a 17 week randomized, prospective study (n = 18 arm) combined with omics.
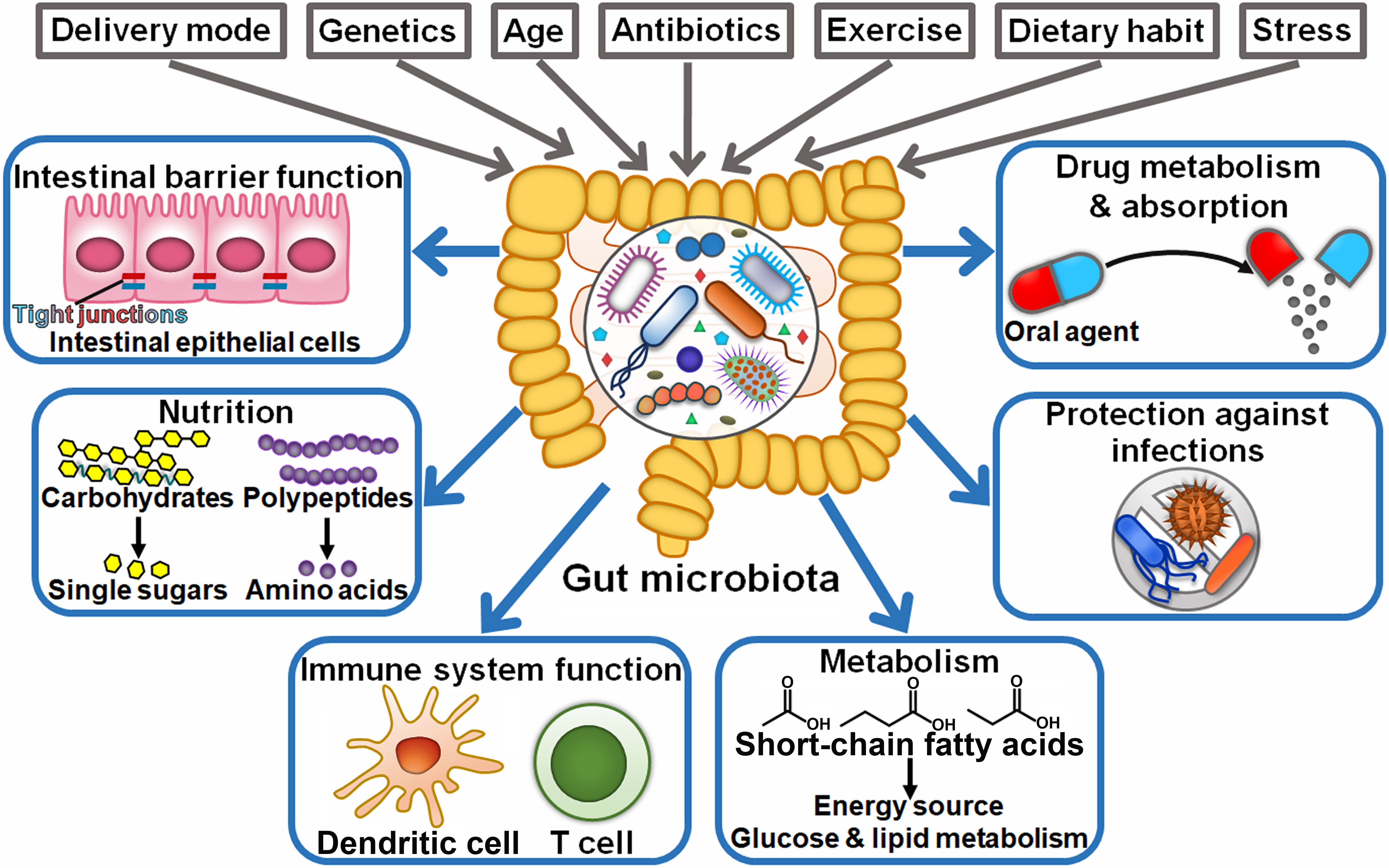
Frontiers The Crosstalk Between The Gut Microbiota And Tumor Immunity The intestine exhibits distinct characteristics along its length, with a substantial immune cell reservoir and diverse microbiota crucial for maintaining health. this study investigates how anatomical location and regional microbiota influence intestinal immune cell abundance. using conventionally colonized and germ free mice, segment specific. Abstract. diet modulates the gut microbiome, which in turn can impact the immune system. here, we determined how two microbiota targeted dietary interventions, plant based fiber and fermented foods, influence the human microbiome and immune system in healthy adults. using a 17 week randomized, prospective study (n = 18 arm) combined with omics.
