Pythagoras Theorem Explained
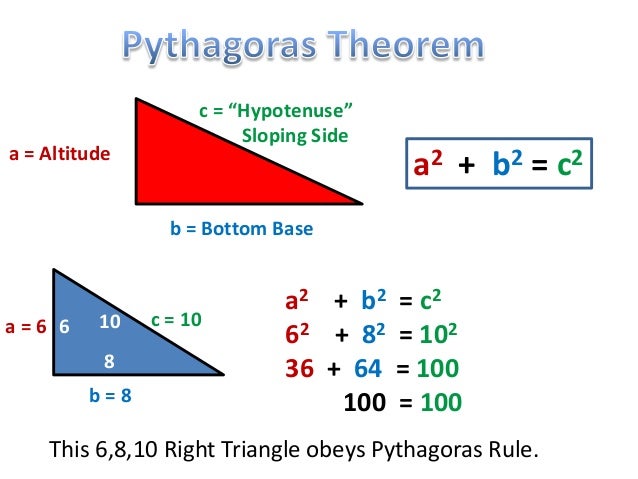
Pythagoras Theorem Explained Learn the definition, formula and proof of pythagoras' theorem, which relates the lengths of the sides of a right angled triangle. see examples, activities and animations to help you understand and apply this important mathematical concept. The pythagorean theorem can be summarized in a short and compact equation as shown below. for a given right triangle, it states that the square of the hypotenuse, in right a triangle, the square of longest side known as the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. the pythagorean theorem guarantees that if we know.
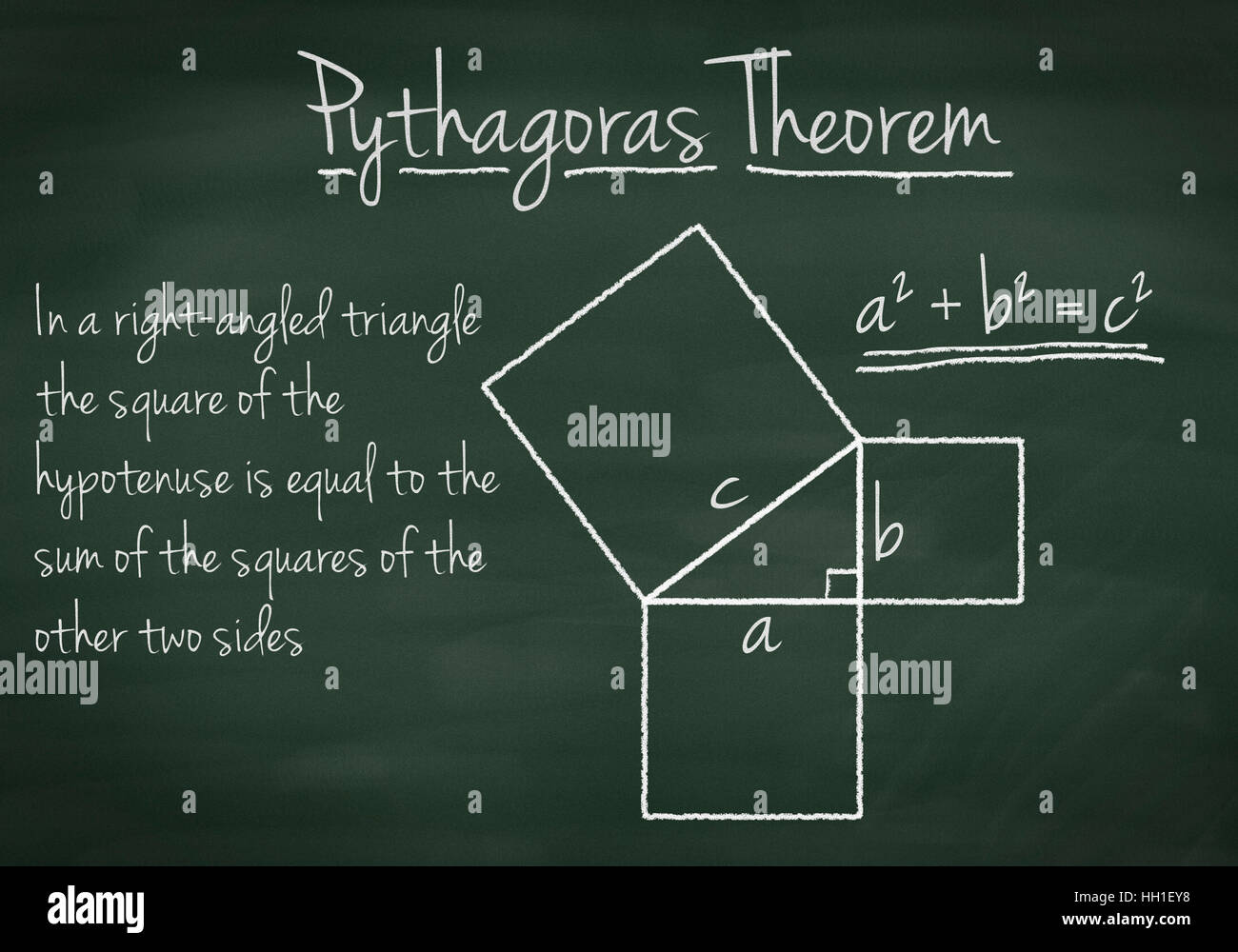
Pythagoras Theorem Explained On A Chalkboard Stock Photo Alamy In mathematics, the pythagorean theorem or pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle.it states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. Learn the pythagoras theorem, which explains the relation between the sides of a right angled triangle. find the formula, proof, examples, applications and problems with solutions. Learn the pythagoras theorem, which explains the relationship between the three sides of a right angled triangle. find out the formula, proof, examples, and history of this theorem with cuemath. The pythagorean theorem states that if a triangle has one right angle, then the square of the longest side, called the hypotenuse, is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two shorter sides, called the legs. so if a a and b b are the lengths of the legs, and c c is the length of the hypotenuse, then a^2 b^2=c^2 a2 b2 = c2.

