Nervous System Structure And Function
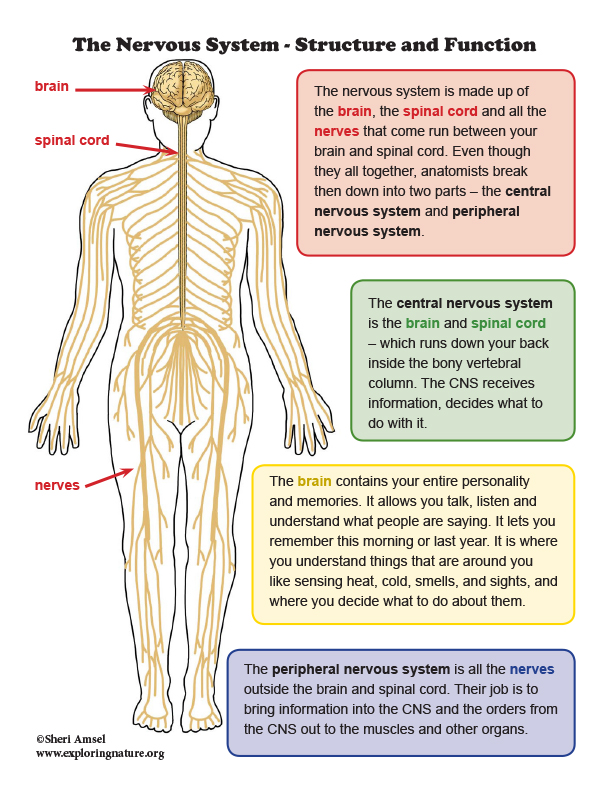
Nervous System Structure And Function Mini Poster The nervous system is a network of neurons whose main feature is to generate, modulate and transmit information between all the different parts of the human body. this property enables many important functions of the nervous system, such as regulation of vital body functions (heartbeat, breathing, digestion), sensation and body movements. Learn about the nervous system, which consists of your brain, spinal cord and nerves. find out how it works, what it does and what conditions can affect it.
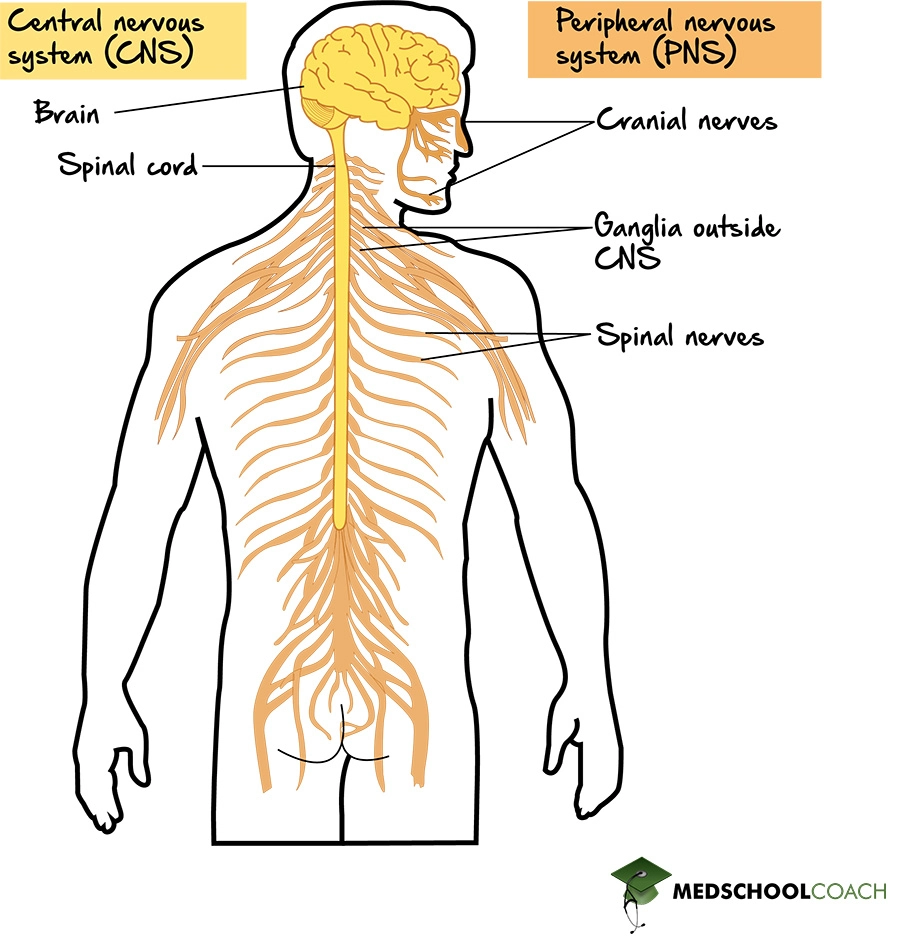
Nervous System Structure Function вђ Mcat Biology Medschoolcoach There are two ways to consider how the nervous system is divided functionally. first, the basic functions of the nervous system are sensation, integration, and response. secondly, control of the body can be somatic or autonomic—divisions that are largely defined by the structures that are involved in the response. There are two ways to consider how the nervous system is divided functionally. first, the basic functions of the nervous system are sensation, integration, and response. secondly, control of the body can be somatic or autonomic—divisions that are largely defined by the structures that are involved in the response. Unlike some other protozoans, an amoeba lacks highly developed structures that function in the reception of stimuli and in the production or conduction of a response. the amoeba behaves as though it had a nervous system, however, because the general responsiveness of its cytoplasm serves the functions of a nervous system. an excitation produced. There are two ways to consider how the nervous system is divided functionally. first, the basic functions of the nervous system are sensation, integration, and response. secondly, control of the body can be somatic or autonomic—divisions that are largely defined by the structures that are involved in the response.

