Table 1 From Hypothermia Versus Normothermia After Out Of Hospitalо

Hypothermia Versus Normothermia After Out Of Hospital Grepmed A total of 1850 patients were evaluated for the primary outcome. at 6 months, 465 of 925 patients (50%) in the hypothermia group had died, as compared with 446 of 925 (48%) in the normothermia. Arrhythmia resulting in hemodynamic compromise was more common in the hypothermia group than in the normothermia group (24% vs. 17%, p<0.001). the incidence of other adverse events did not differ significantly between the two groups. conclusions: in patients with coma after out of hospital cardiac arrest, targeted hypothermia did not lead to a.

Table 1 From Hypothermia Versus Normothermia After Out Of Relevance for patients. six randomized controlled trials were included in this review. there was no significant difference between the hypothermia and normothermia groups in mortality till 6 months follow up after out of hospital cardiac arrest (or 0.88, 95% ci 0.67–1.16; n = 3243; i 2 = 51%), or favorable neurological outcome (or 1.31, 95% ci 0.93–1.84; n = 3091; i 2 = 68%). Outcomes were consistent in the prespecified subgroups. arrhythmia resulting in hemodynamic compromise was more common in the hypothermia group than in the normothermia group (24% vs. 17%, p<0.001. After the publication of the ttm trial, the use of hypothermia decreased, with a reported increase in mortality. 7 the new ttm 2 (targeted hypothermia versus targeted normothermia after out of hospital cardiac arrest) trial (2021) assessed 1,850 patients with ohca randomly assigned to undergo targeted hypothermia (th; 33°c) or targeted. In patients with coma after out of hospital cardiac arrest, targeted hypothermia did not lead to a lower incidence of death by 6 months than targeted normothermia and outcomes were consistent in the prespecified subgroups. background: targeted temperature management is recommended for patients after cardiac arrest, but the supporting evidence is of low certainty. methods: in an open label.
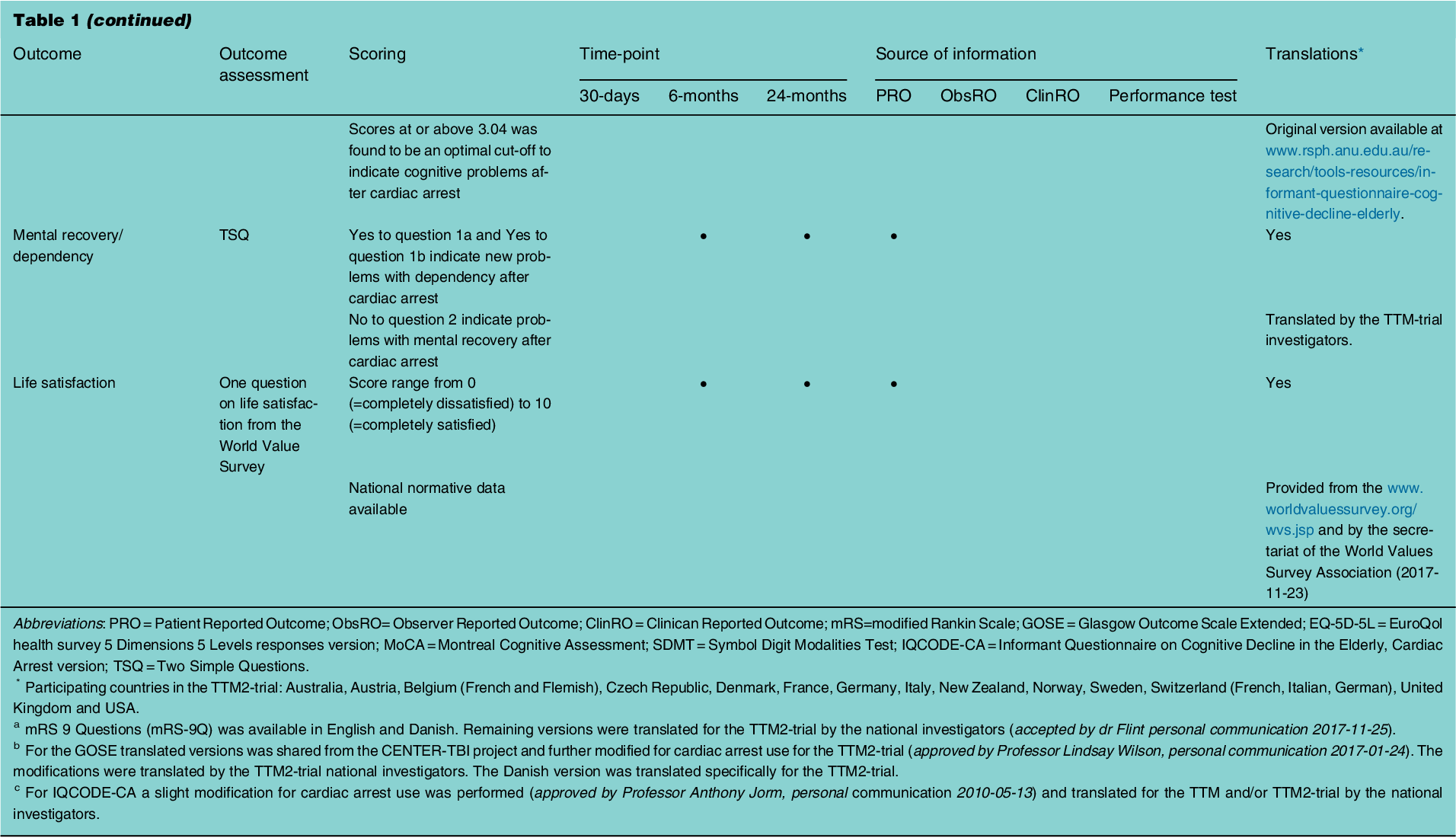
Table 1 From Protocol For Outcome Reporting And Follow Up In The After the publication of the ttm trial, the use of hypothermia decreased, with a reported increase in mortality. 7 the new ttm 2 (targeted hypothermia versus targeted normothermia after out of hospital cardiac arrest) trial (2021) assessed 1,850 patients with ohca randomly assigned to undergo targeted hypothermia (th; 33°c) or targeted. In patients with coma after out of hospital cardiac arrest, targeted hypothermia did not lead to a lower incidence of death by 6 months than targeted normothermia and outcomes were consistent in the prespecified subgroups. background: targeted temperature management is recommended for patients after cardiac arrest, but the supporting evidence is of low certainty. methods: in an open label. Dankiewicz j et al. hypothermia versus normothermia after out of hospital cardiac arrest. nejm 2021. pmid: 34133859; nielsen n, et al. targeted temperature management at 33°c versus 36°c after cardiac arrest. n engl j med. dec 2013. pmid: 24237006; johnson nj, et al. targeted temperature management at 33 versus 36 degrees: a retrospective. Hypothermia versus normothermia after out of hospital cardiac arrest; the effect on post intervention serum concentrations of sedatives and analgesics and time to awakening author links open overlay panel martin annborn a , ameldina ceric b , ola borgquist c , joachim during b , marion moseby knappe d , anna lybeck c.

Comments are closed.