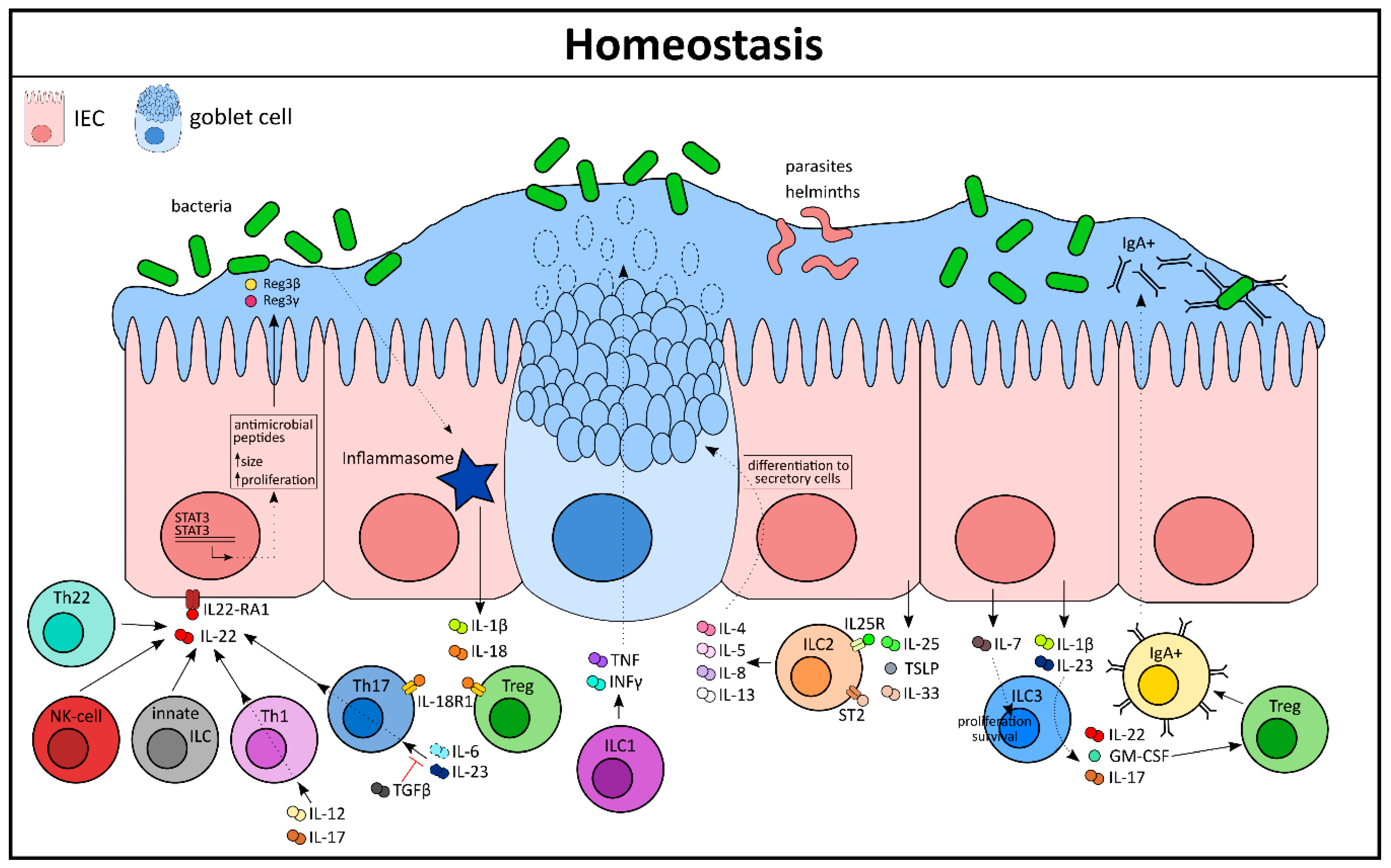
Cells Free Full Text Cytokine Mediated Crosstalk Between Immune

Comments are closed.