Physiology Chpt 3 Naaaaidbdwd Chapter 3 Cell Metabolism Metabolism

Chapter 3 Cell Metabolism Chapter 3 в Cell Metabolismођ Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like one way to define "chemical reactions" is to say that a chemical reaction occurs whenever covalent bonds are made or broken. with that definition, then the sum total of all production and destruction of covalent bonds in cells is called ., the word "catabolic" refers to reactions or pathways that ., adding a. Chapter 3 cell metabolism. metabolism – general or individual – chemical reactions (involve conversion of reactants into products) chemical reactions can go in either direction, but not all– they are reversible o more products created – forward reaction; more reactants produced – reverse reaction o forward and reverse = net reaction resulting from all individual reactions catabolic.

Ppt Cell Physiology Metabolism Powerpoint Presentation Free A) the primary site of the synthesis of the triglycerides is in the liver. b) proteins are transcribed from dna in the nucleus. c) proteins are degraded by mrna in the cytoplasm. d) the primary site of the breakdown of triglycerides is in the adipose tissue. e)glycogen is synthesized in the cytosol from glucose. Terms in this set (43) metabolism. the sum total of all chemical reactions that occur in cells. energy metabolism. set of reactions involved in energy storage and use (aka energy exchange) catabolic reaction. any reaction that involves the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones; example: breakdown of proteins into amino acids. Chapter 3 functions of a cell. cell metabolism and energy use. synthesis of molecules. communication. cells produce and receive electrical and chemical signals. reproduction and inheritance. each cell contains dna. plasma membrane selectively permeable. separation of intracellular vs. extracellular materials. Osmosis occurs when there’s an imbalance of solutes outside of a cell versus inside the cell isotonic when the concentration of water molecules is the same inside the cell & their extracellular environment a. maintain normal shape & function b. homeostasis→ internal environment in which all cells are in a isotonic solution.
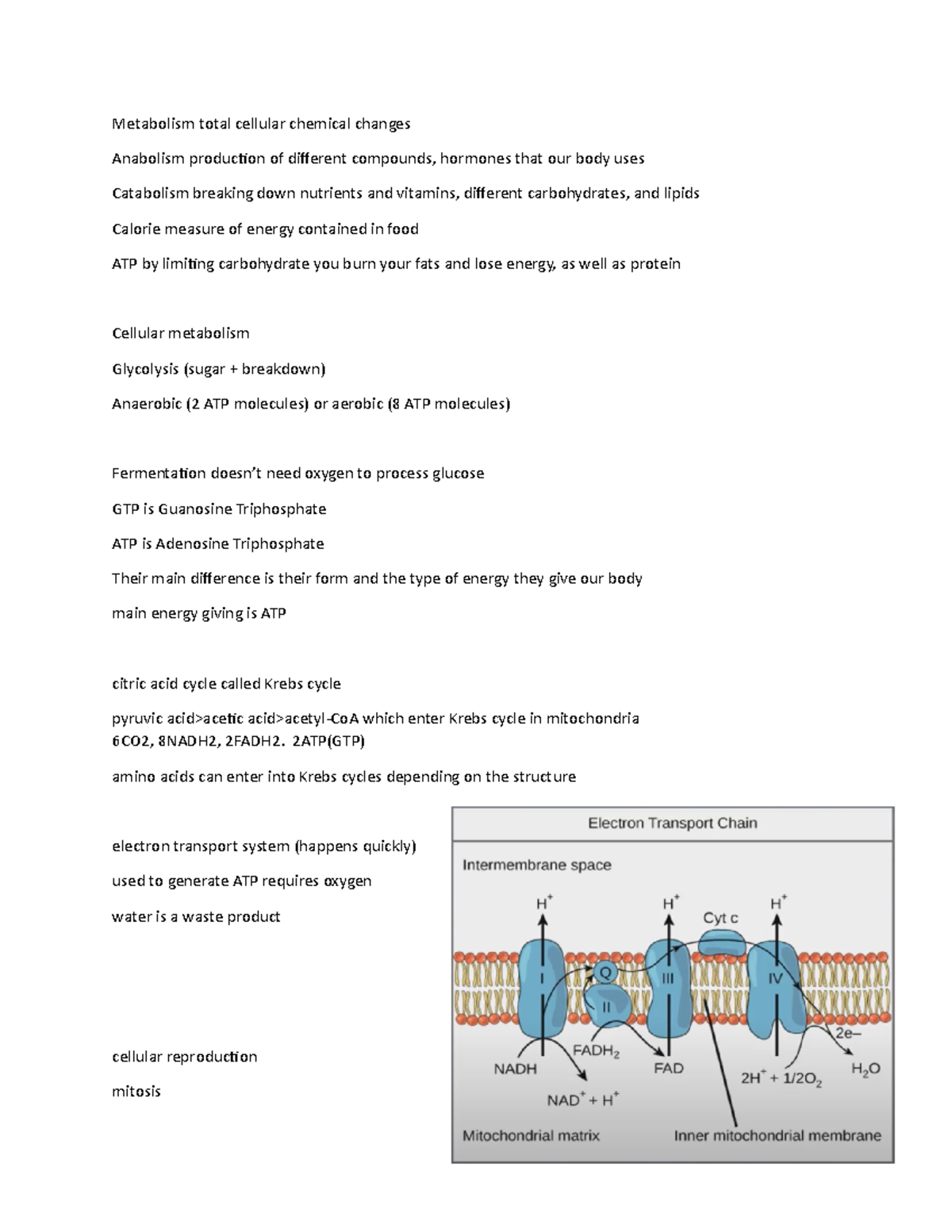
Anatomy And Physiology 3 Metabolism Total Cellular Chemical Changes Chapter 3 functions of a cell. cell metabolism and energy use. synthesis of molecules. communication. cells produce and receive electrical and chemical signals. reproduction and inheritance. each cell contains dna. plasma membrane selectively permeable. separation of intracellular vs. extracellular materials. Osmosis occurs when there’s an imbalance of solutes outside of a cell versus inside the cell isotonic when the concentration of water molecules is the same inside the cell & their extracellular environment a. maintain normal shape & function b. homeostasis→ internal environment in which all cells are in a isotonic solution. 2.3.1: prelude to metabolism. virtually every task performed by living organisms requires energy. energy is needed to perform heavy labor and exercise, but humans also use a great deal of energy while thinking, and even during sleep. in fact, the living cells of every organism constantly use energy. nutrients and other molecules are imported. Metabolism refers to the whole sum of reactions that occur throughout the body within each cell and that provide the body with energy. this energy gets used for vital processes and the synthesis of new organic material. every living organism uses its environment to survive by taking nutrients and substances as building blocks for movement, growth, development, and reproduction. all of these.

Chapter 3 Cell Structure Function Microbial Metabolism Metabolism 2.3.1: prelude to metabolism. virtually every task performed by living organisms requires energy. energy is needed to perform heavy labor and exercise, but humans also use a great deal of energy while thinking, and even during sleep. in fact, the living cells of every organism constantly use energy. nutrients and other molecules are imported. Metabolism refers to the whole sum of reactions that occur throughout the body within each cell and that provide the body with energy. this energy gets used for vital processes and the synthesis of new organic material. every living organism uses its environment to survive by taking nutrients and substances as building blocks for movement, growth, development, and reproduction. all of these.

Comments are closed.