Second Law Of Thermodynamics Diagram

Second Law Of Thermodynamics In Terms Of Entropy The second law of thermodynamics: a law stating that states that the entropy of an isolated system never decreases, because isolated systems spontaneously evolve toward thermodynamic equilibrium—the state of maximum entropy. equivalently, perpetual motion machines of the second kind are impossible. heat engine: any device which converts heat. T. e. the second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on universal empirical observation concerning heat and energy interconversions. a simple statement of the law is that heat always flows spontaneously from hotter to colder regions of matter (or 'downhill' in terms of the temperature gradient).

Second Law Of Thermodynamics Definition Equation Kelvin Plank Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat, work, temperature, and energy. the second law of thermodynamics can be precisely stated in the following two forms, as originally formulated in the 19th century by the scottish physicist william thomson (lord kelvin) and the german physicist rudolf clausius, respectively: a cyclic. The second law of thermodynamics puts restrictions upon the direction of heat transfer and achievable efficiencies of heat engines. the first law of thermodynamics states that the energy of the universe remains constant; though energy can be exchanged between system and surroundings, it can’t be created or destroyed. The law that forbids these processes is called the second law of thermodynamics. we shall see that the second law can be stated in many ways that may seem different, but which in fact are equivalent. like all natural laws, the second law of thermodynamics gives insights into nature, and its several statements imply that it is broadly applicable. The first law of thermodynamics focuses on energy conservation. it does not describe any restrictions or possibilities for a process to take place. a process satisfying the first law of thermodynamics may or may not be achievable in reality. in fact, whether a process is possible is governed by both the first and the second laws of thermodynamics.
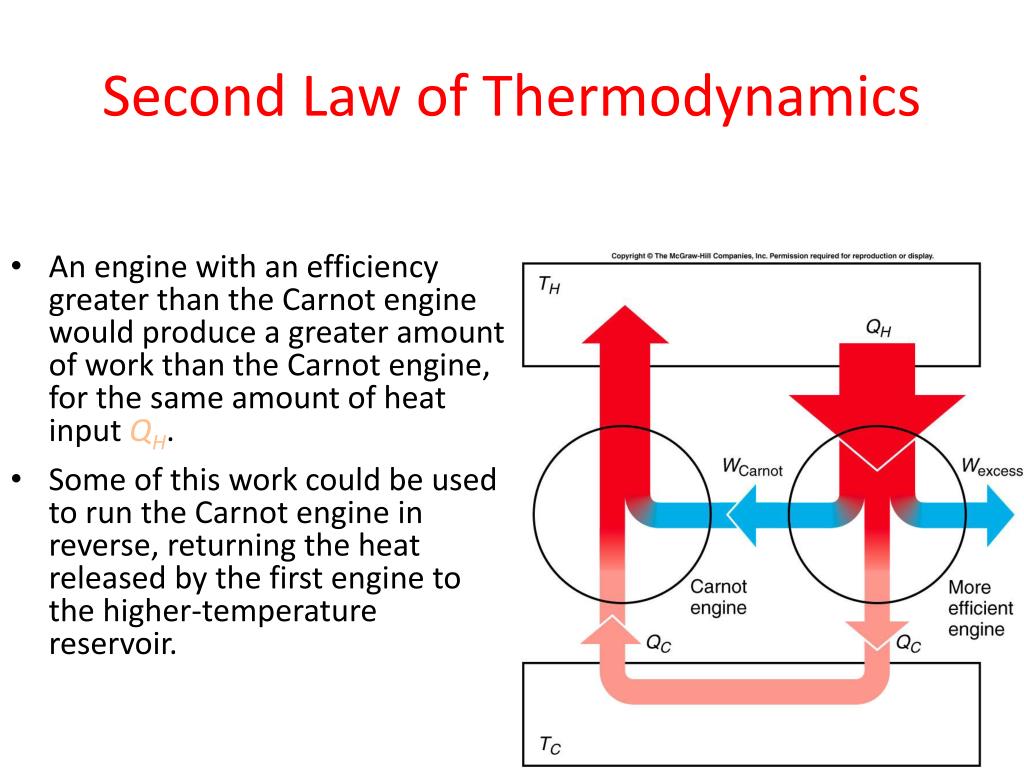
Second Law Of Thermodynamics Diagram The law that forbids these processes is called the second law of thermodynamics. we shall see that the second law can be stated in many ways that may seem different, but which in fact are equivalent. like all natural laws, the second law of thermodynamics gives insights into nature, and its several statements imply that it is broadly applicable. The first law of thermodynamics focuses on energy conservation. it does not describe any restrictions or possibilities for a process to take place. a process satisfying the first law of thermodynamics may or may not be achievable in reality. in fact, whether a process is possible is governed by both the first and the second laws of thermodynamics. Figure 15.14 these ice floes melt during the arctic summer. some of them refreeze in the winter, but the second law of thermodynamics predicts that it would be extremely unlikely for the water molecules contained in these particular floes to reform the distinctive alligator like shape they formed when the picture was taken in the summer of 2009. As for pv diagram, another process that can be depicted on a state diagram must be quasi static such that every point along the process between an initial and final state define the system as equilibrium. figure 4.3.1: temperature vs entropy, ts diagram. in the case of heat the sign of the change in entropy is directly related to the sign of heat.

Comments are closed.