Secondary Consumer Animals
Consumer Examples Biology Learn what secondary consumers are, how they function in the food chain, and what types of animals are secondary consumers. find out how they differ from primary consumers and tertiary consumers, and see examples of aquatic and terrestrial secondary consumers. Learn what secondary consumers are, how they fit into the trophic pyramid, and what types of animals are secondary consumers. find out the importance of secondary consumers for energy flow, biodiversity, and nutrient cycling in ecosystems.

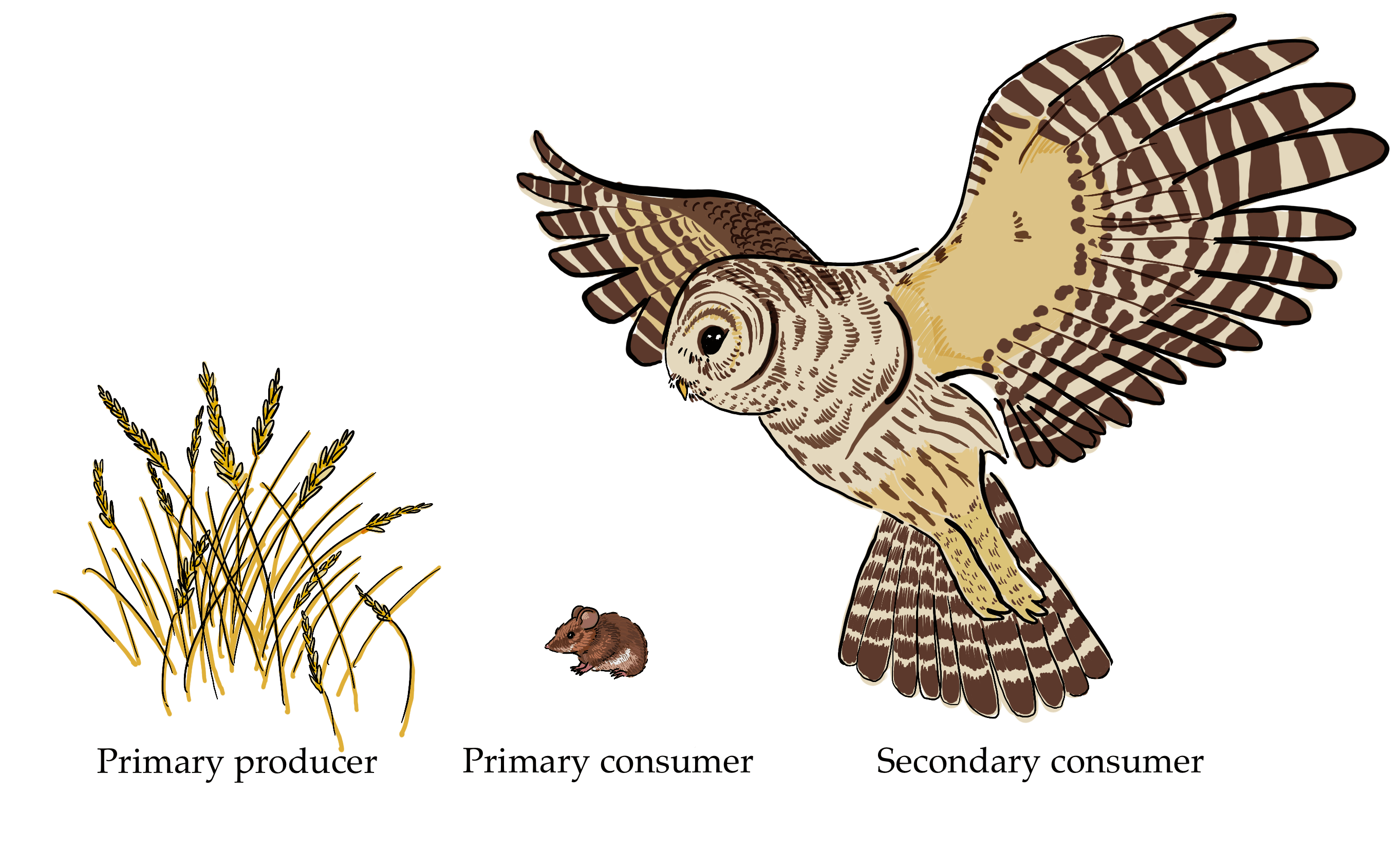
What Do Animals Eat Foxes At Ronald Mcwilliams Blog Secondary consumers occupy the third trophic level in a typical food chain. they are organisms that feed on primary consumers for nutrients and energy. while primary consumers are always herbivores; organisms that only feed on autotrophic plants, secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores eat only animals, but omnivores eat. Definition of secondary consumers. secondary consumers are organisms that primarily feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores, who eat only other animals, or omnivores, who consume both animal and plant matter. their role is vital in transferring energy. Learn how food chains describe who eats whom in the wild and what are the trophic levels of organisms. find out what are secondary consumers and see examples of food chains in different habitats. Learn what secondary consumers are and how they fit into the ecological pyramid. see examples of secondary consumers, such as bears, wolves, and lions, and how they get their energy from primary consumers.
