Ppt Ch 3 Alkane Structure Vs Reactivity I Alkane Structure And
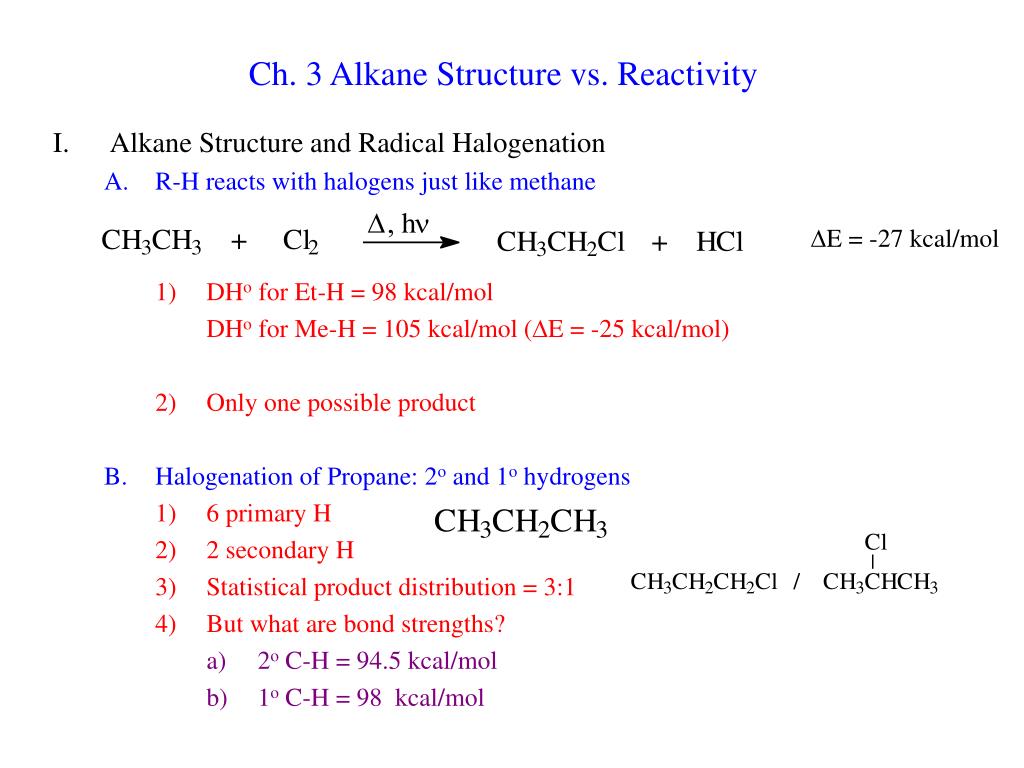
Ppt Ch 3 Alkane Structure Vs Reactivity Powerpoint Present Ch. 3 alkane structure vs. reactivity. alkane structure and radical halogenation r h reacts with halogens just like methane dh o for et h = 98 kcal mol dh o for me h = 105 kcal mol ( d e = 25 kcal mol) only one possible product halogenation of propane: 2 o and 1 o hydrogens. Key points covered include the molecular formula and naming conventions of alkenes, cis trans isomerism, nucleophilic and electrophilic addition reactions, and the thermodynamic and kinetic parameters that govern reaction rates such as activation energy, rate constants, and reaction order. read less.
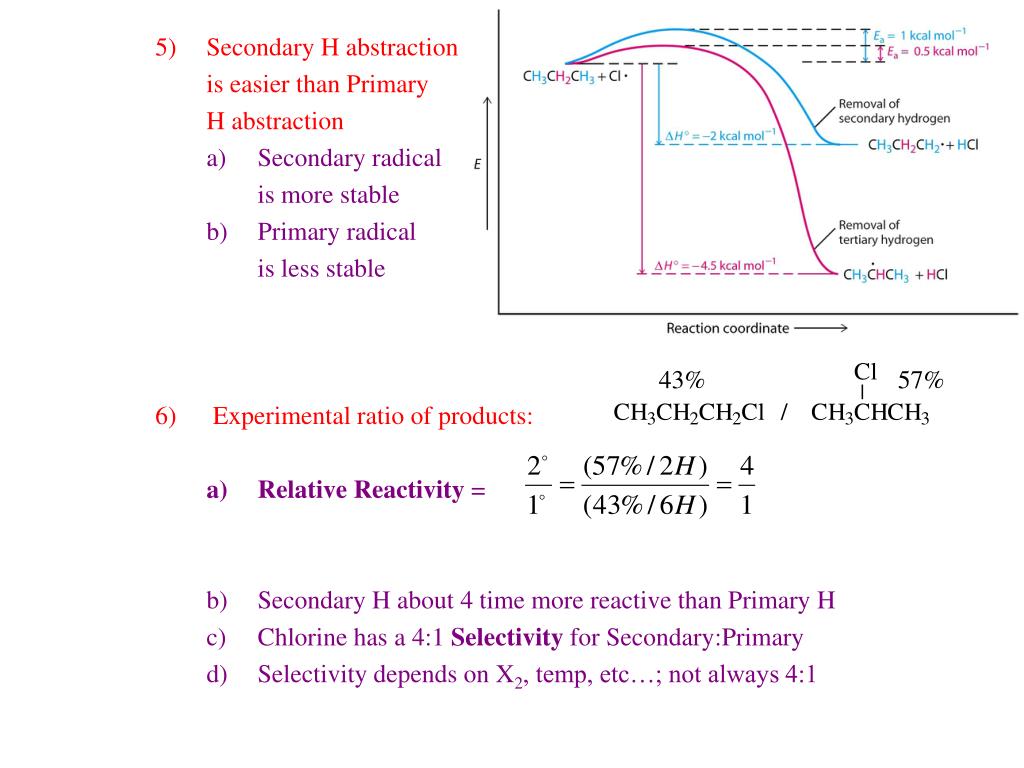
Ppt Ch 3 Alkane Structure Vs Reactivity Powerpoint Present Figure 22.2.1 22.2. 1: pictured are the lewis structures, ball and stick models, and space filling models for molecules of methane, ethane, and pentane. a common method used by organic chemists to simplify the drawings of larger molecules is to use a skeletal structure (also called a line angle structure). The key points are: 1. alkanes have the general formula cnh2n 2 and are characterized by single carbon carbon and carbon hydrogen bonds, making them saturated. 2. physical properties of alkanes, such as melting boiling points, viscosity, and density, increase with increasing number of carbon atoms due to stronger intermolecular forces. 3. Ch. 3 alkane structure vs. reactivity. ch. 3 alkane structure vs. reactivity. alkane structure and radical halogenation r h reacts with halogens just like methane dh o for et h = 98 kcal mol dh o for me h = 105 kcal mol ( d e = 25 kcal mol) only one possible product halogenation of propane: 2 o and 1 o hydrogens. 391 views • 6 slides. Alkanes, alkenes &alkynes. this document provides information on the nomenclature, structures, and isomerism of alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. it discusses their classification as saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbons and how they form homologous series. the key reactions of alkanes and alkenes discussed are substitution, addition, elimination.
