The Electromagnetic Spectrum Microwaves Infrared X Rays Etc

The Electromagnetic Spectrum Microwaves Infrared X Rays Etc Also, the sun is an important source of ultraviolet rays. x rays. in the electromagnetic spectrum, x rays lie beyond the ultraviolet region. x rays have wavelengths ranging from about 10 8 m or 10 nm to 10 13 m or 10 4; x rays are particularly well known due to their use as a diagnostic tool in medicine. The electromagnetic spectrum is the continuous spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. it covers an enormous frequency range, from about 1 hertz (hz) at the extreme low end to over 10 25 hz at the high end, with no gaps in the frequency range. electromagnetic radiation refers to the waves of the electromagnetic field, propagating through space.
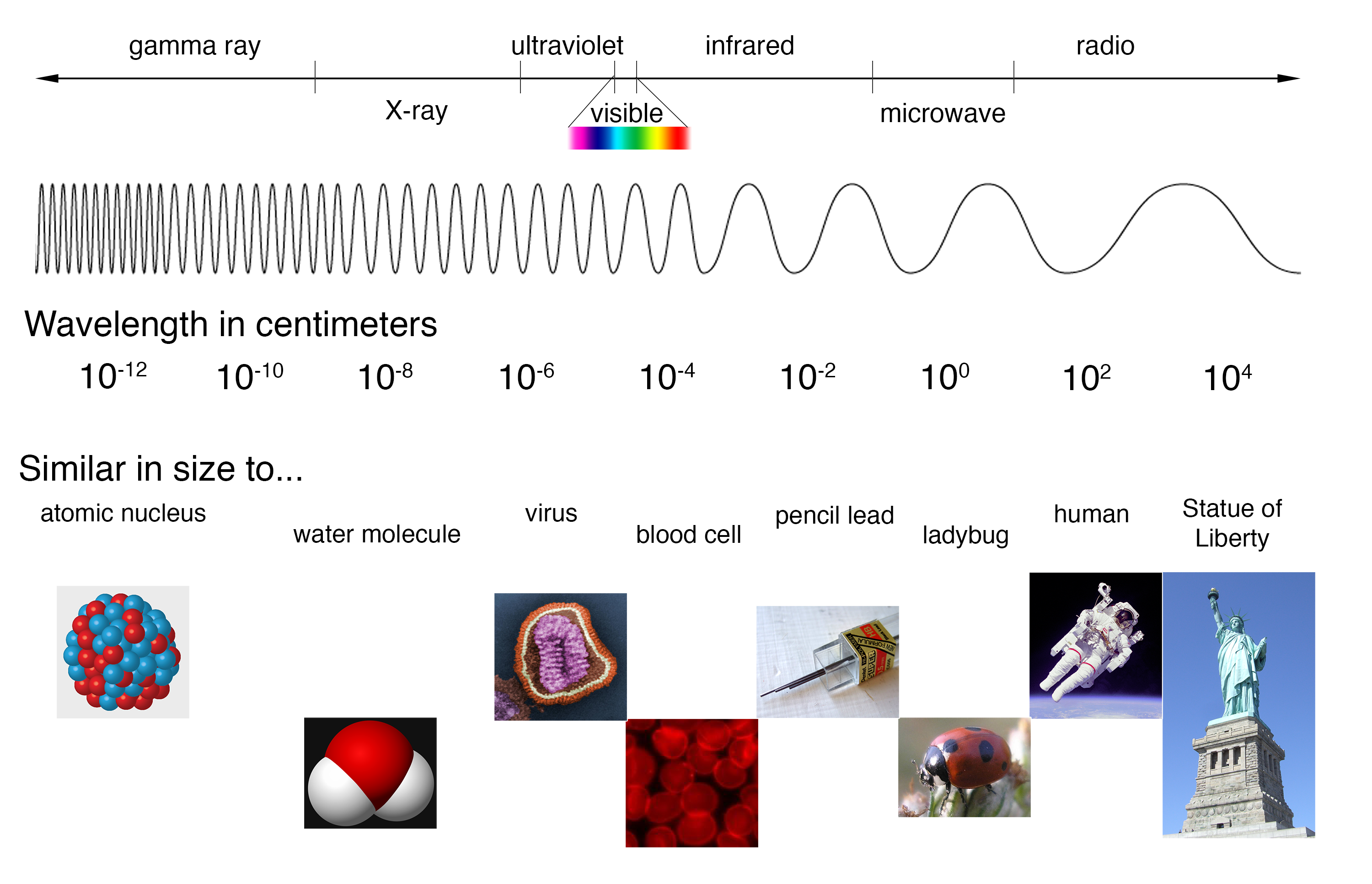
Spectra Introduction Radiation is energy that travels and spreads out as it goes – the visible light that comes from a lamp in your house and the radio waves that come from a radio station are two types of electromagnetic radiation. the other types of em radiation that make up the electromagnetic spectrum are microwaves, infrared light, ultraviolet light, x rays. The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. the spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. from low to high frequency these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x rays, and. The electromagnetic spectrum. 28368 views 82 likes. esa science & exploration space science integral. light, or electromagnetic radiation, comes in many forms. there are radio waves, microwaves, infrared light, visible light, ultraviolet light, x rays and gamma rays, all of which form what is known as the 'electromagnetic spectrum'. Other types of light include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, ultraviolet rays, x rays and gamma rays — all of which are imperceptible to human eyes. all light, or electromagnetic radiation, travels through space at 186,000 miles (300,000 kilometers) per second — the speed of light.
