The Electromagnetic Spectrum Properties And Uses
Electromagnetic Spectrum Explained Discover Tutoring Electromagnetic waves travel at 300,000,000 metres per second (m s) through a vacuum. electromagnetic waves can be separated into seven distinct groups in the spectrum. each group contains a range. Learn about the speed of light transverse waves that make the electromagnetic spectrum, the order of these waves, their uses and dangers with this guide for ks3 physics students aged 11 14 from.
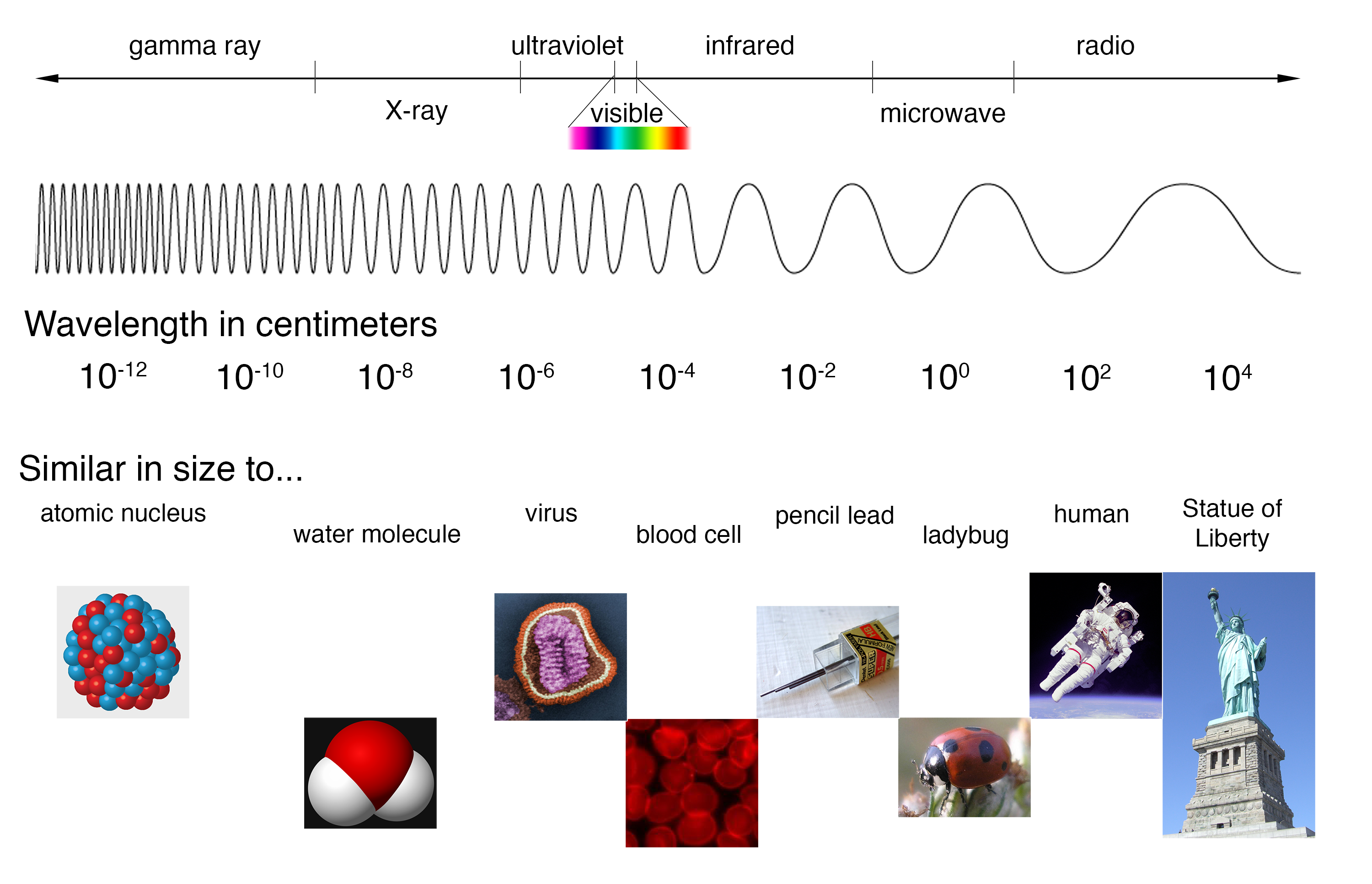
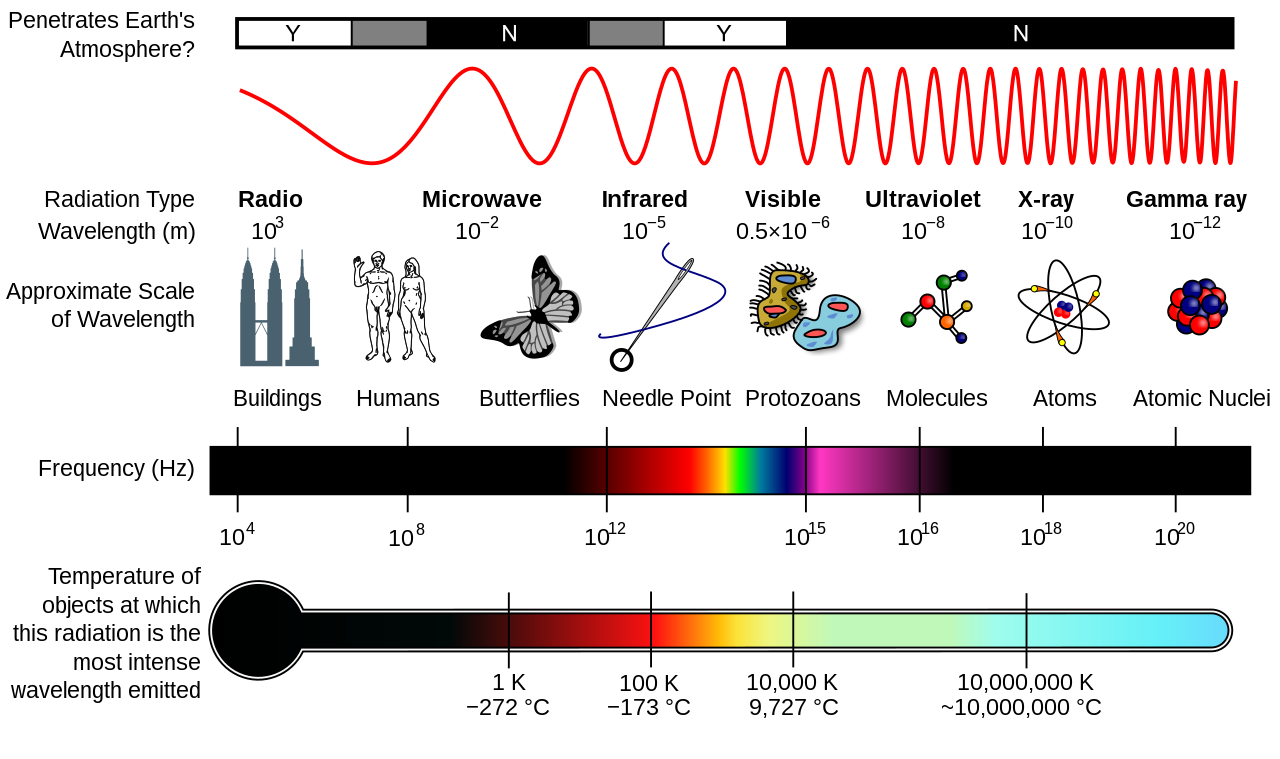
Spectra Introduction Electromagnetic spectrum, the entire distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to frequency or wavelength. although all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, they do so at a wide range of frequencies, wavelengths, and photon energies. the electromagnetic spectrum comprises the span of all electromagnetic. The electromagnetic spectrum is the continuous spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. it covers an enormous frequency range, from about 1 hertz (hz) at the extreme low end to over 10 25 hz at the high end, with no gaps in the frequency range. electromagnetic radiation refers to the waves of the electromagnetic field, propagating through space. A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths. the electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. the spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. Each frequency has an associated wavelength. as frequency increases across the spectrum, wavelength decreases. energy also increases with frequency. because of this, higher frequencies penetrate matter more readily. some of the properties and uses of the various em spectrum bands are listed in table 15.1.

Schoolphysics Welcome A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths. the electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. the spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. Each frequency has an associated wavelength. as frequency increases across the spectrum, wavelength decreases. energy also increases with frequency. because of this, higher frequencies penetrate matter more readily. some of the properties and uses of the various em spectrum bands are listed in table 15.1. What is electromagnetic energy? electromagnetic energy travels in waves and spans a broad spectrum from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays. the human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. a radio detects a different portion of the spectrum, and an x ray machine uses yet another portion. The hubble space telescope can view objects in more than just visible light, including ultraviolet, visible and infrared light. these observations enable astronomers to determine certain physical characteristics of objects, such as their temperature, composition and velocity. the electromagnetic spectrum consists of much more than visible light.
