Microorganisms Free Full Text Gut Dysbiosis During Covid 19 And

Microorganisms Free Full Text Gut Dysbiosis During Covid 19 And These alterations cause the decreased secretion of antimicrobial peptides and disturbance in the gut microbiome [10]. therefore, covid 19 impacts the human gut microbiome, with a decline in microbial diversity and beneficial microbes [11]. 2. the interaction between respiratory tract diseases and gut microbiota. In contrast, in an american cohort including recovered covid 19 cases, the dysbiosis could rapidly recover with a return of the human gut microbiota to an uninfected status . although the great diversity in the ability of the microbiota return was disclosed, it was evident that the recovery of gut microbiota could be regarded as an indicator of.
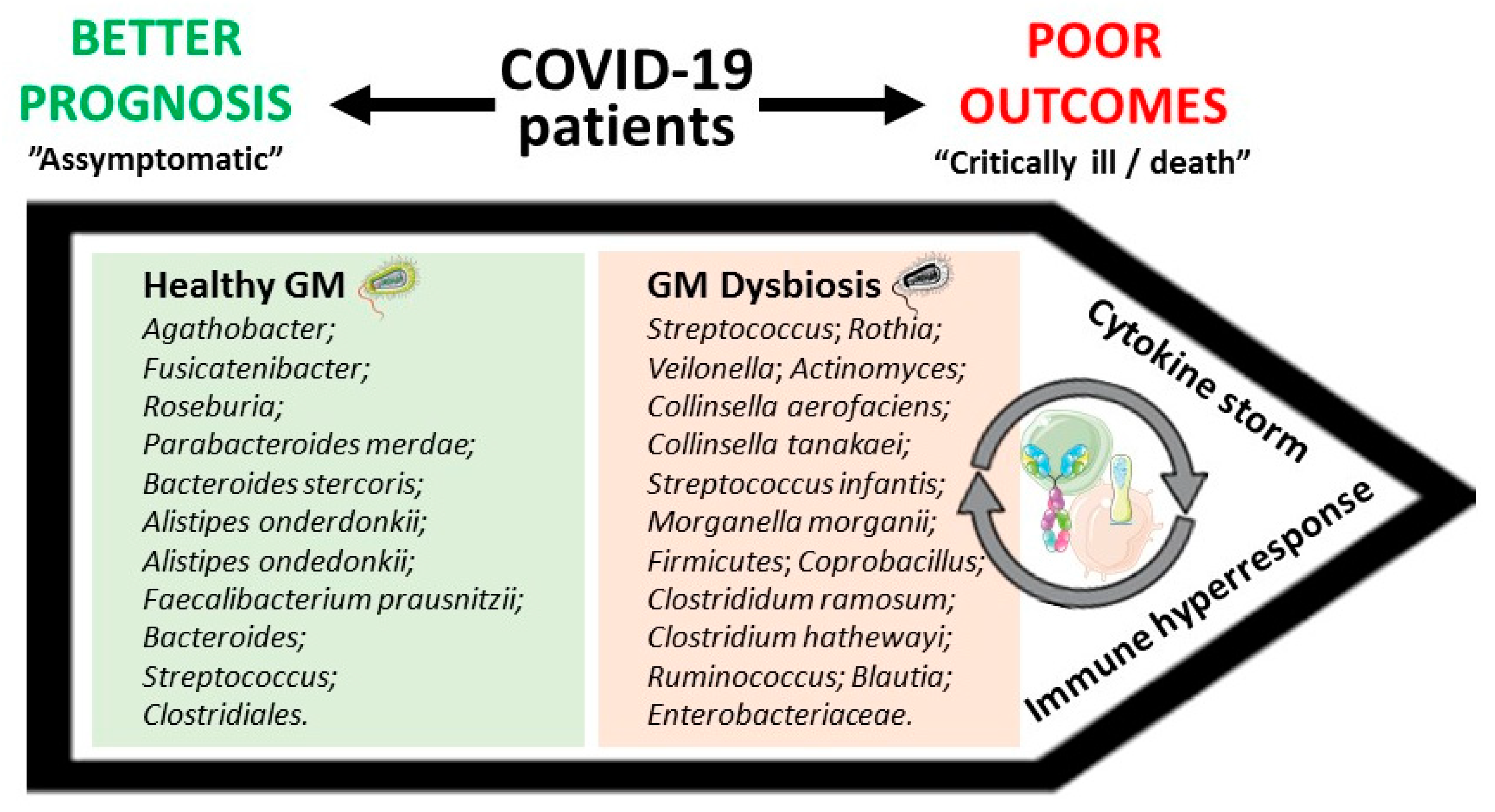
Microorganisms Free Full Text Is Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis A A significant change in fecal microbiomes, namely dysbiosis, was characterized by the enrichment of opportunistic pathogens and the depletion of beneficial commensals and their crucial association to covid 19 severity has been evidenced. oral probiotics had been evidenced to improve gut health in achieving homeostasis by exhibiting their. The gastrointestinal tract is involved in coronavirus disease 2019 (covid 19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (sars cov 2). the gut microbiota has important roles in. A recent study revealed that gut dysbiosis might play a vital role in pacs. 110 stool samples were collected from 68 covid 19 patients of whom 50 (73.5%) presented with pacs at six months after. Taken together, our findings support a scenario in which gut to blood translocation of microorganisms following microbiome dysbiosis leads to dangerous bsis during covid 19, a complication seen in.

Ijms Free Full Text Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis In Covid 19 A recent study revealed that gut dysbiosis might play a vital role in pacs. 110 stool samples were collected from 68 covid 19 patients of whom 50 (73.5%) presented with pacs at six months after. Taken together, our findings support a scenario in which gut to blood translocation of microorganisms following microbiome dysbiosis leads to dangerous bsis during covid 19, a complication seen in. Follow ups of patients with covid 19 (e.g., 3 months to 1 year after clearing the virus) are needed to address questions related to (i) the duration of gut microbiota dysbiosis post recovery, (ii) the link between microbiota dysbiosis and long term persistent symptoms, and (iii) whether the enrichment depletion of specific gut microorganisms. Faecalibacterium is an immunosupportive clostridiales genus that is a prominent member of the human gut microbiome 30 – 32, and its reduction is associated with disruption to intestinal barrier function 33, 34, perhaps via ecological network effects 34. open in a separate window. figure 3.

Comments are closed.