Overview Of Plant Cells Geeksforgeeks
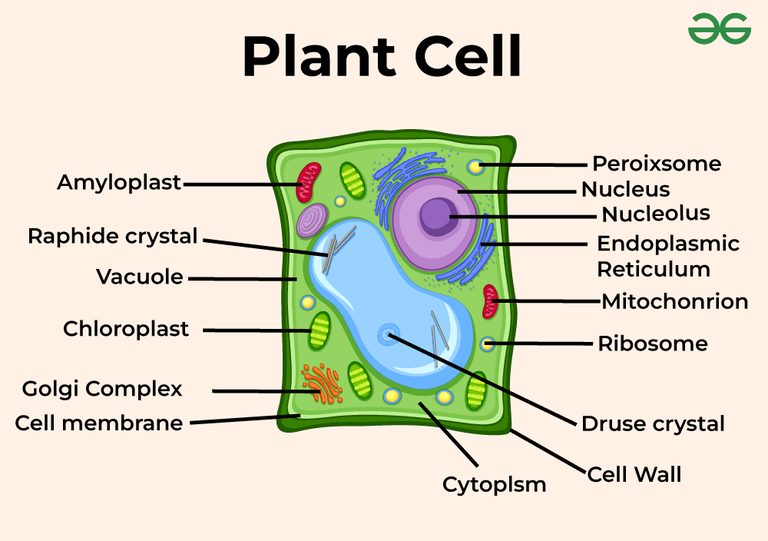
Overview Of Plant Cells Geeksforgeeks The building blocks of plants are called plant cells. plant cells’ primary job is to perform photosynthesis. in the chloroplasts of the plant cell, photosynthesis takes place. it is the method through which plants prepare food by utilizing water, carbon dioxide, and sunshine. atp is created throughout the process, which releases energy. A plant cell is a fundamental unit of a plant’s structure. a plant cell is a eukaryotic cell, i.e., it has a defined nucleus enclosed within a membrane. plant cells and animal cells difference occurs as they possess unique features that allow them to carry out essential functions. plant cell structure consists of a freely permeable cell wall.

Overview Of Plant Cells Geeksforgeeks Structure of plant cell. the diagram of plant cell class 8 and 9 are beneficial for examinations. the structure of plant cell is an composed of the following parts: cell wall . the outermost rigid layer of a plant cell. animal cells lack this. the main role of a cell wall is to give the cell rigidity and support against mechanical stress , and. 3d model of a plant cell overview of plant cells. animals, fungi, and protists are made of at least one eukaryotic cell. in contrast, bacteria and archaea are made up of a single prokaryotic cell. plant cells are differentiated from the cells of other organisms by their cell walls, chloroplasts, and central vacuole. The primary function of the cell wall is to protect and provide structural support to the cell. the plant cell wall is also involved in protecting the cell against mechanical stress and providing form and structure to the cell. it also filters the molecules passing in and out of it. the formation of the cell wall is guided by microtubules. A plant cell is the basic unit of all plants. plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. their characteristic cell wall is composed of cellulose, and they contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis.

Diagram Of Cell And Structure Geeksforgeeks The primary function of the cell wall is to protect and provide structural support to the cell. the plant cell wall is also involved in protecting the cell against mechanical stress and providing form and structure to the cell. it also filters the molecules passing in and out of it. the formation of the cell wall is guided by microtubules. A plant cell is the basic unit of all plants. plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. their characteristic cell wall is composed of cellulose, and they contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis. Structure of a plant cell. plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom plantae.their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capability to perform photosynthesis and store starch, a large vacuole that regulates turgor pressure, the absence of flagella or. The cell wall provides structural support and protection. pores in the cell wall allow water and nutrients to move into and out of the cell. the cell wall also prevents the plant cell from bursting when water enters the cell. microtubules guide the formation of the plant cell wall. cellulose is laid down by enzymes to form the primary cell wall.

Plant Cells Overview Structure Functions And Types Structure of a plant cell. plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom plantae.their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capability to perform photosynthesis and store starch, a large vacuole that regulates turgor pressure, the absence of flagella or. The cell wall provides structural support and protection. pores in the cell wall allow water and nutrients to move into and out of the cell. the cell wall also prevents the plant cell from bursting when water enters the cell. microtubules guide the formation of the plant cell wall. cellulose is laid down by enzymes to form the primary cell wall.

Comments are closed.