Science Motion Difference Between Scalar And Vector Quantity

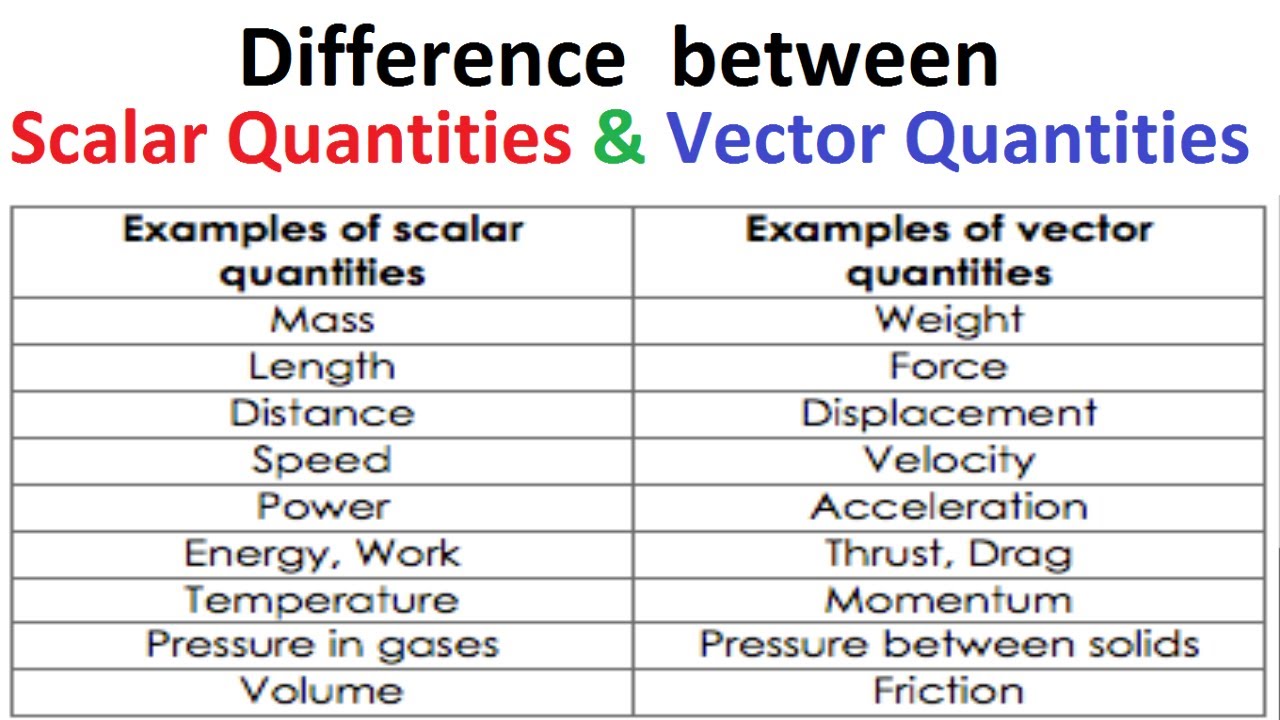
Science Motion Difference Between Scalar And Vector Quantity Difference between scalar and vector. a scalar quantity is different from a vector quantity in terms of direction. scalars don’t have direction, whereas a vector has. due to this feature, the scalar quantity can be said to be represented in one dimension, whereas a vector quantity can be multi dimensional. from the table given below, let us. In mathematics and physics, a scalar is a quantity that only has magnitude (size), while a vector has both magnitude and direction. examples of scalar quantities include pure numbers, mass, speed, temperature, energy, volume, and time. examples of vector quantities include velocity, acceleration, momentum, displacement, and forces, such as.

Examples Of Vector And Scalar Quantity In Physics Yourdictionary Equation 2.2 is a scalar equation because the magnitudes of vectors are scalar quantities (and positive numbers). if the scalar α is negative in the vector equation equation 2.1, then the magnitude | b → | of the new vector is still given by equation 2.2, but the direction of the new vector b → is antiparallel to the direction of a →. The important difference between scalar and vector: a scalar quantity has only magnitude, but no direction. vector quantity has both magnitude and direction. every scalar quantity is one dimensional. vector quantity can be one, two or three dimensional. it changes with the change in their direction or magnitude or both. Equation 2.3.2 is a scalar equation because the magnitudes of vectors are scalar quantities (and positive numbers). if the scalar α is negative in the vector equation equation 2.3.1, then the magnitude | →b | of the new vector is still given by equation 2.3.2, but the direction of the new vector →b is antiparallel to the direction of →a. Scalars are quantities that are fully described by a magnitude (or numerical value) alone. vectors are quantities that are fully described by both a magnitude and a direction. the remainder of this lesson will focus on several examples of vector and scalar quantities (distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration).
Difference Between Scalar And Vector Quantities Youtube Equation 2.3.2 is a scalar equation because the magnitudes of vectors are scalar quantities (and positive numbers). if the scalar α is negative in the vector equation equation 2.3.1, then the magnitude | →b | of the new vector is still given by equation 2.3.2, but the direction of the new vector →b is antiparallel to the direction of →a. Scalars are quantities that are fully described by a magnitude (or numerical value) alone. vectors are quantities that are fully described by both a magnitude and a direction. the remainder of this lesson will focus on several examples of vector and scalar quantities (distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration). Describe the difference between vector and scalar quantities. identify the magnitude and direction of a vector. explain the effect of multiplying a vector quantity by a scalar. describe how one dimensional vector quantities are added or subtracted. explain the geometric construction for the addition or subtraction of vectors in a plane. Displacement is an example of a vector quantity. distance is an example of a scalar quantity. a vector is any quantity with both magnitude and direction. other examples of vectors include a velocity of 90 km h east and a force of 500 newtons straight down. the direction of a vector in one dimensional motion is given simply by a plus ( ) ( ) or.

Comments are closed.