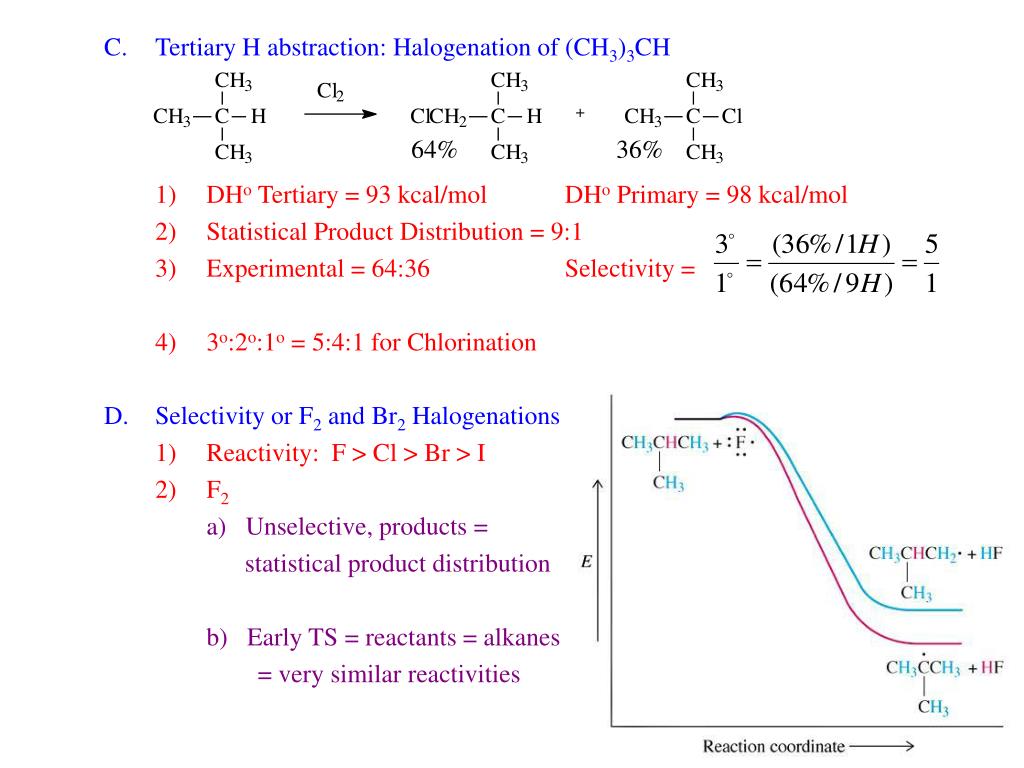
Ppt Ch 3 Alkane Structure Vs Reactivity Powerpoint Present Ch. 3 alkane structure vs. reactivity. ch. 3 alkane structure vs. reactivity. alkane structure and radical halogenation r h reacts with halogens just like methane dh o for et h = 98 kcal mol dh o for me h = 105 kcal mol ( d e = 25 kcal mol) only one possible product halogenation of propane: 2 o and 1 o hydrogens. 391 views • 6 slides. Alkanes, alkenes &alkynes. this document provides information on the nomenclature, structures, and isomerism of alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. it discusses their classification as saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbons and how they form homologous series. the key reactions of alkanes and alkenes discussed are substitution, addition, elimination. Ch. 3 alkane structure vs. reactivity. ch. 3 alkane structure vs. reactivity. alkane structure and radical halogenation r h reacts with halogens just like methane dh o for et h = 98 kcal mol dh o for me h = 105 kcal mol ( d e = 25 kcal mol) only one possible product halogenation of propane: 2 o and 1 o hydrogens. 391 views • 6 slides. Chapter 6. kenes: structure and stabilityc. oh. oh. steric acid (saturated fatty acid) linoleic acid (unsaturated fatty acid) degrees of unsaturation saturated hydrocarbon cycloalkane (1 ring) alkene (1 p bond) alkyne (2 p bonds) cnh2n 2 cnh2n cnh2n cnh2n 2. 2h from the formula of the saturated alkanedegrees of unsaturati.

Comments are closed.