Motion Graphs
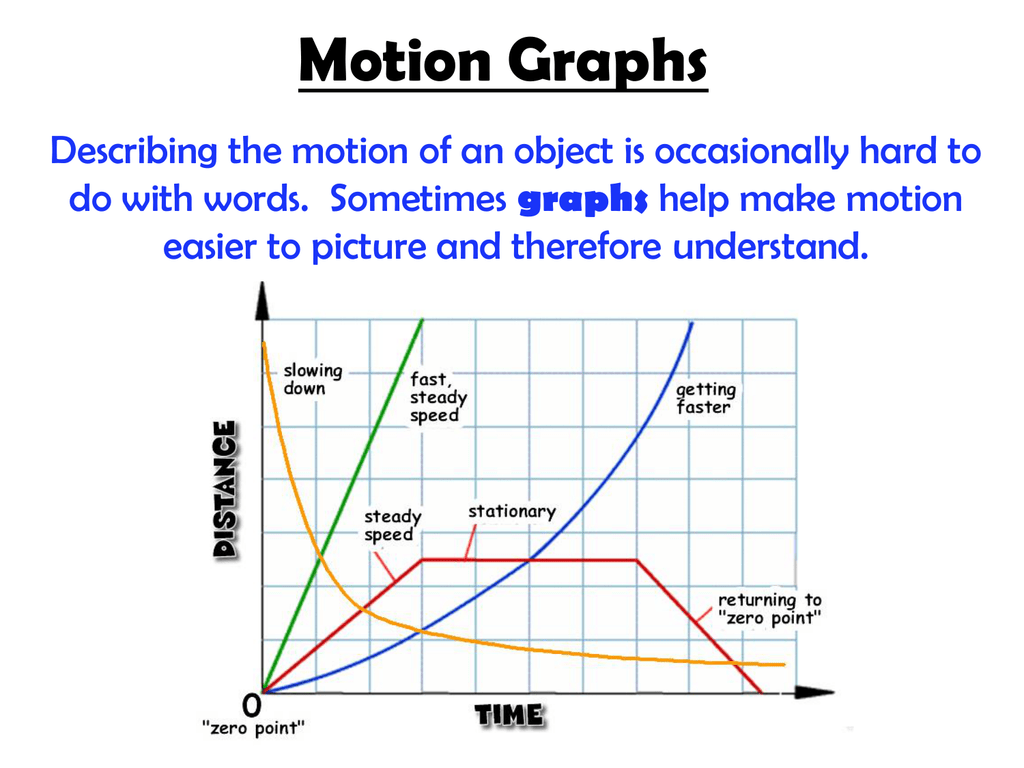
Motion Graphs Motion graphs allow scientists to learn a lot about an object’s motion with just a quick glance. this article will cover the basics for interpreting motion graphs including different types of graphs, how to read them, and how they relate to each other. interpreting motion graphs, such as position vs time graphs and velocity vs time graphs. Learn how to use graphs to describe and analyze motion with constant velocity, acceleration, and position. see examples, equations, and animations of position time graphs and their applications.