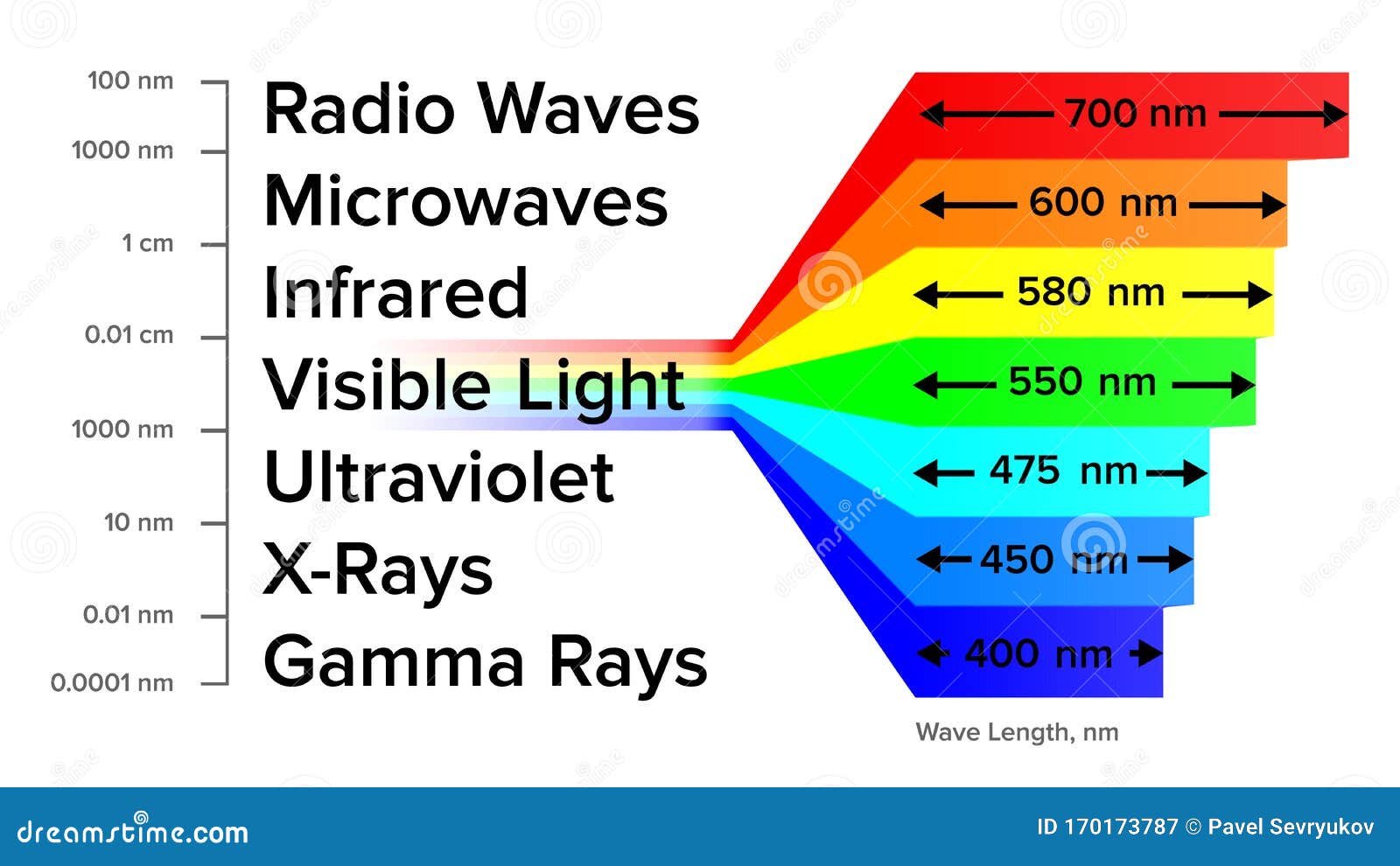
Electromagnetic Spectrum Information Gamma Rays Scheme Vector Stock The electromagnetic spectrum. 28368 views 82 likes. esa science & exploration space science integral. light, or electromagnetic radiation, comes in many forms. there are radio waves, microwaves, infrared light, visible light, ultraviolet light, x rays and gamma rays, all of which form what is known as the 'electromagnetic spectrum'. Other types of light include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, ultraviolet rays, x rays and gamma rays — all of which are imperceptible to human eyes. all light, or electromagnetic radiation, travels through space at 186,000 miles (300,000 kilometers) per second — the speed of light. Quick facts: electromagnetic spectrum. also known as: electromagnetic radiation. type: radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x ray, and gamma ray. size: we can describe light waves in terms of wavelength, or distance from one wave peak to the next. each type of light has a different range of wavelengths. What is electromagnetic energy? electromagnetic energy travels in waves and spans a broad spectrum from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays. the human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. a radio detects a different portion of the spectrum, and an x ray machine uses yet another portion.
