Scientific Diagram Illustrate The Explanation And Concept Of Metabolic

Scientific Diagram Illustrate Explanation Concept Metabolic Stoc Here comes the concept of metabolism. metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions taking place in the cells of the living organisms. this involves both breaking and making of biomolecules. catabolism and anabolism are two types of metabolism. catabolism (breaking of bonds) involves the breaking of biomolecules while anabolism. Metabolism, the sum of chemical reactions that take place in living cells, providing energy for life processes and the synthesis of cellular material. living organisms are unique in that they extract energy from their environments via hundreds of coordinated, multistep, enzyme mediated reactions.

Overview Of Metabolic Reactions Anatomy Physiology Study Guide 2024 The processes of making and breaking down sugar molecules illustrate two examples of metabolic pathways. a metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions that takes a starting molecule and modifies it, step by step, through a series of metabolic intermediates, eventually yielding a final product. in the example of sugar metabolism, the. Metabolic pathways. the processes of making and breaking down sugar molecules illustrate two types of metabolic pathways. a metabolic pathway is a series of interconnected biochemical reactions that convert a substrate molecule or molecules, step by step, through a series of metabolic intermediates, eventually yielding a final product or products. Metabolism pathways, enzymes, reactions: there are two main reasons for studying a metabolic pathway: (1) to describe, in quantitative terms, the chemical changes catalyzed by the component enzymes of the route; and (2) to describe the various intracellular controls that govern the rate at which the pathway functions. studies with whole organisms or organs can provide information that one. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic processes. the cells break down the glucose molecule to convert its stored biochemical energy into energy coin adenosine triphosphate (atp). it occurs within the cells of all living organisms, including both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. cellular respiration is categorized as an oxidative process because.
