Neural Processes Involved In Social Value Conversion In The Human Brain
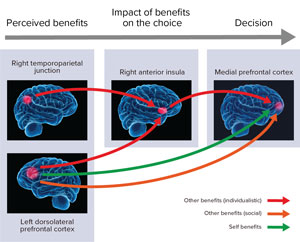
Neural Processes Involved In Social Value Conversion In The Human Brain These social influences modulate valuation and decision signals in the brain, suggesting a fundamental process called value conversion that translates social information into self referenced decisions. however, little is known about the conversion process and its underlying brain mechanisms. we investigated value conversion using human fmri. Here, we study how a fundamental social signal, social value (others' reward value), is converted into self oriented decision making in the human brain. using behavioral analysis, modeling, and neuroimaging, we show three stage processing of social value conversion from the offer to the effective value and then to the final decision value.

The Neural Network Engaged In Social Cognitive Processing A An Neuroscientists at riken have discovered how the brain factors in the benefits our decisions bring to others in the decision making process 1. it turns out that the neural processes differ between socially oriented people and those who are more self focused. many decisions we make affect not just us, but also those around us. We examined social value conversion as the behavior modifying effect on choice behavior of an additional reward to others (other bonus reward) versus an additional re ward to the self (self bonus reward). we used computational modeling and quantitative fmri analysis to derive and track three major stages of social value conversion. Together, our findings support a central role of human specific cortical areas in the brain dynamics of dyadic interactions and provide an approach for the noninvasive examination of the neural. The 'extended common currency schema' assumes that identical neural processes assign motivational relevance to social and non social factors.however, these value related processes may incorporate.
Frontiers Neurobiological Bases Of Social Networks Together, our findings support a central role of human specific cortical areas in the brain dynamics of dyadic interactions and provide an approach for the noninvasive examination of the neural. The 'extended common currency schema' assumes that identical neural processes assign motivational relevance to social and non social factors.however, these value related processes may incorporate. It is demonstrated that the variability in the conversion underlies the difference between prosocial and selfish subjects, as seen from the differential strength of the rai and ldlpfc coupling to the mpfc responses, respectively. social signals play powerful roles in shaping self oriented reward valuation and decision making. these signals activate social and valuation decision areas, but the. Abstract. social cognition in humans is distinguished by psychological processes that allow us to make inferences about what is going on inside other people—their intentions, feelings, and thoughts. some of these processes likely account for aspects of human social behavior that are unique, such as our culture and civilization.

Neural Representations Of Social Value A A Whole Brain Balanced It is demonstrated that the variability in the conversion underlies the difference between prosocial and selfish subjects, as seen from the differential strength of the rai and ldlpfc coupling to the mpfc responses, respectively. social signals play powerful roles in shaping self oriented reward valuation and decision making. these signals activate social and valuation decision areas, but the. Abstract. social cognition in humans is distinguished by psychological processes that allow us to make inferences about what is going on inside other people—their intentions, feelings, and thoughts. some of these processes likely account for aspects of human social behavior that are unique, such as our culture and civilization.

Comments are closed.