Signal To Noise Ratio вђ S N Ratio Shot Noise Det

Signal To Noise Ratio вђ S N Ratio Shot Noise Detect The quality of optical and other measurements is often characterized with a signal to noise ratio (snr, s n ratio). this is generally understood to be the ratio of the detected powers (not amplitudes), and is often expressed in decibels. usually, the definition refers to electrical powers in the output of some detector. Definition. one definition of signal to noise ratio is the ratio of the power of a signal (meaningful input) to the power of background noise (meaningless or unwanted input): where p is average power. both signal and noise power must be measured at the same or equivalent points in a system, and within the same system bandwidth.
Nice And Easy What Is Snr Signal To Noise Ratio The Solid Signal Blog Instrumental noise. thermal or johnson noise →. vrms = (4ktr∆f)1 2. k = 1.38 x 10 23 j k t = temperature (k) r = ohms. thermal agitation of electrons across resistive and capacitive components in circuits. voltage fluctuations. ∆f (bandwidth) = 1 3tr. tr = response time – time required for output to increase from 10 90% of final value. Uctuating input current for the shot noise, and a second, independent uctuating thermal noise source from the feedback resistance (figure 3). this pulls a lot of material together and allows us to calculate an essential quantity for any measurement, i:e:, the signal to noise ratio (s n). for the detector, the magnitude of the output voltage. The s n ratio is consistent with that expected from the sensitivity of the camera (lesson 1), so the right hand column does deserve the title “noise.” typically, noise is about 1000 dn. in lesson 2, we showed that the signal exhibited the expected trend with secant z … lesson 9 astronomy 244 444, spring 2020 4 sec z signal, dn rms noise, dn. Figure 5.1.1 5.1. 1: plots showing (a) the signal and the noise in blue with the signal superimposed as a smooth line; (b) the noise only; and (c) the signal only. the signal consists of three peaks at times of 250, 500, and 750, and with maximum values of 100, 60, and 30, respectively. the noise is drawn at random from a normal distribution.
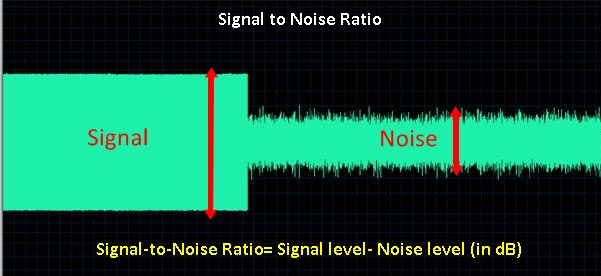
What Is Signal To Noise Ratio The s n ratio is consistent with that expected from the sensitivity of the camera (lesson 1), so the right hand column does deserve the title “noise.” typically, noise is about 1000 dn. in lesson 2, we showed that the signal exhibited the expected trend with secant z … lesson 9 astronomy 244 444, spring 2020 4 sec z signal, dn rms noise, dn. Figure 5.1.1 5.1. 1: plots showing (a) the signal and the noise in blue with the signal superimposed as a smooth line; (b) the noise only; and (c) the signal only. the signal consists of three peaks at times of 250, 500, and 750, and with maximum values of 100, 60, and 30, respectively. the noise is drawn at random from a normal distribution. Noise is any unsteady component of the measurement signal that causes the instantaneous value of the signal to differ from the instrument’s rendition of the “true value”. x(t) s(t) time. n(t) x(t) average signal power. average power (in watts) dissipated when voltage signal v connected to a 1 resistor:. The magnitude of shot noise increases according to the square root of the expected number of events, such as the electric current or intensity of light. but since the strength of the signal itself increases more rapidly, the relative proportion of shot noise decreases and the signal to noise ratio (considering only shot noise) increases anyway.

Ppt Analytical Figures Of Merit Noise And S N Ratio Powerpoint Noise is any unsteady component of the measurement signal that causes the instantaneous value of the signal to differ from the instrument’s rendition of the “true value”. x(t) s(t) time. n(t) x(t) average signal power. average power (in watts) dissipated when voltage signal v connected to a 1 resistor:. The magnitude of shot noise increases according to the square root of the expected number of events, such as the electric current or intensity of light. but since the strength of the signal itself increases more rapidly, the relative proportion of shot noise decreases and the signal to noise ratio (considering only shot noise) increases anyway.

Comments are closed.