Structure And Function Of Dna I Dna Structure Class 12 I Scientech

Structure And Function Of Dna I Dna Structure Class 12 I Scientech #scientechbiologythrough this video i am going to explain the structure and function of dna i dna structure class 12 i scientech biology i model of dna.the d. There are three different dna types: a dna: it is a right handed double helix similar to the b dna form. dehydrated dna takes an a form that protects the dna during extreme conditions such as desiccation. protein binding also removes the solvent from dna, and the dna takes an a form.

Dna Structure Simplified Structure Of Dna Grade 12 Life Sciences Dna structure and functions. dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, a macromolecule that carries genetic information in all living organisms, from the tiniest microorganisms to the most complex multicellular humans. dna is a fundamental molecule that holds life’s blueprint. within a eukaryotic cell (plant and animal), they are found inside the. It is a double stranded molecule and has a unique twisted helical structure. dna is made up of nucleotides, each nucleotide has three components: a backbone made up of a sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate group and a nitrogen containing base attached to the sugar. each strand has many nucleotides or says numerous sugar, a phosphate group, and. Our genetic information is coded within the macromolecule known as deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). dna belongs to a class of organic molecules called nucleic acids. the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. a nucleotide has three parts: phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen base. 13.3: dna structure and sequencing. the building blocks of dna are nucleotides. the important components of the nucleotide are a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), and a phosphate group. the nucleotide is named depending on the nitrogenous base. the nitrogenous base can be a purine such as adenine (a) and guanine (g), or a.
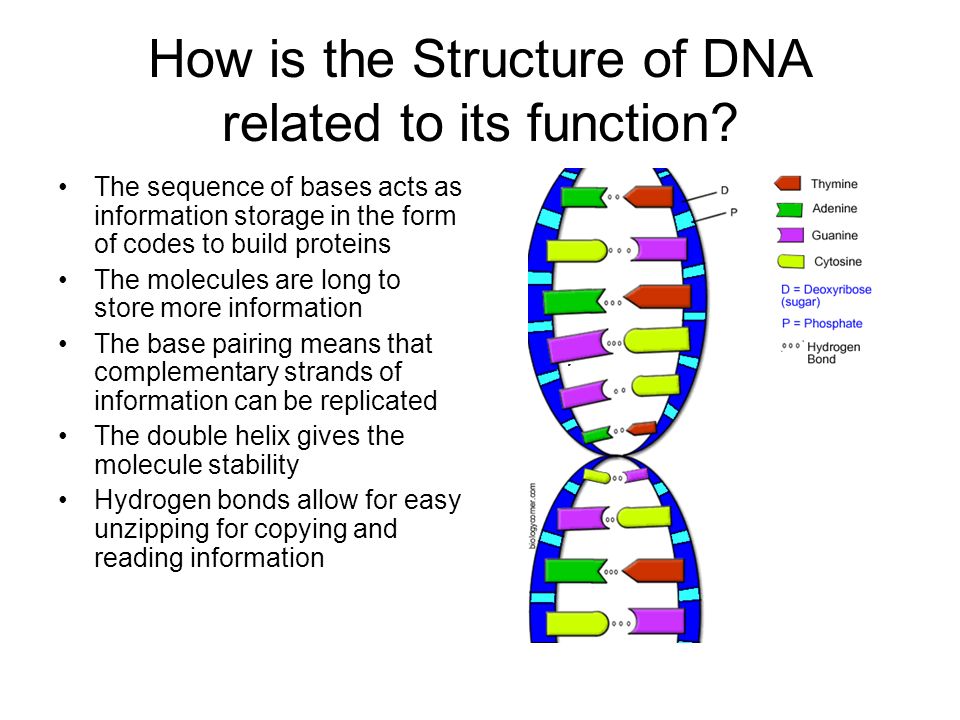
Dna Structure And Function Protein Synthesis Parker S Ap Bio 3rd Period Our genetic information is coded within the macromolecule known as deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). dna belongs to a class of organic molecules called nucleic acids. the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. a nucleotide has three parts: phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen base. 13.3: dna structure and sequencing. the building blocks of dna are nucleotides. the important components of the nucleotide are a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), and a phosphate group. the nucleotide is named depending on the nitrogenous base. the nitrogenous base can be a purine such as adenine (a) and guanine (g), or a. Salient features of dna double helix. it consists of two polynucleotide chains where the sugar and phosphate group form the backbone and the nitrogenous bases project inside the helix. the two polynucleotide chains have anti parallel polarity i.e. if one strand has 5′ → 3′ polarity, the other strand has 3′ → 5′ polarity. Dna definition. deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. dna is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. large compressed dna molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, are mostly present inside the.

Comments are closed.