Position Vs Time Graph Examples

Position Vs Time Graph Examples Learn how to use position vs. time graphs to analyze and identify the type of motion, find displacement, average speed and acceleration. see solved examples with graphs and explanations for high school physics students. The graph of position versus time in figure 2.13 is a curve rather than a straight line. the slope of the curve becomes steeper as time progresses, showing that the velocity is increasing over time. the slope at any point on a position versus time graph is the instantaneous velocity at that point.
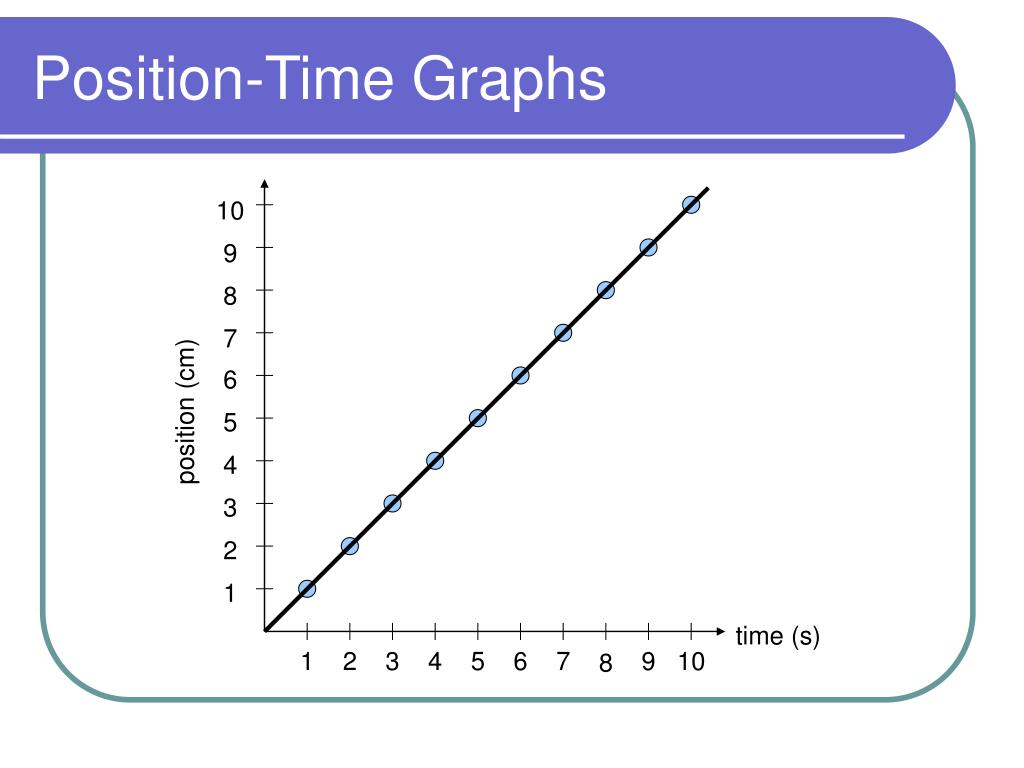
Time And Position Graphs Explained It’s easy to calculate the average velocity of a moving object from a position time graph. average velocity equals the change in position (represented by Δd) divided by the corresponding change in time (represented by Δt): vavg = Δd Δt v a v g = Δ d Δ t. for example, in graph 2 in the figure above, the average velocity between 0 seconds. Motion graphs allow scientists to learn a lot about an object’s motion with just a quick glance. this article will cover the basics for interpreting motion graphs including different types of graphs, how to read them, and how they relate to each other. interpreting motion graphs, such as position vs time graphs and velocity vs time graphs. The principle is that the slope of the line on a position time graph reveals useful information about the velocity of the object. it is often said, "as the slope goes, so goes the velocity." whatever characteristics the velocity has, the slope will exhibit the same (and vice versa). if the velocity is constant, then the slope is constant (i.e. Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org science high school physics one dim.

Comments are closed.