The Pythagoras Theorem Formula Explained With Examples Youtube Learn the pythagoras theorem, which explains the relationship between the three sides of a right angled triangle. find out the formula, proof, examples, and history of this theorem with cuemath. The pythagorean theorem states that if a triangle has one right angle, then the square of the longest side, called the hypotenuse, is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two shorter sides, called the legs. so if a a and b b are the lengths of the legs, and c c is the length of the hypotenuse, then a^2 b^2=c^2 a2 b2 = c2. The pythagorean theorem, also referred to as the ‘pythagoras theorem,’ is arguably the most famous formula in mathematics that defines the relationships between the sides of a right triangle. the theorem is attributed to a greek mathematician and philosopher named pythagoras (569 500 b.c.e.). he has many contributions to mathematics, but. The formula for the pythagorean theorem describes the relationship between the sides a and b of a right triangle to its hypotenuse, c. a right triangle is one containing a 90° or right angle. the hypotenuse is the side of the triangle opposite from the right angle (which is the largest angle in a right triangle). a2 b2 = c2.
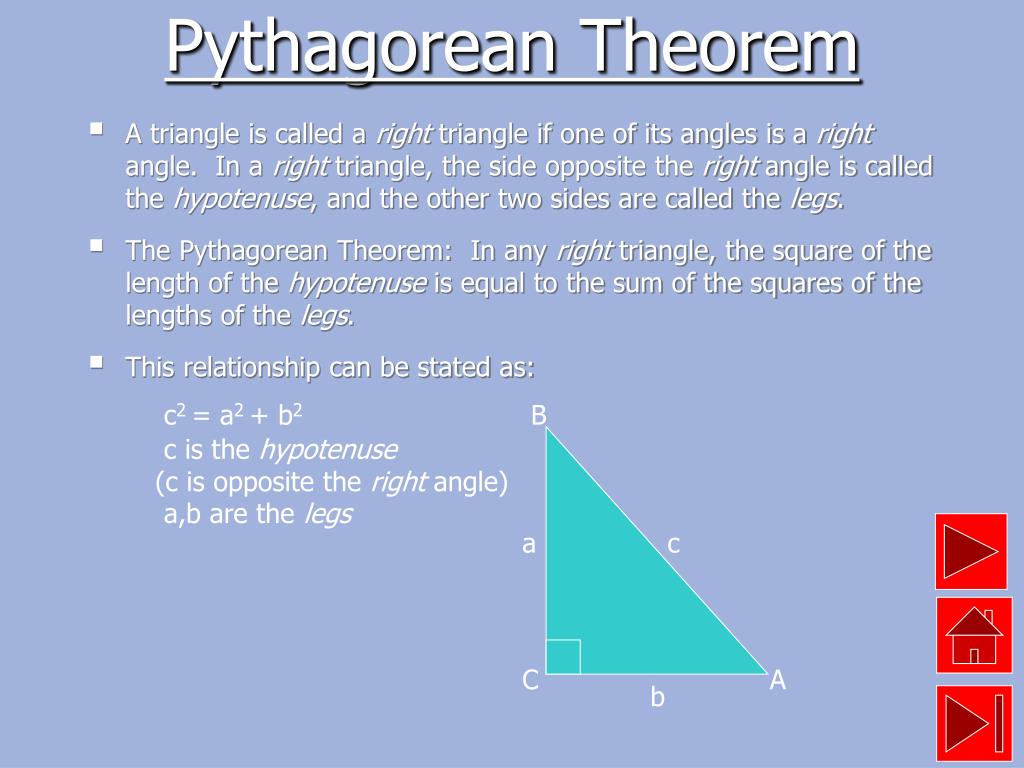
Pythagoras Theorem Explained The pythagorean theorem, also referred to as the ‘pythagoras theorem,’ is arguably the most famous formula in mathematics that defines the relationships between the sides of a right triangle. the theorem is attributed to a greek mathematician and philosopher named pythagoras (569 500 b.c.e.). he has many contributions to mathematics, but. The formula for the pythagorean theorem describes the relationship between the sides a and b of a right triangle to its hypotenuse, c. a right triangle is one containing a 90° or right angle. the hypotenuse is the side of the triangle opposite from the right angle (which is the largest angle in a right triangle). a2 b2 = c2.

Solution Pythagoras Theorem Explained Studypool

Comments are closed.