Normal Head Ct Scan Anatomy Made Simple Neuroradiology

Normal Head Ct Scan Anatomy Made Simple Neuroradiology Youtube This video is a part of basic radiologic head ct scan anatomy series. the video shows the basic ct anatomy of the brain.for each slice we have highlighted. Normal ct brain anatomy by sunil kumar agrawal; aula de hidrocefalia by ronaldo dornelas; ssc preso 7 6 2023 by john joseph; head ct basics by michael baumgartner; mri tutorial by stanley xue; neuroradiology cases for medical students by louis saada; brain scan by goddowell daniel goddowell; normal brain ct by lado natroshvili; normal ctb by.
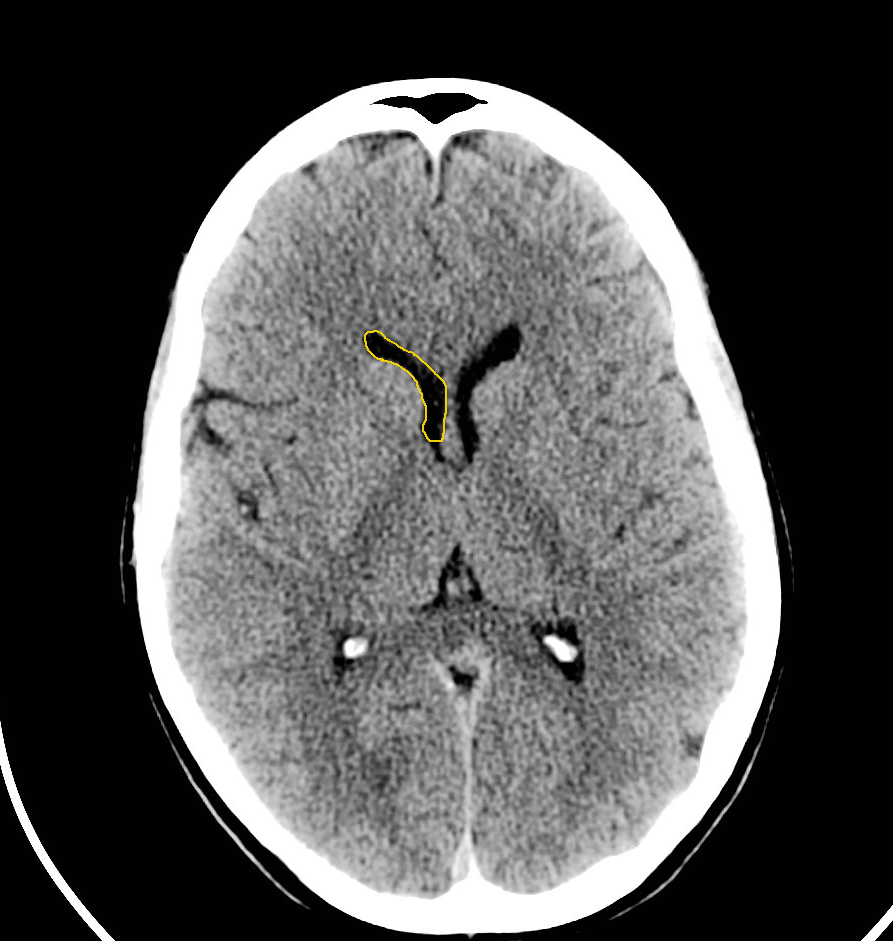
Head Ct Scan Labeled Normal anatomy of brain (ct) by kyaing yi mon thin; 111 normal anatomy by mohamed shweel; braın by hmb * ct brain by gourab mitro plaban; ct head by mohit kumar; dr abid cases by abid hussain; annotated ct brain by dr manzoor ahmed; illustrations annotated images by mini singhal; ed 3 by alexander kirwan; ct head tutorial radsig by alexander. Week 1 case 1 by osama al jibury. 2020 y4 neuroimaging by derek smith . sept 2020 by alisa tanakit md. imaging intracranial haemorrhage by radiology registrar pulse teaching. stroke by osama al jibury. clerkship tutorial by neel dixit. normal ct head (radioart) by rt.moamil ali. year 2 revision session 1 by dominic mahoney. Neck ct anatomy and basic interpretation. what to look at on a neck ct. • brain • orbits globes • aerodigestive tract. – nasal cavities & sinuses – oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus – larynx & trachea. • lymph nodes • salivary glands –parotid, sm, sl • thyroid • vessels –carotids, verts, ijs • lung apices mediastinum. Neuroimaging in neurology is divided into several sections. the first section is normal imaging, which includes: • magnetic resonance imaging (mri) of the brain. • mri of the spine. • magnetic resonance angiography (mra) • magnetic resonance venography (mrv) • computed tomography (ct) of the brain. • conventional angiography.

Normal Head Ct Scan Anatomy Made Simple Neuroradiology 40 Off Neck ct anatomy and basic interpretation. what to look at on a neck ct. • brain • orbits globes • aerodigestive tract. – nasal cavities & sinuses – oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus – larynx & trachea. • lymph nodes • salivary glands –parotid, sm, sl • thyroid • vessels –carotids, verts, ijs • lung apices mediastinum. Neuroimaging in neurology is divided into several sections. the first section is normal imaging, which includes: • magnetic resonance imaging (mri) of the brain. • mri of the spine. • magnetic resonance angiography (mra) • magnetic resonance venography (mrv) • computed tomography (ct) of the brain. • conventional angiography. This tutorial takes you through the important anatomy required to understand ct images of the brain. tutorial orientation. ct images of the brain are conventionally viewed from below, as if looking up into the top of the head. this means that the right side of the brain is on the left side of the viewer. the anterior part of the head is at the. Head ct approach. first evaluate normal anatomical structures, window for optimal brain tissue contrast second – assess for signs of underlying pathology such as: mass effect, edema, midline shift, hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, subdural or epidural collection hematoma, or infarction third – evaluate sinuses and osseous structures with bone.
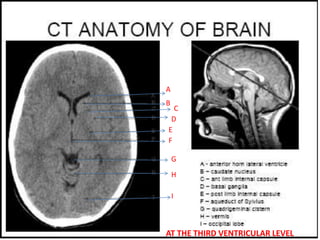
Normal Head Ct Scan Anatomy Made Simple Neuroradiology 40 Off This tutorial takes you through the important anatomy required to understand ct images of the brain. tutorial orientation. ct images of the brain are conventionally viewed from below, as if looking up into the top of the head. this means that the right side of the brain is on the left side of the viewer. the anterior part of the head is at the. Head ct approach. first evaluate normal anatomical structures, window for optimal brain tissue contrast second – assess for signs of underlying pathology such as: mass effect, edema, midline shift, hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, subdural or epidural collection hematoma, or infarction third – evaluate sinuses and osseous structures with bone.

Comments are closed.