Opioid Sparing Orthopaedic Surgery
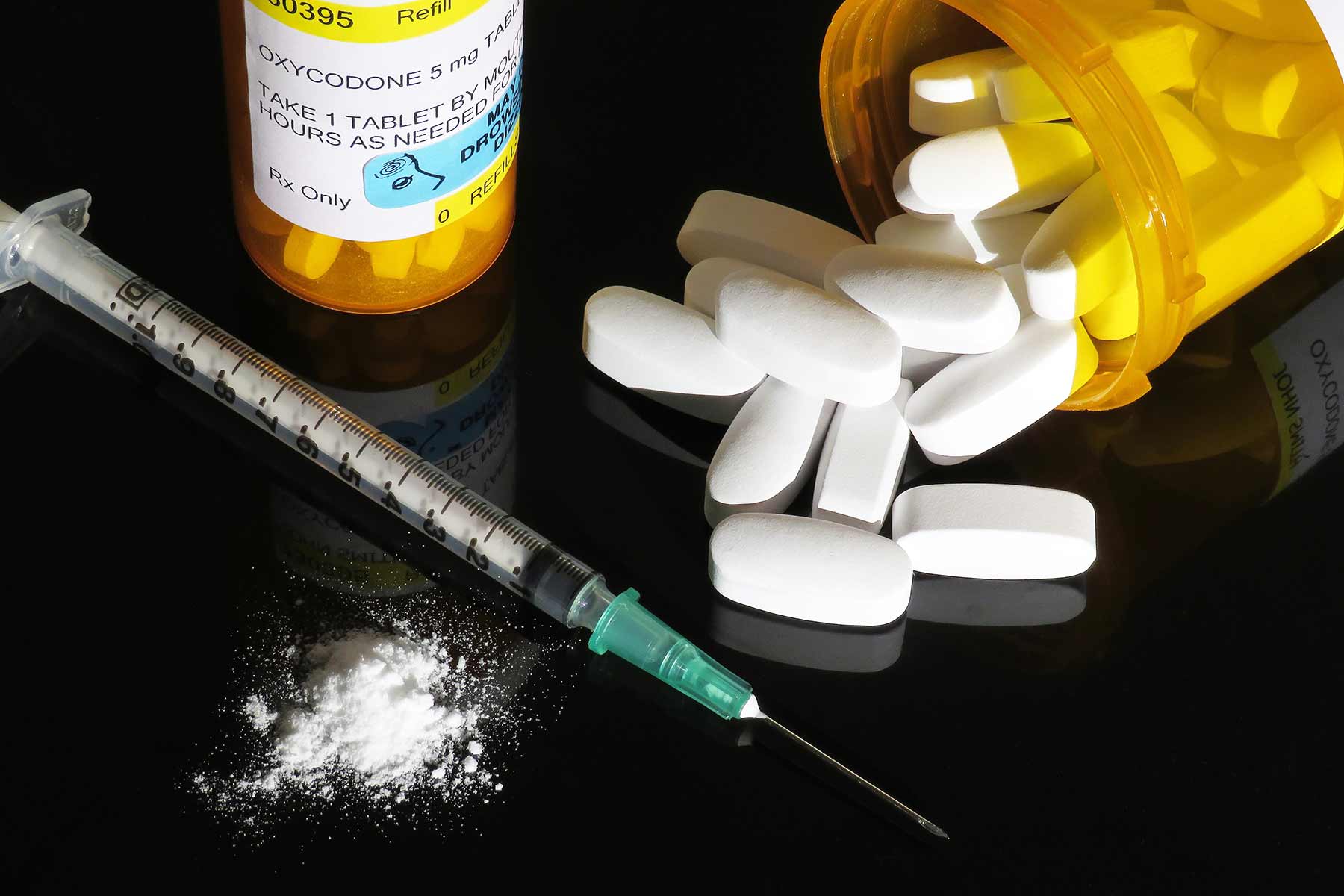
Halting Opioid Abuse Aim Of Several Grants From Nih Cdc вђ Washington To start, orthopaedic surgeons are the third largest prescribers of opioids among physicians 3 – huang and copp found that pain pills were overprescribed by 34% in total knee arthroplasty and 140% in total hip arthroplasty. 4 there’s a reason orthopaedic surgeons are one of the largest groups of opioid prescribers among physicians: the. As opioid related adverse effects) in postoperative patients. in order to evade these opioid related side effects and also improve pain management, multimodal analgesia i.e., combination of different analgesics, was introduced more than a decade ago. both pharmacological and non pharmacological techniques are available as opioid sparing analgesia. research from around the world have proved.
What New Opioid Laws Mean For Pain Relief Harvard Health An opioid sparing strategy for orthopedic surgery, and medicine at large, is possible with the right combination of tools and does not have to come at the expense of the patient experience. reducing opioid exposure during the perioperative period should be a priority. Available data suggest 42–71% of prescribed opioid pills go unused after surgery, with 73% of postoperative orthopedic patients reporting unused opioid pills at one month post procedure [42,46]. this reservoir of unused prescription opioids in community settings has been identified as a potential contributor to the u.s. opioid epidemic. Excessive opioid prescribing has been a major contributor to the ongoing opioid epidemic that started in north america and has spread globally. 1,2 due to their potent analgesic effects, opioids have been widely used for postoperative pain control following orthopedic surgery. 3 as of 2018, orthopedic surgeons have been identified among the. No surgery related bleeding complications were observed. implications: nsaids have the potential to play an important role in reducing postoperative opioid requirements. reducing the amount of opioids used could be expected to reduce opioid related side effects and contribute to reversing the opioid epidemic.

The History Of Opioid Addiction The Long Opioid Drug Crisis Excessive opioid prescribing has been a major contributor to the ongoing opioid epidemic that started in north america and has spread globally. 1,2 due to their potent analgesic effects, opioids have been widely used for postoperative pain control following orthopedic surgery. 3 as of 2018, orthopedic surgeons have been identified among the. No surgery related bleeding complications were observed. implications: nsaids have the potential to play an important role in reducing postoperative opioid requirements. reducing the amount of opioids used could be expected to reduce opioid related side effects and contribute to reversing the opioid epidemic. Acute pain is near universal after surgery. opioids have been a mainstay of postoperative analgesia, but current best practice emphasises a multimodal opioid sparing regimen based on a background of paracetamol, a non steroidal anti inflammatory drug, or both.1 opioids are frequently overused, particularly after hospital discharge.1–3. Multimodal analgesia is based on the principle that combining analgesics with different modes or sites of action will result in better pain control and less side effects through opioid sparing. when used as a part of enhanced recovery protocols, this implementation will accelerate functional recovery, decrease hospital costs, and improve.

Comments are closed.