State Government Powers Responsibilities Models Examples Video

State Government Powers Responsibilities Models Examples Video Learn about state government powers and responsibilities. see the model for all state governments, and look at examples to understand how state. Here are some of the basic powers of state governments: the power to set its own election laws. the power to amend the state's constitution. the power to hold referendums. the power to create.

What Are The Roles And Responsibilities Of State Government Modern democracies divide governmental power in two general ways; some, like the united states, use a combination of both structures. the first and more common mechanism shares power among three branches of government—the legislature, the executive, and the judiciary. the second, federalism, apportions power between two levels of government. State powers. in the tenth amendment, the constitution also recognizes the powers of the state governments. traditionally, these included the “police powers” of health, education, and welfare. State government structure 1. under the tenth amendment to the us constitution, all powers not granted to the federal government are reserved to the states and the people. all state governments are modeled after the federal government and consist of three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. 6.1.1 investigate: the powers of state and national government and the tensions between them. the functions of state and national government in the united states are based on the principle of separation of powers. a power is the legal right of the executive, legislative, or judicial branch of a government to take action.
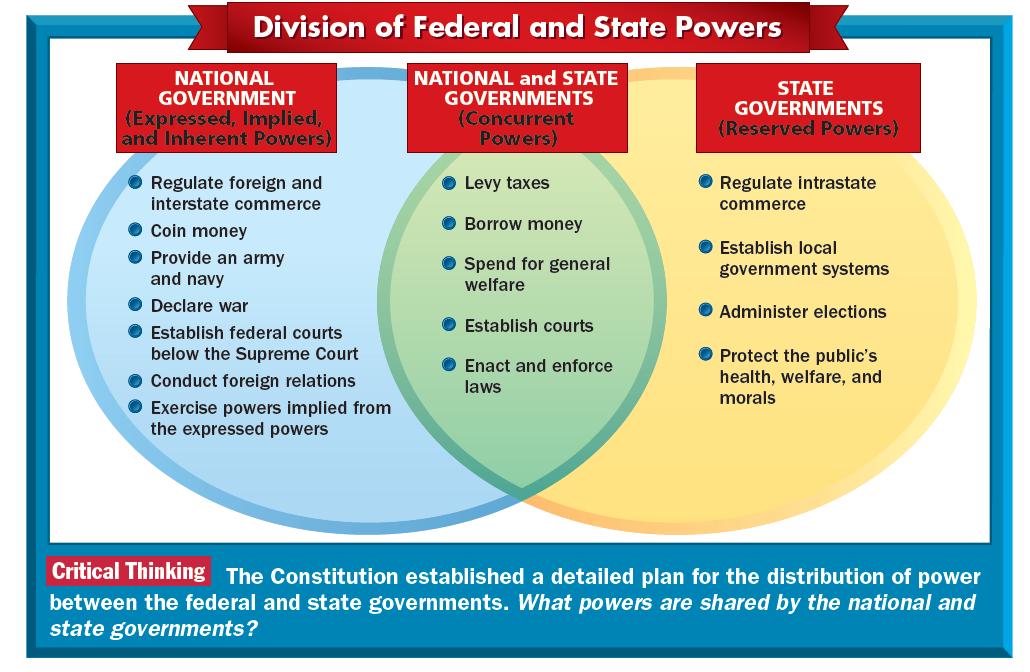
Division Of Federal And State Powers вђ Bello S Reference Page вђ Use State government structure 1. under the tenth amendment to the us constitution, all powers not granted to the federal government are reserved to the states and the people. all state governments are modeled after the federal government and consist of three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. 6.1.1 investigate: the powers of state and national government and the tensions between them. the functions of state and national government in the united states are based on the principle of separation of powers. a power is the legal right of the executive, legislative, or judicial branch of a government to take action. Identify the powers and responsibilities of federal, state, and local governments; modern democracies divide governmental power in two general ways; some, like the united states, use a combination of both structures. the first and more common mechanism shares power among three branches of government—the legislature, the executive, and the. 14.1 state power and delegation. highlights. learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: explain how the balance of power between national and state governments shifted with the drafting and ratification of the constitution. identify parts of the constitution that grant power to the national government and parts that.

Federalism Definition History Characteristics Facts Britannica Identify the powers and responsibilities of federal, state, and local governments; modern democracies divide governmental power in two general ways; some, like the united states, use a combination of both structures. the first and more common mechanism shares power among three branches of government—the legislature, the executive, and the. 14.1 state power and delegation. highlights. learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: explain how the balance of power between national and state governments shifted with the drafting and ratification of the constitution. identify parts of the constitution that grant power to the national government and parts that.

Comments are closed.