Pythagorean Theorem Explained
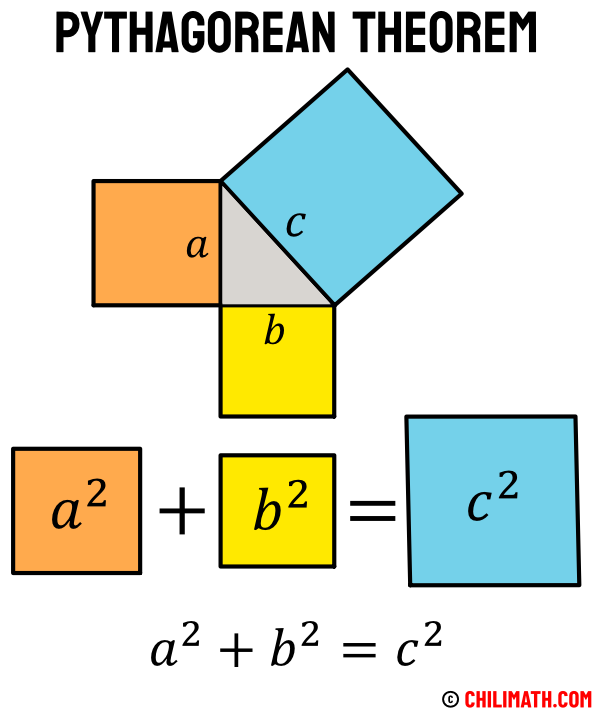
Pythagorean Theorem Definition Formula Examples Chilimath Learn the definition, formula and proof of pythagoras' theorem, which relates the lengths of the sides of a right angled triangle. see examples, activities and animations to help you understand and apply this important mathematical concept. Learn how to use the pythagorean theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse or the legs of a right triangle. see examples, diagrams and applications of the formula in geometry and real life situations.

Pythagorean Theorem Explained Using Algebra In mathematics, the pythagorean theorem or pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle.it states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. Use the pythagorean theorem to determine the length of x. step 1. identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle. the legs have length 6 and 8. x x is the hypotenuse because it is opposite the right angle. step 2. substitute values into the formula (remember 'c' is the hypotenuse). Learn about the pythagorean theorem, a geometric formula that relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. explore its ancient origins, different proofs, and extensions in mathematics and culture. Learn the pythagoras theorem, which explains the relation between the sides of a right angled triangle. find the formula, proof, examples, applications and problems with solutions.

Pythagorean Theorem Explained Using Algebra Learn about the pythagorean theorem, a geometric formula that relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. explore its ancient origins, different proofs, and extensions in mathematics and culture. Learn the pythagoras theorem, which explains the relation between the sides of a right angled triangle. find the formula, proof, examples, applications and problems with solutions. The pythagorean theorem states that if a triangle has one right angle, then the square of the longest side, called the hypotenuse, is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two shorter sides, called the legs. so if a a and b b are the lengths of the legs, and c c is the length of the hypotenuse, then a^2 b^2=c^2 a2 b2 = c2. This article will discuss what the pythagorean theorem is, its converse, and the pythagorean theorem formula. before getting deeper into the topic, let’s recall the right triangle. a right triangle is a triangle with one interior angle equals 90 degrees. in a right triangle, the two short legs meet at an angle of 90 degrees.
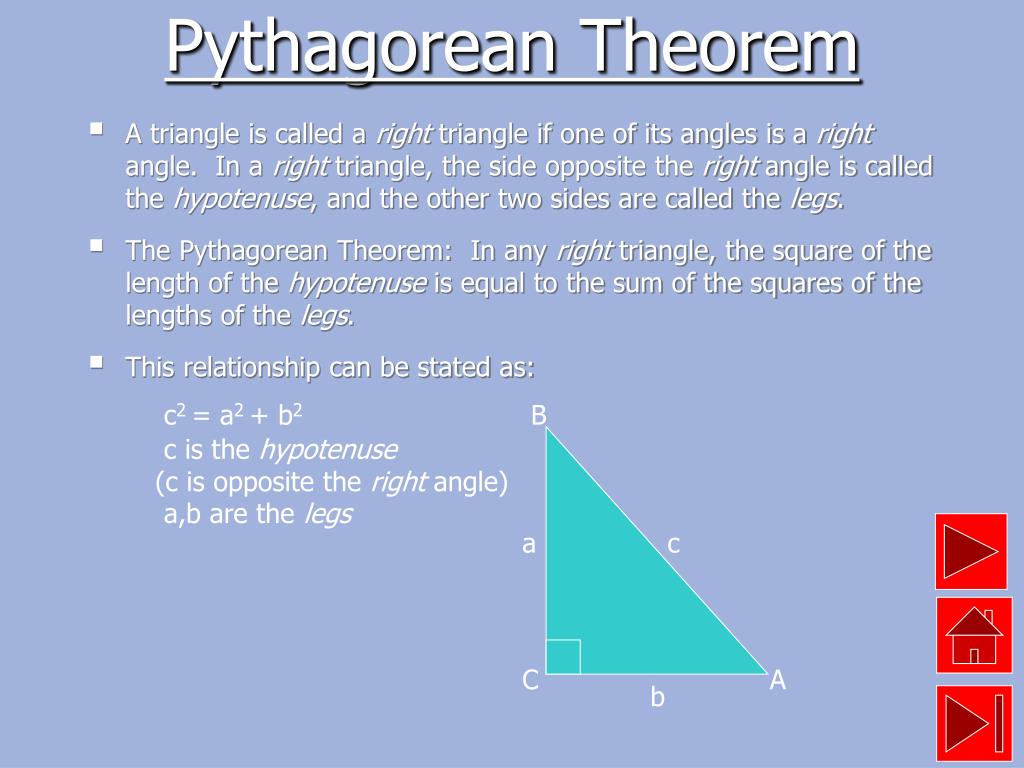
Pythagoras Theorem Explained The pythagorean theorem states that if a triangle has one right angle, then the square of the longest side, called the hypotenuse, is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two shorter sides, called the legs. so if a a and b b are the lengths of the legs, and c c is the length of the hypotenuse, then a^2 b^2=c^2 a2 b2 = c2. This article will discuss what the pythagorean theorem is, its converse, and the pythagorean theorem formula. before getting deeper into the topic, let’s recall the right triangle. a right triangle is a triangle with one interior angle equals 90 degrees. in a right triangle, the two short legs meet at an angle of 90 degrees.

Comments are closed.