Price Elasticity And Tax Incidence Ppt Download
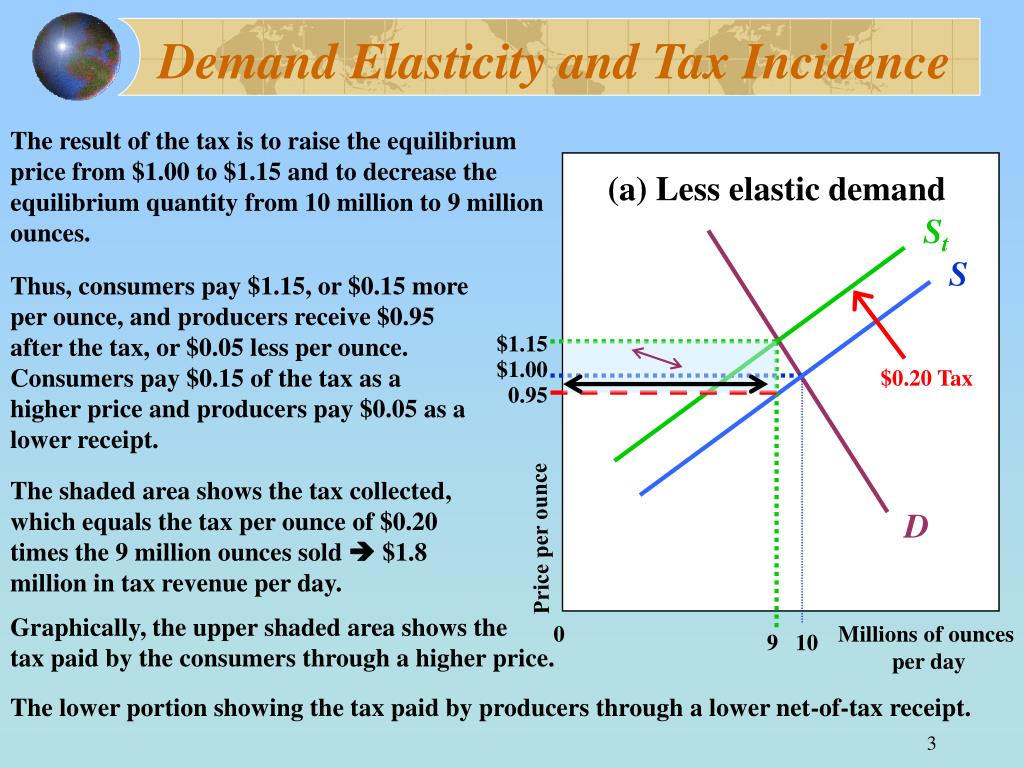
Ppt Price Elasticity And Tax Incidence Powerpoint Presentation Free 4 demand elasticity and tax incidence (a) less elastic demand tax raises equilibrium price from $1.00 to $1.15 and decreases equilibrium quantity from 10m to 9m ounces consumers pay $0.15 more per ounce and producers receive $0.05 less after the tax the top area represents the portion of the tax paid by consumers the bottom area represents the portion of the tax paid by producers st s $1.15 $1. 4 demand elasticity and tax incidence when demand is more elastic: consumers reduce their quantity demanded more sharply in response to a price change, producers cannot as easily pass the tax along as a higher price. here the tax increases the price by $0.05, to $1.05, and the net of tax receipt to suppliers declines by $0.15 to $0.85.

Price Elasticity And Tax Incidence Ppt Download Demand elasticity and tax incidence the result of the tax is to raise the equilibrium price from $1.00 to $1.15 and to decrease the equilibrium quantity from 10 million to 9 million ounces. (a) less elastic demand st s thus, consumers pay $1.15, or $0.15 more per ounce, and producers receive $0.95 after the tax, or $0.05 less per ounce. Tax incidence. demand for good x is d(q) decreases with q = p t. supply for good x is s(p) increases with p. equilibrium condition: q = s(p) = d(p t) start from t = 0 and s(p) = d(p). we want to characterize dp dt: effect of a small tax increase on price, which determines who bears effective burden of tax:. Price controls. policymakers believe that the market price of a good or service is unfair to buyers or sellers. can generate inequities. taxes. to raise revenue for public purposes. to influence market outcomes. price ceiling. a legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold. rent control laws. Elasticity: percentage change in quantity when price changes by one percent i εd = ∂d ∂p q d(p) denotes the price elasticity of demand. f (consumer faces q = p t) i εs = ∂s ∂p p s(p) denotes the price elasticity of supply. dp dt = ε d (ε s ε d) note: 1 < dp dt < 0 and dq dt = 1 dp dt hilary hoynes incidence uc davis, winter 2013.

Price Elasticity And Tax Incidence Ppt Download Price controls. policymakers believe that the market price of a good or service is unfair to buyers or sellers. can generate inequities. taxes. to raise revenue for public purposes. to influence market outcomes. price ceiling. a legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold. rent control laws. Elasticity: percentage change in quantity when price changes by one percent i εd = ∂d ∂p q d(p) denotes the price elasticity of demand. f (consumer faces q = p t) i εs = ∂s ∂p p s(p) denotes the price elasticity of supply. dp dt = ε d (ε s ε d) note: 1 < dp dt < 0 and dq dt = 1 dp dt hilary hoynes incidence uc davis, winter 2013. 3⁄4. than 1, and. 3⁄4. if the price elasticity of demand is less. exactly 1. demand. 3 part iii markets and welfare chapter 7 consumers, producers, and the efficiency of markets welfare economics, the study of how the allocation of resources affects economic well being. 7 1 consumer surplus 7 1a willingness to pay consumer surplus is the amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it. 7 1b using the demand curve to measure consumer.

Ppt Price Elasticity And Tax Incidence Powerpoint Presentation Free 3⁄4. than 1, and. 3⁄4. if the price elasticity of demand is less. exactly 1. demand. 3 part iii markets and welfare chapter 7 consumers, producers, and the efficiency of markets welfare economics, the study of how the allocation of resources affects economic well being. 7 1 consumer surplus 7 1a willingness to pay consumer surplus is the amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it. 7 1b using the demand curve to measure consumer.

Comments are closed.