Newtons Laws Of Motion Motion Force Acceleration
Newton S 3 Laws Of Motion Force Mass And Acceleration Owlcation In equation form, newton’s second law of motion is a = fnet m a = f net m, often written in the more familiar form: fnet = ma f net = m a. the weight w w of an object is defined as the force of gravity acting on an object of mass mm. given acceleration due to gravity g g, the magnitude of weight is: w = mg w = m g. Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. these laws, which provide the basis for newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows: a body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except insofar as it is acted upon by.
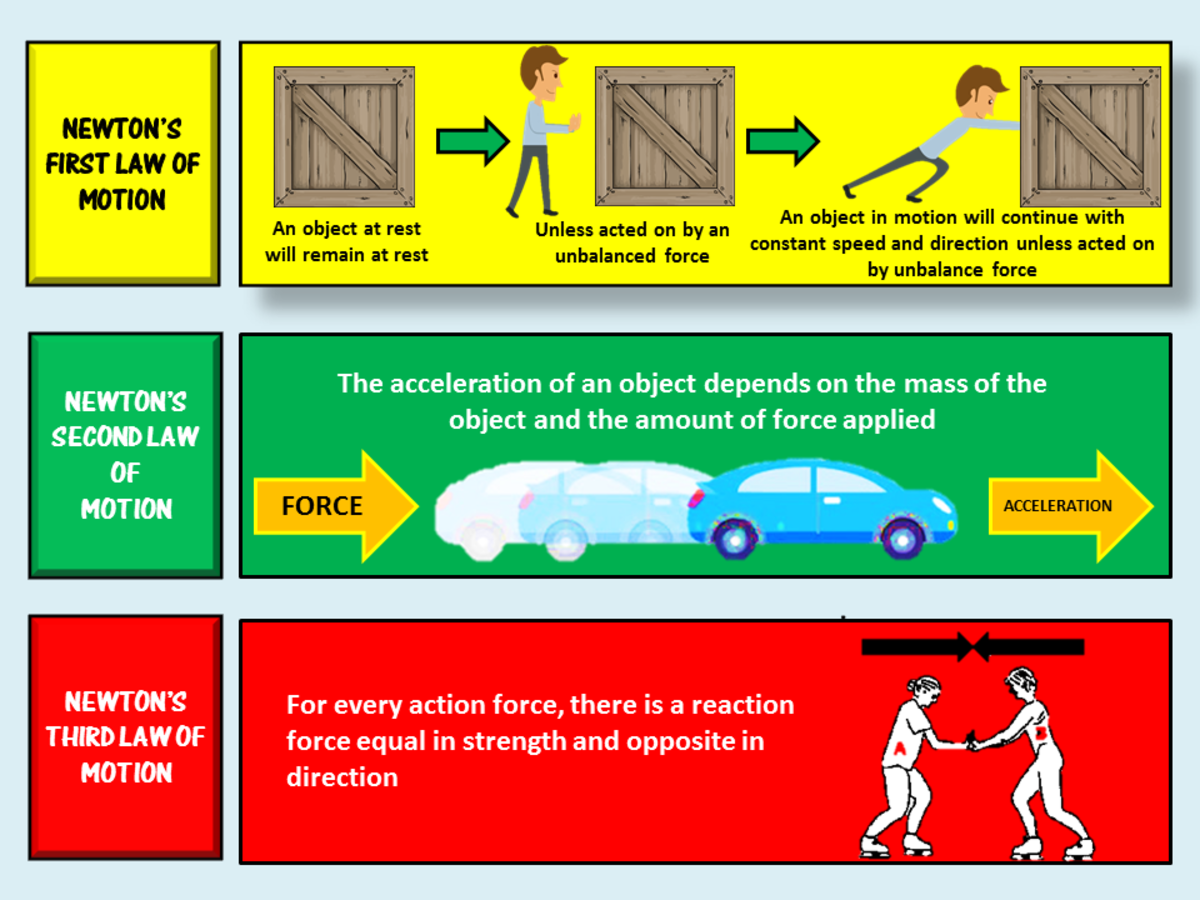
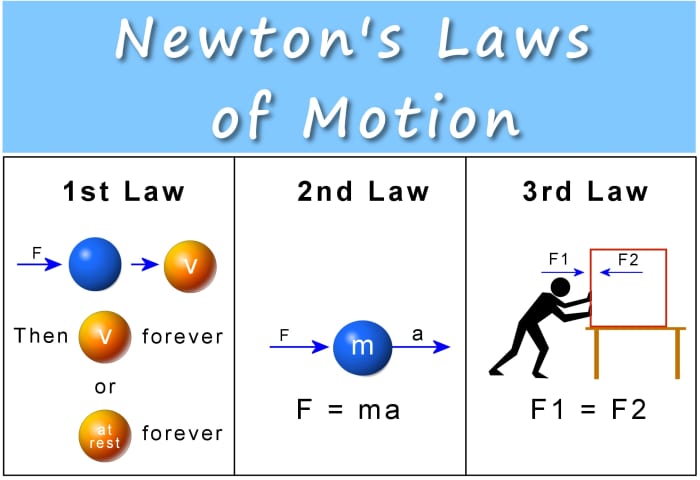
Newton S 3 Laws Of Motion Explained Owlcation 1. newton’s first law of motion (inertia) an object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion at constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. 2. newton’s second law of motion (force) the acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied. 3. Newton’s laws of motion relate an object’s motion to the forces acting on it. in the first law, an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it. in the second law, the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. in the third law, when two objects interact, they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude. Newton's third law of motion. newton's third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. this means that pushing on an object causes that object to push back against you, the same amount but in the opposite direction. for example, when you are standing on the ground, you are pushing down on the earth. Newton’s laws of motion are three laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting upon it. a body in motion remains in motion or a body at rest remains at rest, unless acted upon by a force. force equals mass times acceleration: f = m*a.

Force Acceleration Relationship Acceleration Newtons Second Law How Newton's third law of motion. newton's third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. this means that pushing on an object causes that object to push back against you, the same amount but in the opposite direction. for example, when you are standing on the ground, you are pushing down on the earth. Newton’s laws of motion are three laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting upon it. a body in motion remains in motion or a body at rest remains at rest, unless acted upon by a force. force equals mass times acceleration: f = m*a. Go ad free for 1 year. newton's laws of motion describe the connection between the forces that act upon an object and the manner in which the object moves. an understanding of forces and their tendency to balance or not balance each other is crucial to understanding how the object will change or not change its state of motion. Newton’s laws of motion force, mass, acceleration: newton’s second law is a quantitative description of the changes that a force can produce on the motion of a body. it states that the time rate of change of the momentum of a body is equal in both magnitude and direction to the force imposed on it. the momentum of a body is equal to the.

Comments are closed.