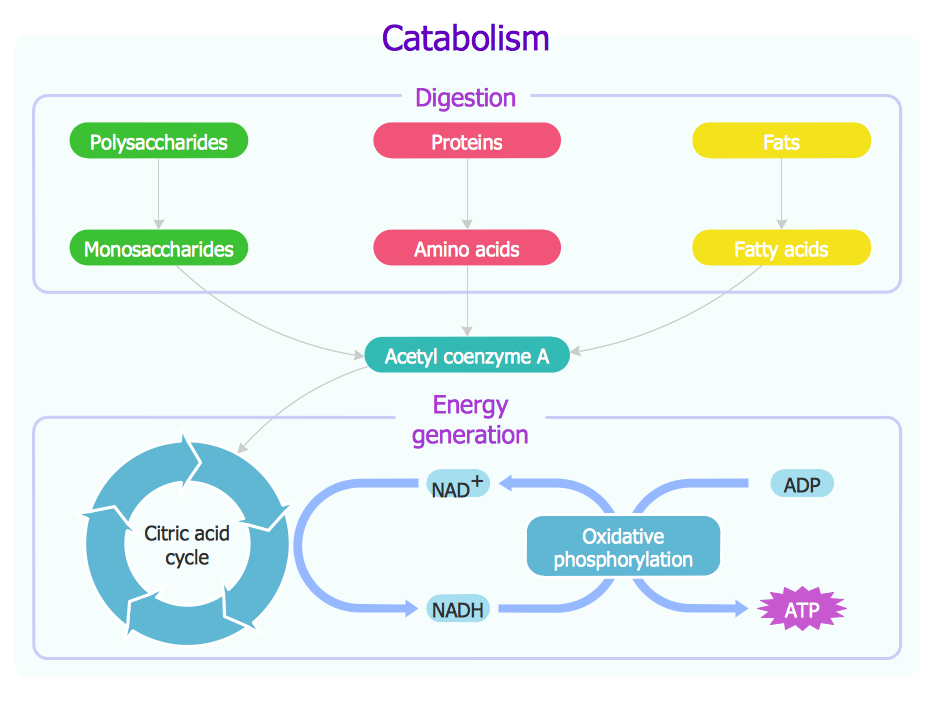
Metabolic Pathways Concept Map Metabolism pathways, enzymes, reactions: there are two main reasons for studying a metabolic pathway: (1) to describe, in quantitative terms, the chemical changes catalyzed by the component enzymes of the route; and (2) to describe the various intracellular controls that govern the rate at which the pathway functions. studies with whole organisms or organs can provide information that one. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic processes. the cells break down the glucose molecule to convert its stored biochemical energy into energy coin adenosine triphosphate (atp). it occurs within the cells of all living organisms, including both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. cellular respiration is categorized as an oxidative process because. The reaction is summarized as: c 6 h 12 o 6 6o 2 –>6h 2 o 6co 2. both of these reactions involve many steps. the processes of making and breaking down sugar molecules illustrate two examples of metabolic pathways. a metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions that takes a starting molecule and modifies it, step by step, through a. Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic processes that take place within a cell in which the biochemical energy is harvested from an organic substance (e.g. glucose) and then stored in an energy carrying biomolecule (e.g. atp) for use in energy requiring activities of the cell. synonyms: cell respiration.
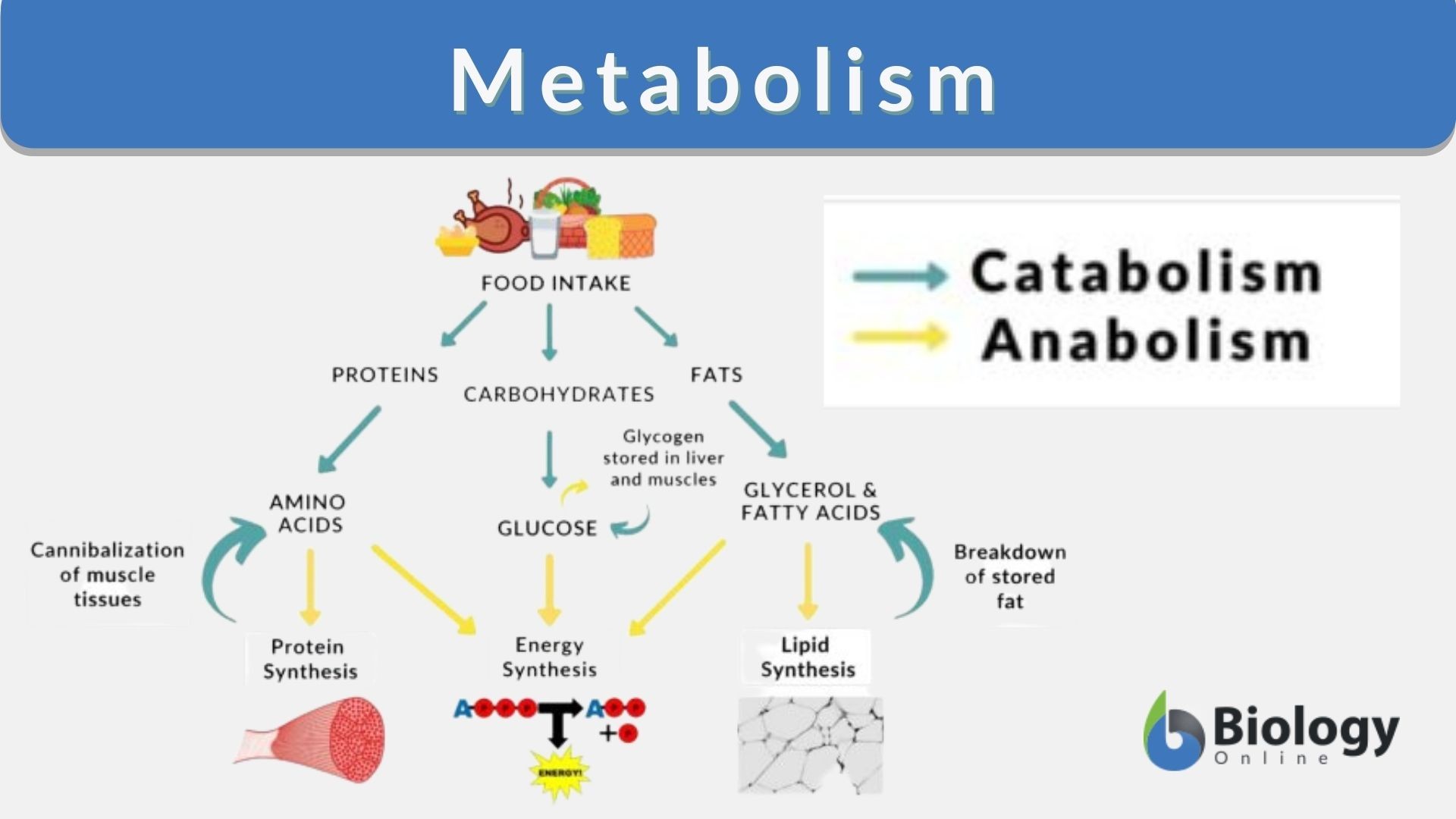
Metabolism Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary The reaction is summarized as: c 6 h 12 o 6 6o 2 –>6h 2 o 6co 2. both of these reactions involve many steps. the processes of making and breaking down sugar molecules illustrate two examples of metabolic pathways. a metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions that takes a starting molecule and modifies it, step by step, through a. Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic processes that take place within a cell in which the biochemical energy is harvested from an organic substance (e.g. glucose) and then stored in an energy carrying biomolecule (e.g. atp) for use in energy requiring activities of the cell. synonyms: cell respiration.

Comments are closed.