Reading Kinematics Graphs Mini Physics Free Physics Notes 1. figure 2.8.2.1 2.8.2. 1: (a) position of the train over time. notice that the train’s position changes slowly at the beginning of the journey, then more and more quickly as it picks up speed. its position then changes more slowly as it slows down at the end of the journey. in the middle of the journey, while the velocity remains constant. This physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into motion graphs such as position time graphs, velocity time graphs, and acceleration time graphs. The velocity time graphs give all three variables for motion–velocity which can be read off at any time. area is displacement and gradient is acceleration. Interpreting graphs. motion graphs represent what is happening to the various dependent variables (\(x\), \(v\), and \(a\)) over time. there are three goals here: to interpret a graph in terms of the physical motion of the object it represents. to sketch a graph that represents the physical motion of an object, given a description of that motion.
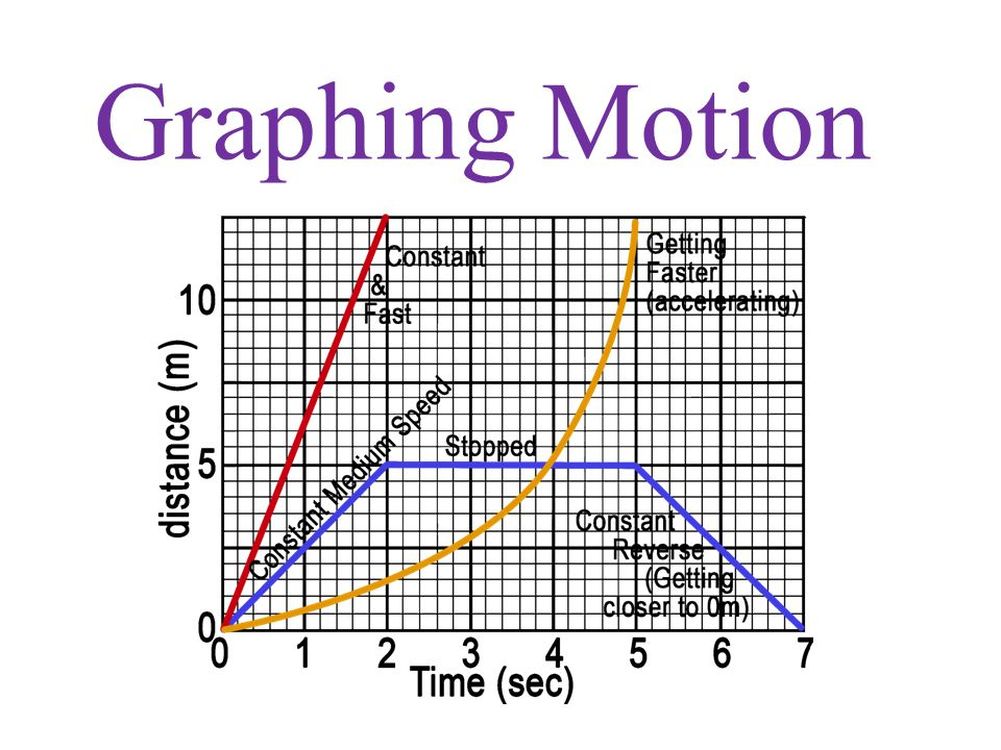
Motion Graphs Science Quiz Quizizz The velocity time graphs give all three variables for motion–velocity which can be read off at any time. area is displacement and gradient is acceleration. Interpreting graphs. motion graphs represent what is happening to the various dependent variables (\(x\), \(v\), and \(a\)) over time. there are three goals here: to interpret a graph in terms of the physical motion of the object it represents. to sketch a graph that represents the physical motion of an object, given a description of that motion. Learn how to interpret and draw graphs of motion for displacement, velocity and acceleration. find out how to calculate and compare different types of motion using graphs and equations. Learn how to use motion graphs to analyze constant and variable acceleration motion. find out how to calculate the slopes of position, velocity and acceleration graphs and how they relate to the areas under the curves.
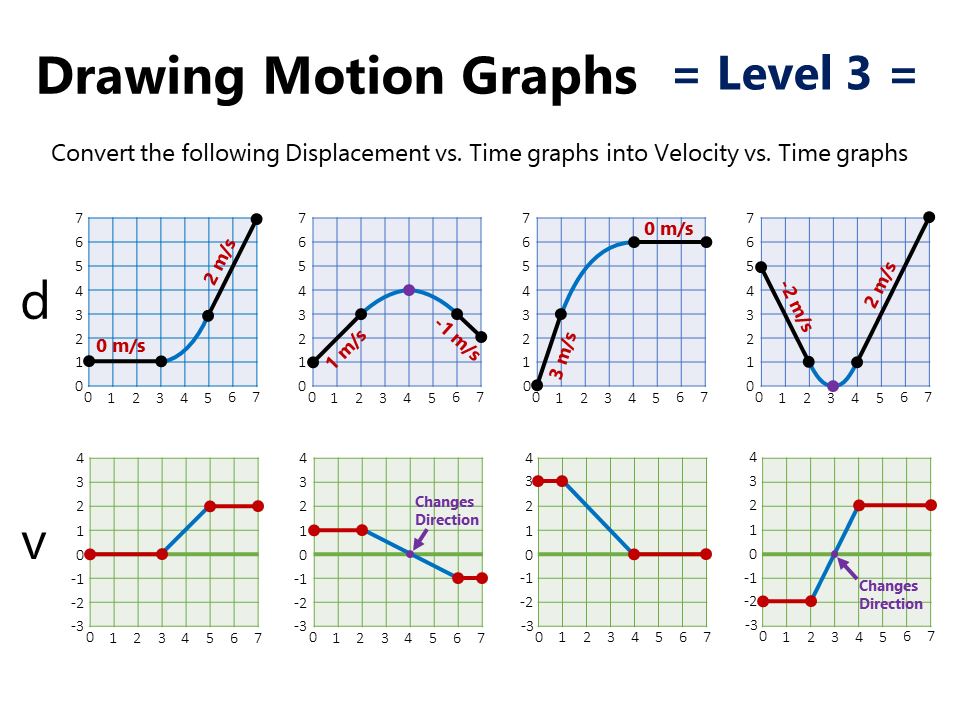
Motion Graphs Practice Worksheet Learn how to interpret and draw graphs of motion for displacement, velocity and acceleration. find out how to calculate and compare different types of motion using graphs and equations. Learn how to use motion graphs to analyze constant and variable acceleration motion. find out how to calculate the slopes of position, velocity and acceleration graphs and how they relate to the areas under the curves.

Motion Graphs Explained Youtube

Comments are closed.