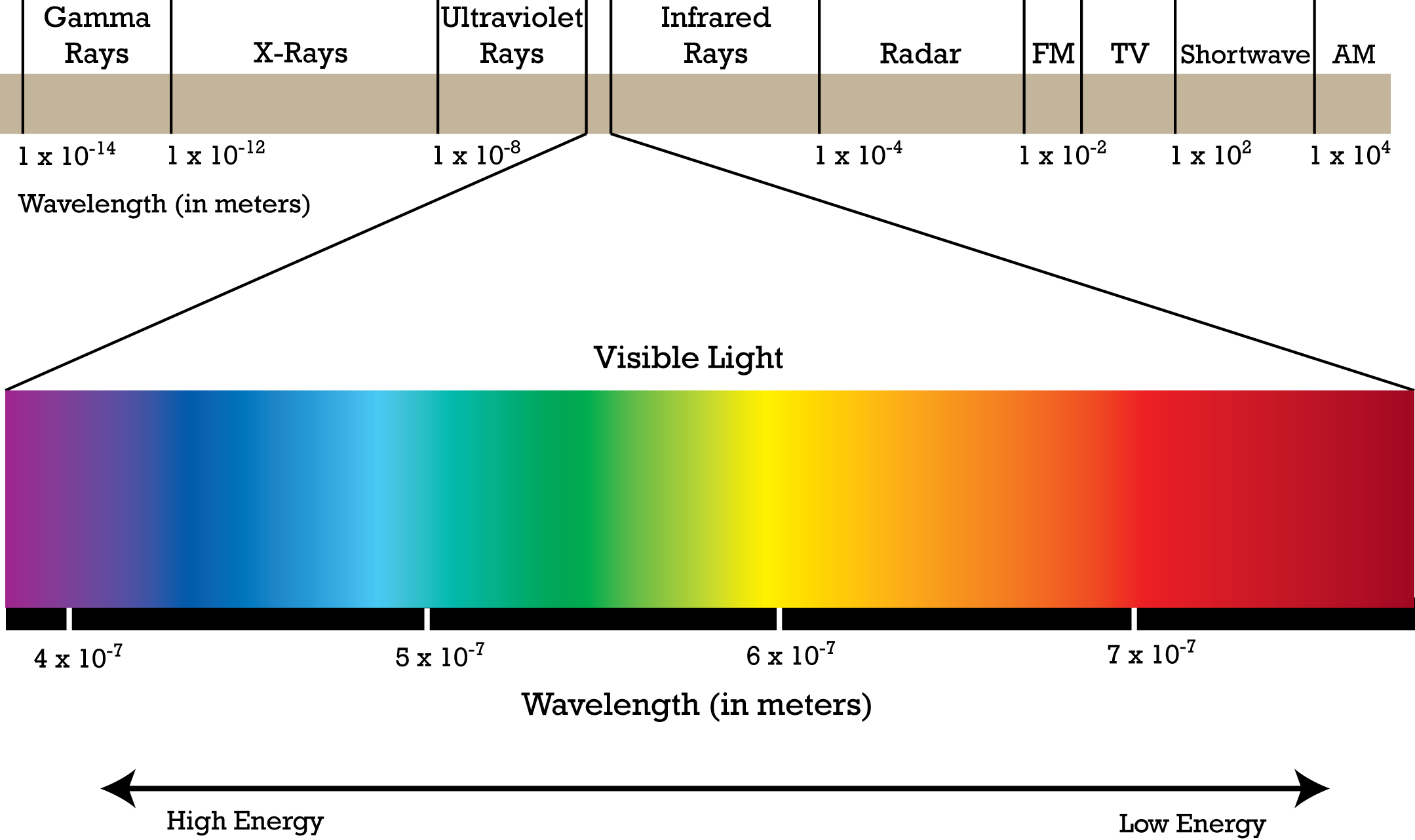
The Electromagnetic Spectrum What is electromagnetic energy? electromagnetic energy travels in waves and spans a broad spectrum from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays. the human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. a radio detects a different portion of the spectrum, and an x ray machine uses yet another portion. The hubble space telescope can view objects in more than just visible light, including ultraviolet, visible and infrared light. these observations enable astronomers to determine certain physical characteristics of objects, such as their temperature, composition and velocity. the electromagnetic spectrum consists of much more than visible light.

Waves And The Electromagnetic Spectrum

Comments are closed.