Normal Palatine Tonsils Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
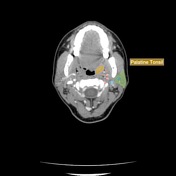
Tonsillitis Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org Case discussion. palatine tonsils can be seen during ultrasound examination of the neck. this helps to identify tonsillitis and its complications like tonsillar abscess. the striated (tigroid) appearance is due to the cortex infoldings and crypts inbetween them. enhanced cortex in post contrast ct or mri (tigroid enhancement) is a sign of acute. The palatine tonsils, also known as the faucial tonsils or simply the tonsils, are a bilateral collection of lymphoid tissue in the oropharyngeal mucosa. they form part of waldeyer's ring. gross anatomy. the palatine tonsils are located in the oropharyngeal isthmus (isthmus of fauces). each is often described to have two borders, two poles, and.

Normal Palatine Tonsils Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Neck. bilateral palatine tonsils are enlarged, and touching each other forming a 'kissing tonsils' sign. it causes significant airway obstruction. adenoid tonsils are also enlarged. however, no airway obstruction. multiple enlarged cervical nodes. deep spaces of the neck are normal. bilateral internal jugular veins and internal carotid arteries. In total, we found 110 abscesses by mr imaging (2 false positive findings were excluded) (table 3). the mean maximal abscess diameter was 33 mm, and volume was 3.2 ml. most (ie, 69, 63%) of the abscesses were multilocular, and 78 (71%) had a striated tonsillar appearance in post gd t1 weighted images. Although histologically stained sections of the palatine tonsil are widely available, they represent normal or pathologic tissue in two dimensions only, lacking reference to three dimensional space. however, tomographic imaging techniques suitable for 3d imaging and routinely used in clinical applications, such as pet ct or mri, are unable to. The palatine (or faucial) tonsils are bundles of muscoa associated lymphoid tissue (malt) located bilaterally in the tonsillar bed of the lateral oropharynx, in the isthums of the fauces between the palatoglossal arch and the palatopharyngeal arch of the soft palate. it forms part of a ringed arragnment of lymphatic tissue known as waldeyer’s.
Palatine Tonsil Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org Although histologically stained sections of the palatine tonsil are widely available, they represent normal or pathologic tissue in two dimensions only, lacking reference to three dimensional space. however, tomographic imaging techniques suitable for 3d imaging and routinely used in clinical applications, such as pet ct or mri, are unable to. The palatine (or faucial) tonsils are bundles of muscoa associated lymphoid tissue (malt) located bilaterally in the tonsillar bed of the lateral oropharynx, in the isthums of the fauces between the palatoglossal arch and the palatopharyngeal arch of the soft palate. it forms part of a ringed arragnment of lymphatic tissue known as waldeyer’s. Purpose to quantify fluorine 18 (18f) fluorodeoxyglucose (fdg) uptake in the palatine tonsils to identify a sensitive and specific metric for distinguishing physiologic asymmetric uptake from squamous cell carcinoma (scc). materials and methods this hipaa compliant retrospective study was approved by institutional review board. informed consent requirements were waived. twenty six patients. Of these, 110 patients (83%) had $1 abscess (99 unilateral, 11 bilateral; aver age volume, 3.2ml). most abscesses were peritonsillar, and we found no evidence of intratonsillar abscess. imaging showed evidence of para pharyngeal and retropharyngeal extension in 36% and 10% of patients, respectively. mr imaging had a high positive predictive.

Palatine Tonsil Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org Purpose to quantify fluorine 18 (18f) fluorodeoxyglucose (fdg) uptake in the palatine tonsils to identify a sensitive and specific metric for distinguishing physiologic asymmetric uptake from squamous cell carcinoma (scc). materials and methods this hipaa compliant retrospective study was approved by institutional review board. informed consent requirements were waived. twenty six patients. Of these, 110 patients (83%) had $1 abscess (99 unilateral, 11 bilateral; aver age volume, 3.2ml). most abscesses were peritonsillar, and we found no evidence of intratonsillar abscess. imaging showed evidence of para pharyngeal and retropharyngeal extension in 36% and 10% of patients, respectively. mr imaging had a high positive predictive.

Comments are closed.