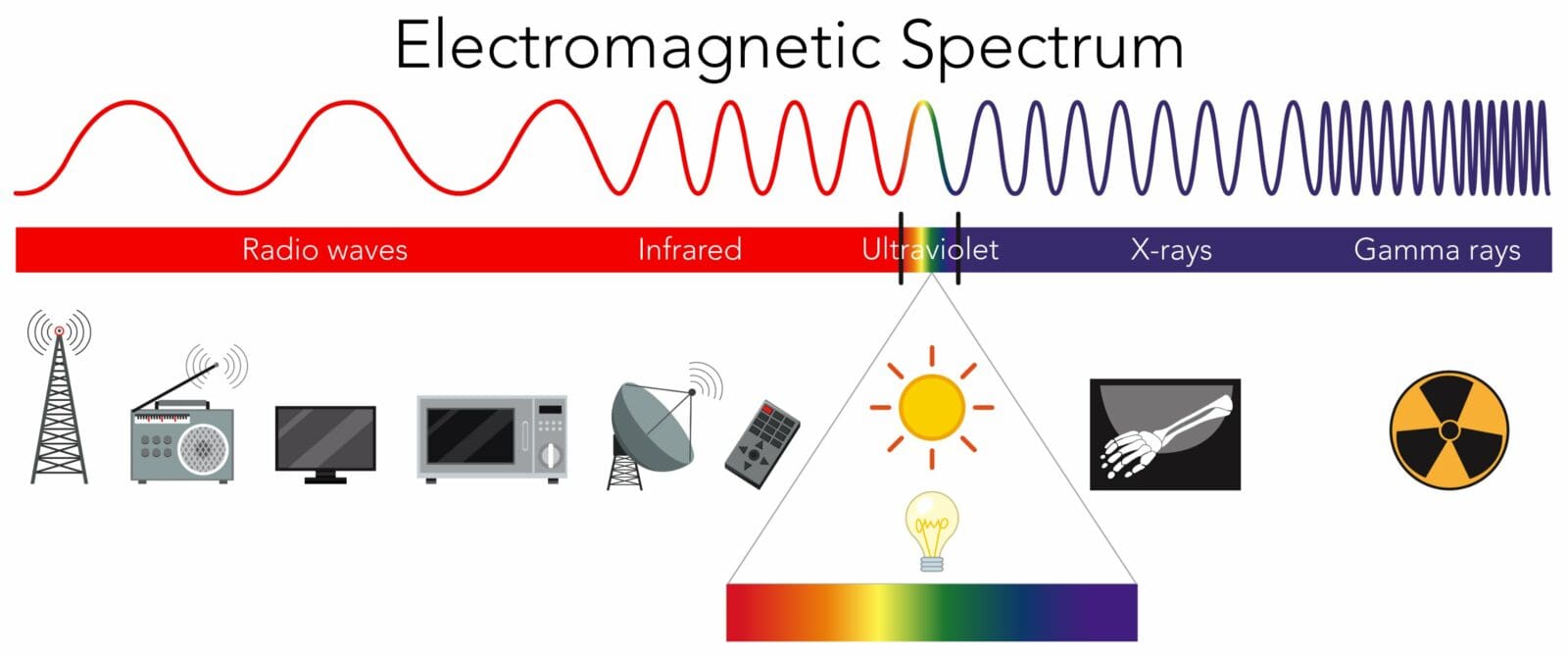
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Microwaves Infrared X Rays Etc Quick facts: electromagnetic spectrum. also known as: electromagnetic radiation. type: radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x ray, and gamma ray. size: we can describe light waves in terms of wavelength, or distance from one wave peak to the next. each type of light has a different range of wavelengths. What is electromagnetic energy? electromagnetic energy travels in waves and spans a broad spectrum from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays. the human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. a radio detects a different portion of the spectrum, and an x ray machine uses yet another portion.

Comments are closed.