Neurogenesis The Brain Growing
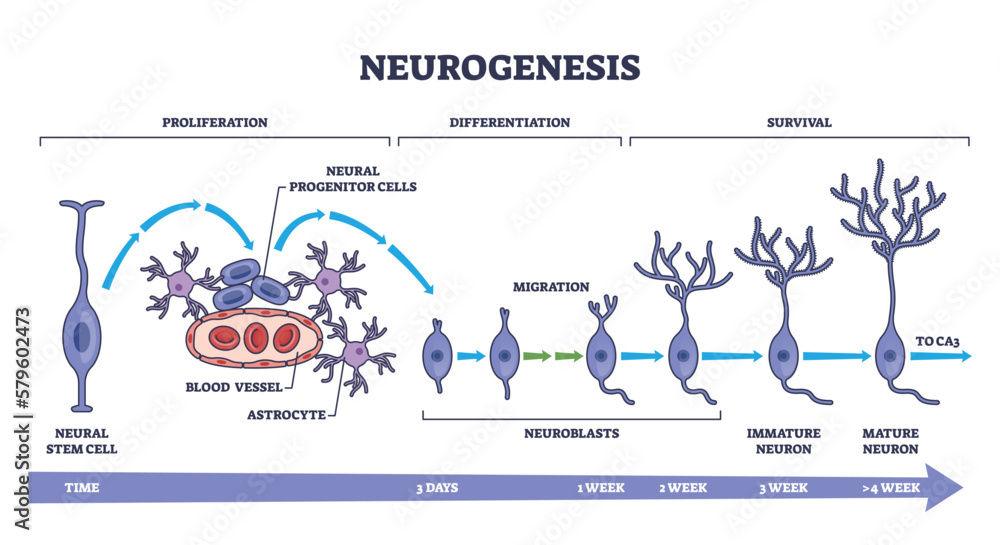
Neurogenesis As Detailed Neuron Development Process Stages Outline Neurogenesis refers to the formation of new neurons in the brain. it is an integral part of prenatal development, but neurogenesis in adults has been a topic of debate among scientists. today, research suggests that neurogenesis continues in certain areas of the brain after birth and even into adulthood. conventional wisdom has long suggested. This article was originally published with the title “ the adult brain does grow new neurons after all, study says ” in sa health & medicine vol. 1 no. 3 (june 2019) doi:10.1038.
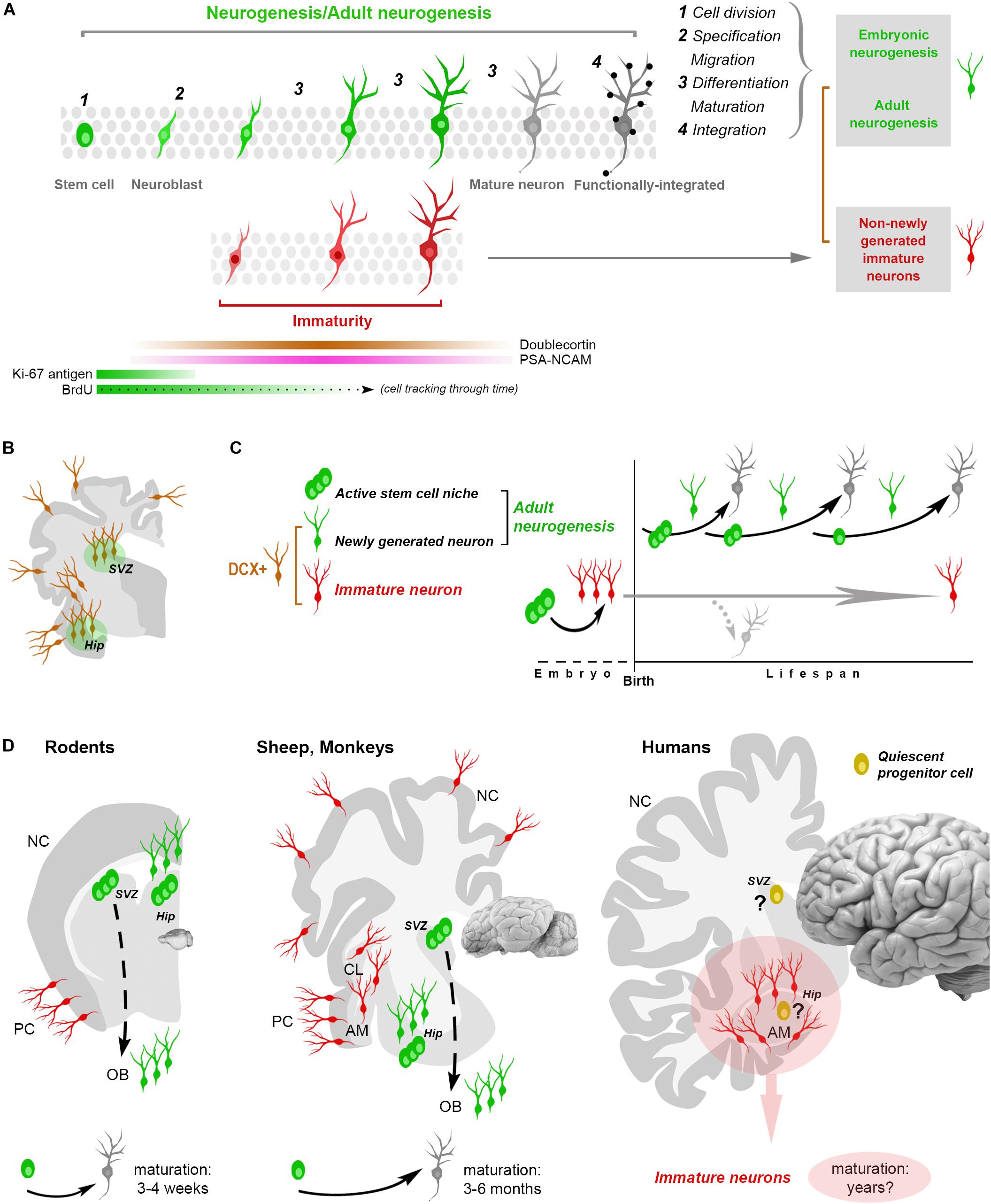
Frontiers Brain Structural Plasticity From Adult Neurogenesis To Growing spurts. the average brain contains about 100 billion brain cells, most of which were formed before birth. in the earliest stages of childhood, new brain cells continue to be made at a brisk pace. over the years, neurogenesis gradually declines, but the process doesn’t stop even into older age. that’s especially true in the hippocampus. The concept of neurogenesis in adult humans is a controversial topic among researchers in the field of neuroscience. while some researchers report that a sharp drop in neurogenesis occurs as the human brain ages, 1 other researchers report that neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus (dg) of the hippocampus of human brains persists into old age. 2 a clearer understanding of the evidence surrounding. How you can grow new brain cells. listen · 8:36 8:36. toggle more options. download; embed. embed she leads the adult neurogenesis and mental health lab at king's college london. Brain anatomy. neurogenesis is the process by which new neurons are formed in the brain. neurogenesis is crucial when an embryo is developing, but also continues in certain brain regions after birth and throughout our lifespan. the mature brain has many specialised areas of function, and neurons that differ in structure and connections.

Comments are closed.