Nervous Systems Organismal Biology Unlike some other protozoans, an amoeba lacks highly developed structures that function in the reception of stimuli and in the production or conduction of a response. the amoeba behaves as though it had a nervous system, however, because the general responsiveness of its cytoplasm serves the functions of a nervous system. an excitation produced. There are two ways to consider how the nervous system is divided functionally. first, the basic functions of the nervous system are sensation, integration, and response. secondly, control of the body can be somatic or autonomic—divisions that are largely defined by the structures that are involved in the response. The central system is the primary command center for the body, and is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. the peripheral nervous system consists of a network of nerves that connects the rest. Human nervous system, system that conducts stimuli from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord and conducts impulses back to other parts of the body. the conduction of electrochemical stimuli from sensory receptors occurs via organized groups of specialized cells, consisting largely of neurons, various neural support cells, and tracts.
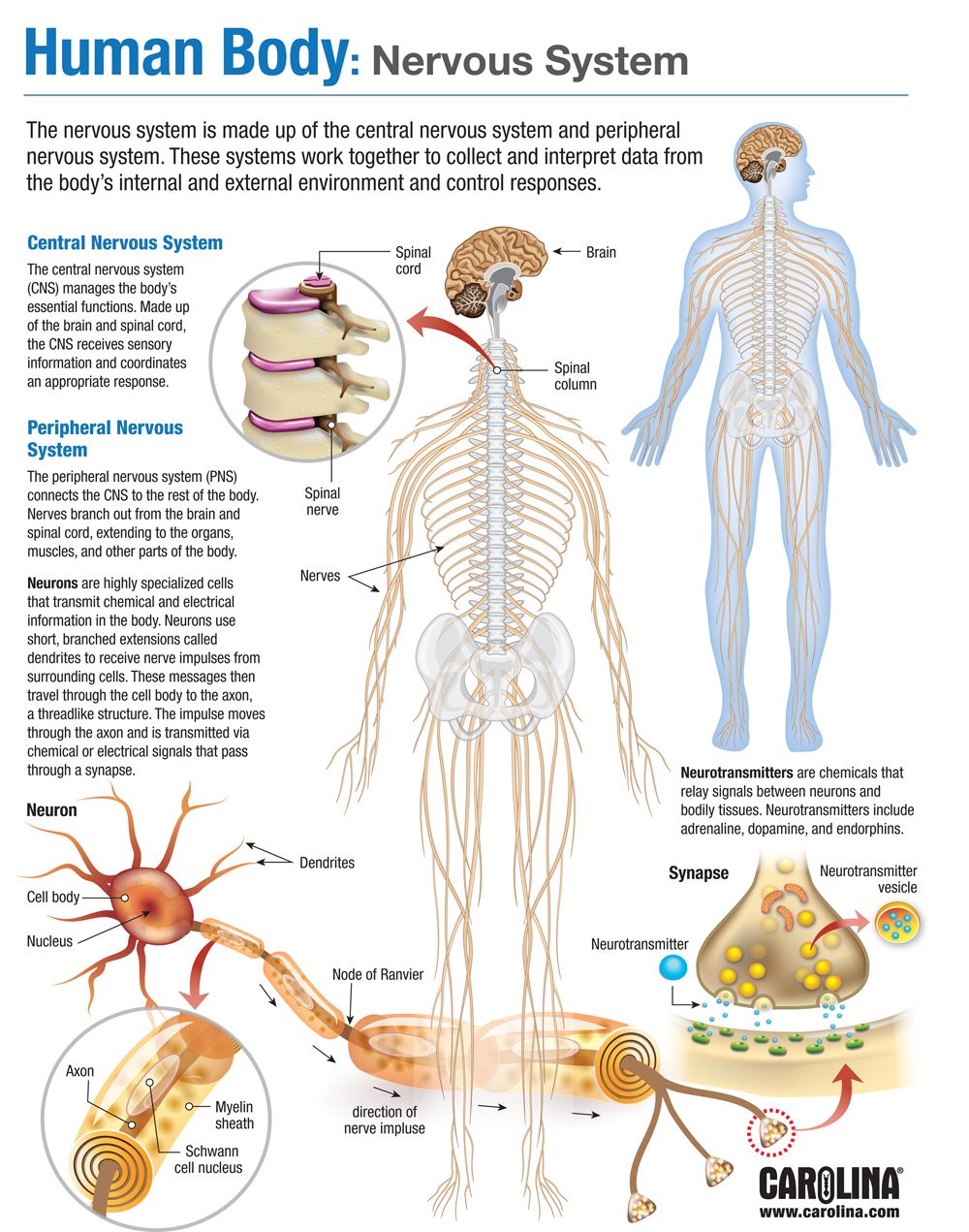
Human Nervous System Structure And Functions Explained With Diagrams The central system is the primary command center for the body, and is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. the peripheral nervous system consists of a network of nerves that connects the rest. Human nervous system, system that conducts stimuli from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord and conducts impulses back to other parts of the body. the conduction of electrochemical stimuli from sensory receptors occurs via organized groups of specialized cells, consisting largely of neurons, various neural support cells, and tracts.
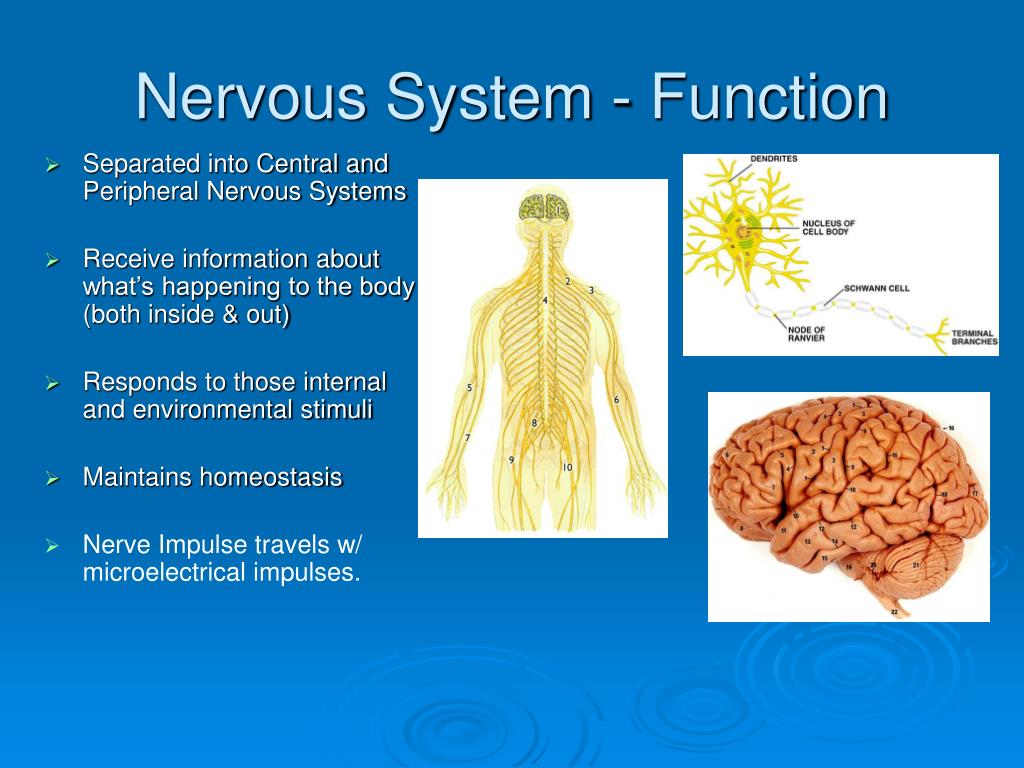
Picture Of Nervus System Ppt The Nervous System Powerpoint

Comments are closed.