Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease A Clinical Update
Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease A Clinical Update Abstract. non alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is currently the most common chronic liver disease in developed countries because of the obesity epidemic. the disease increases liver related morbidity and mortality, and often increases the risk for other comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Non alcoholic fatty liver disease: a clinical update. non alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is currently the most common chronic liver disease in developed countries because of the obesity epidemic. the disease increases liver related morbidity and mortality, and often increases the risk for other comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes and.
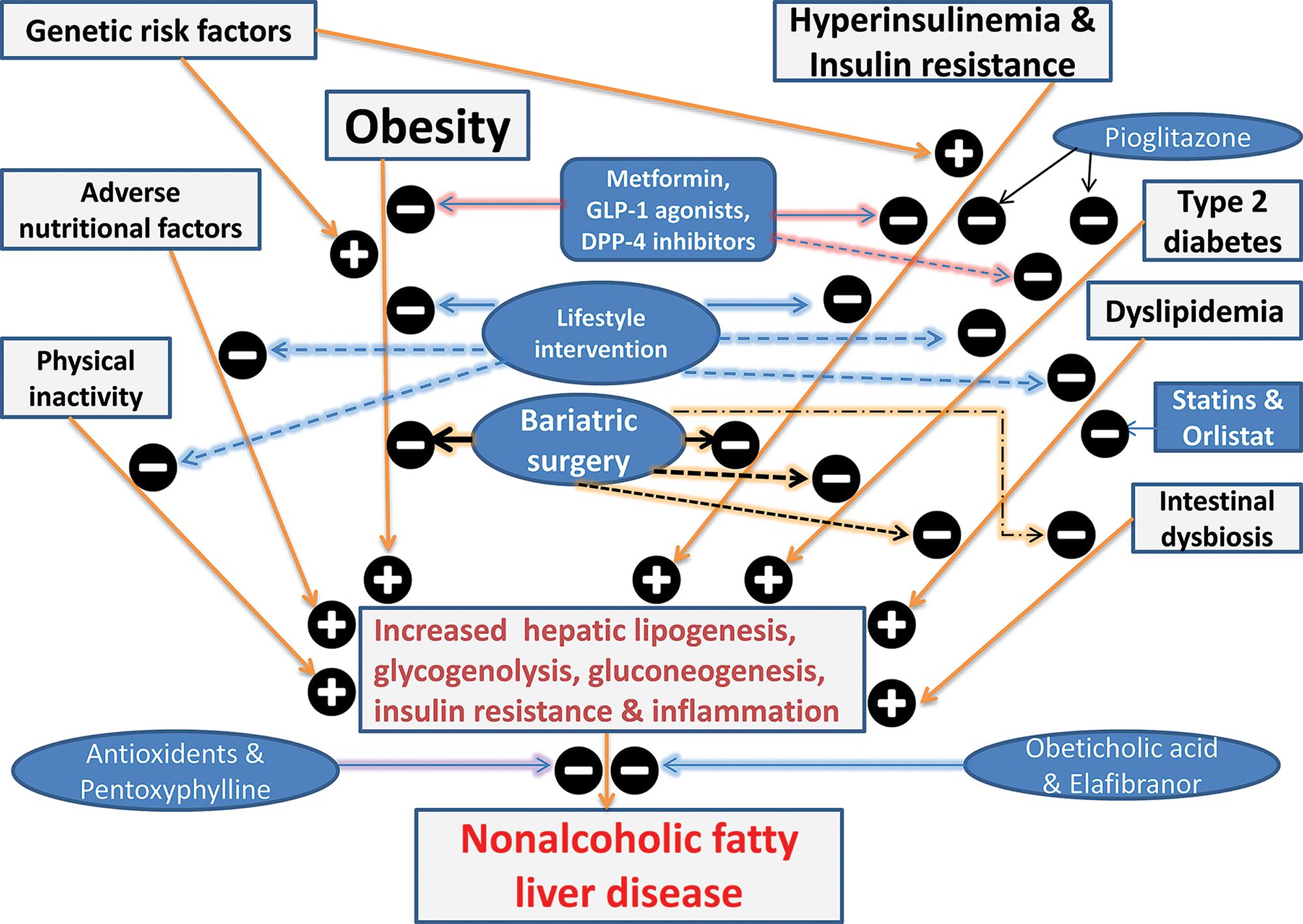
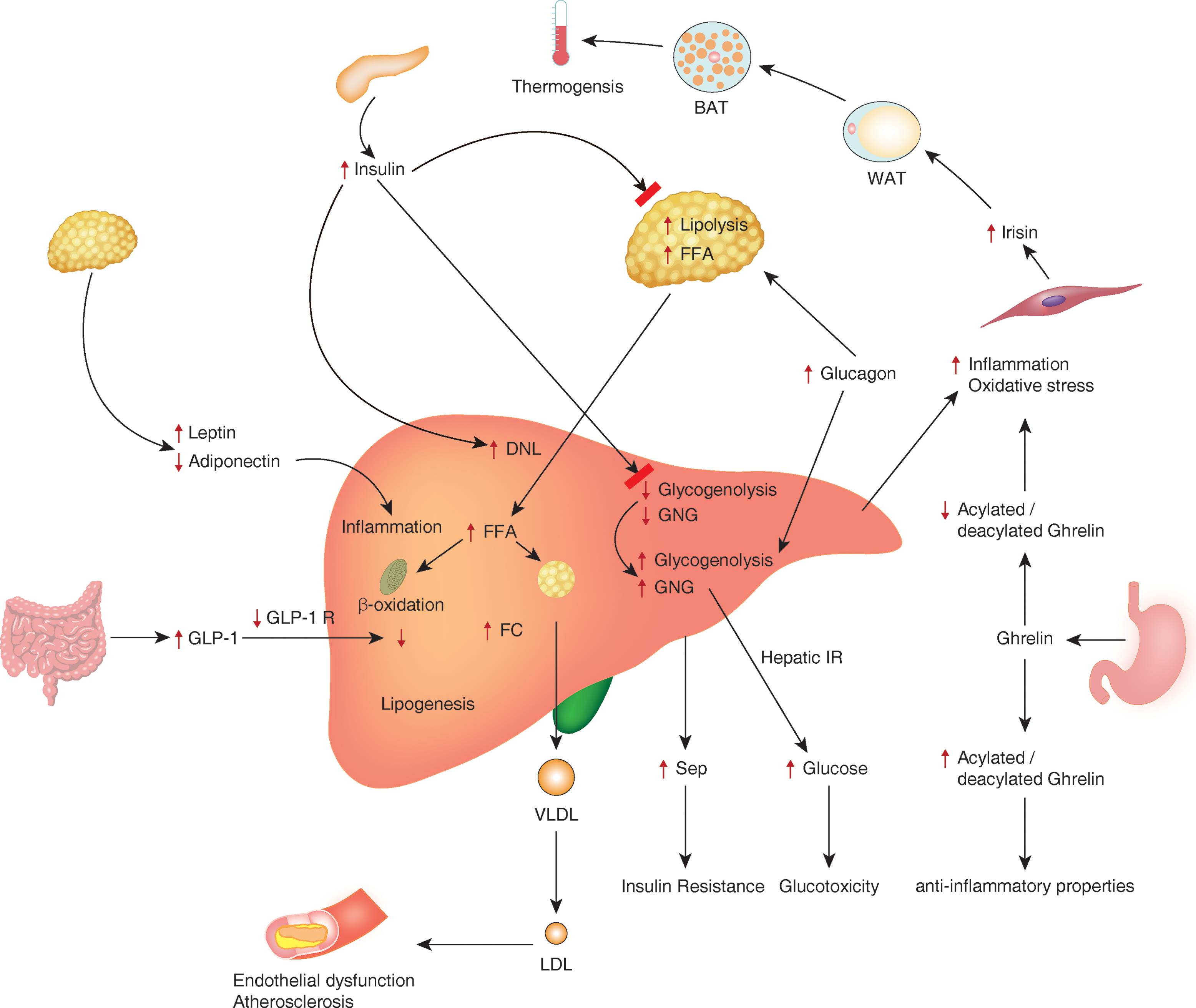
Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease A Clinical Update Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is a common liver disease and a major cause of related complications such as cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc). nafld progresses through the stages of simple steatosis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (nash), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hcc. however, nafld usually cannot be diagnosed in a timely. Description: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is well recognized as a leading etiology for chronic liver disease, affecting >25% of the us and global populations. up to 1 in 4 individuals with nafld have nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, which is associated with significant morbidity and mortality due to complications of liver cirrhosis. Non alcoholic fatty liver (nafld) is the most common liver disease worldwide, progressing from simple steatosis to necroinflammation and fibrosis (leading to non alcoholic steatohepatitis, nash), and in some cases to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin …. The global prevalence of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is rising, along with the epidemic of diabesity. nafld is present in >70% of individuals with type 2 diabetes. although the mutually detrimental relationship between nafld and type 2 diabetes has been well established, a multitude of recent studies have further shown that type.

Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease An Update With Special Focus O Non alcoholic fatty liver (nafld) is the most common liver disease worldwide, progressing from simple steatosis to necroinflammation and fibrosis (leading to non alcoholic steatohepatitis, nash), and in some cases to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin …. The global prevalence of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is rising, along with the epidemic of diabesity. nafld is present in >70% of individuals with type 2 diabetes. although the mutually detrimental relationship between nafld and type 2 diabetes has been well established, a multitude of recent studies have further shown that type. Non alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) has emerged as the. most prevalent chronic liver disease in developed nations in. recent years. it is defined as the presence of $5% steatosis. in the. This review summarizes the latest evidence on the epidemiology, natural history, pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of non alcoholic fatty liver disease. abstract non alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is currently the most common chronic liver disease in developed countries because of the obesity epidemic. the disease increases liver related morbidity and mortality, and often increases.

Comments are closed.