.jpg)
Energy Flow In Ecosystems Ppt Download Learn how food chains describe who eats whom in the wild and what are the trophic levels of organisms. find out what are secondary consumers and see examples of food chains in different habitats. Learn what secondary consumers are and how they fit into the ecological pyramid. see examples of secondary consumers, such as bears, wolves, and lions, and how they get their energy from primary consumers. Secondary consumers eat herbivores. they are at the third trophic level. in a desert ecosystem, a secondary consumer may be a snake that eats a mouse. in the kelp forest, sea otters are secondary consumers that hunt sea urchins. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. they are at the fourth trophic level. Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers, which are mostly plants. they are either carnivores or omnivores, and they play a role in controlling the population of primary consumers and providing energy to tertiary consumers.
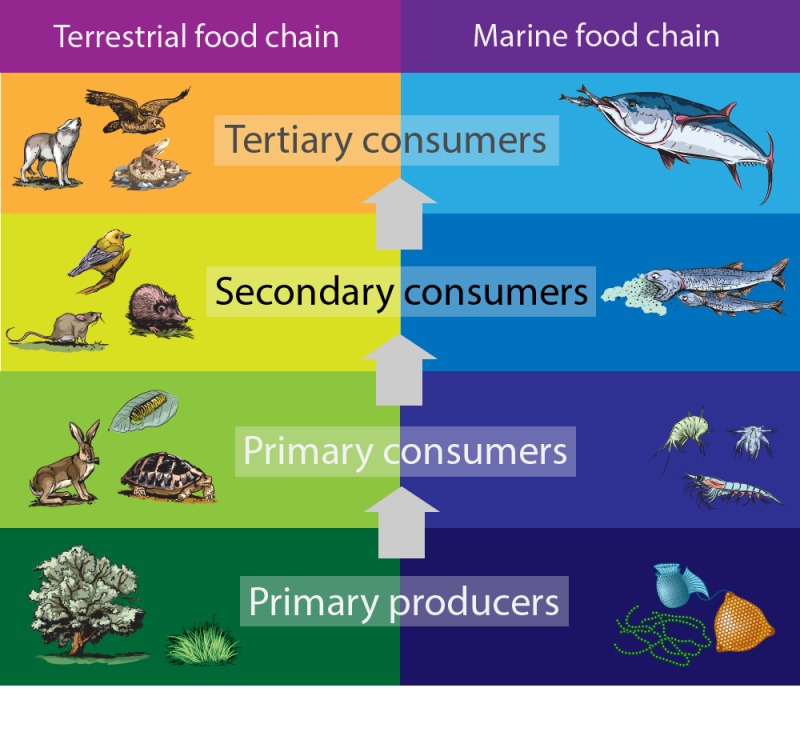
Secondary Consumers Definition Types And Examples Secondary consumers eat herbivores. they are at the third trophic level. in a desert ecosystem, a secondary consumer may be a snake that eats a mouse. in the kelp forest, sea otters are secondary consumers that hunt sea urchins. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. they are at the fourth trophic level. Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers, which are mostly plants. they are either carnivores or omnivores, and they play a role in controlling the population of primary consumers and providing energy to tertiary consumers.

Comments are closed.