Metabolism Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
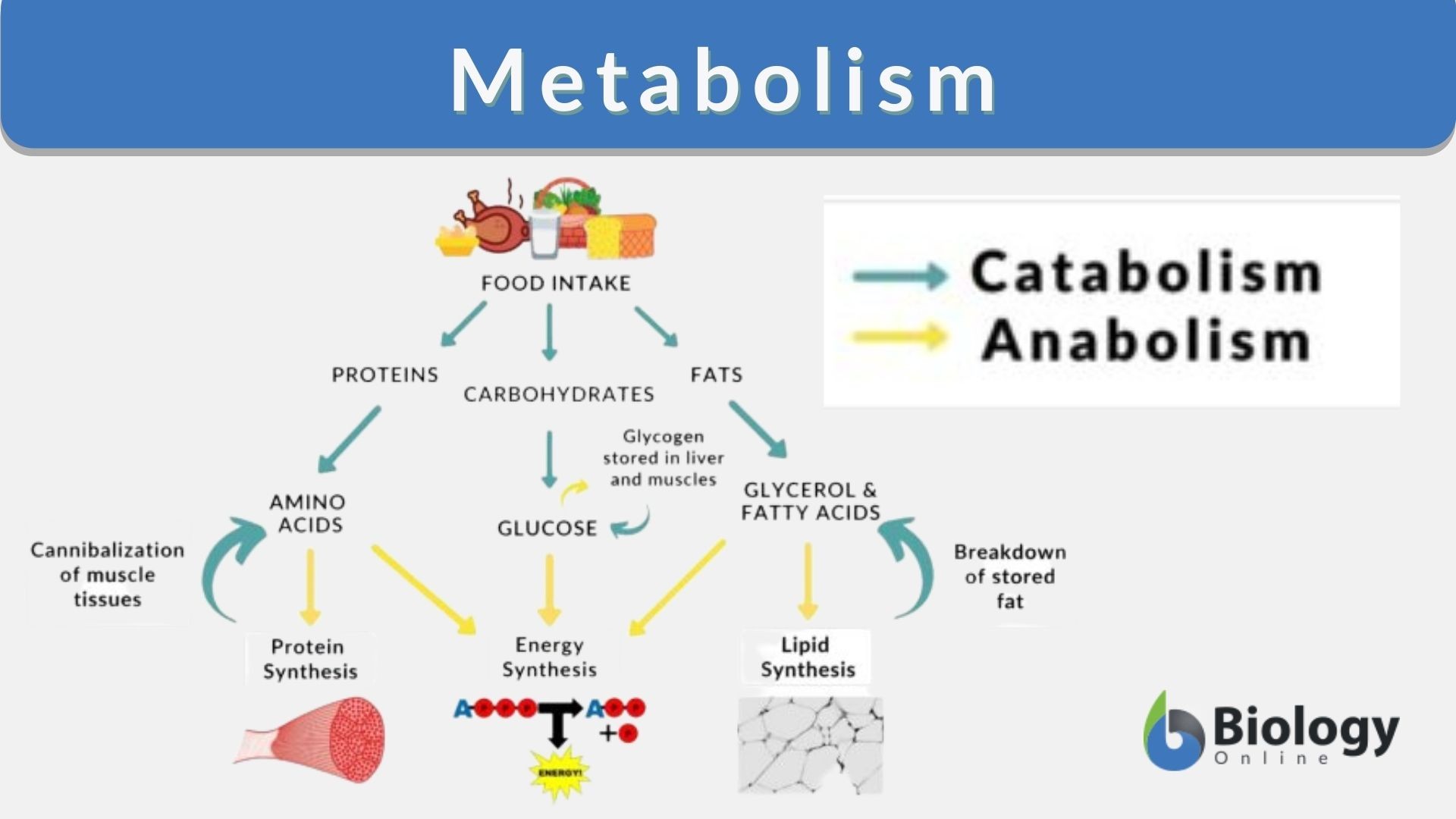
Metabolism Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Metabolism includes processes for cell growth, reproduction, response to the environment, survival mechanisms, sustenance, and maintenance of cell structure and integrity. these chemical reactions utilize various enzymes. metabolism may be categorized into two: catabolism and anabolism. Definition. noun. the intermediate steps within the cells in which the nutrient molecule s or foodstuffs are metabolized and converted into cellular components catalysed by enzyme s. supplement. synonym: intermediate metabolism. last updated on may 29th, 2023.
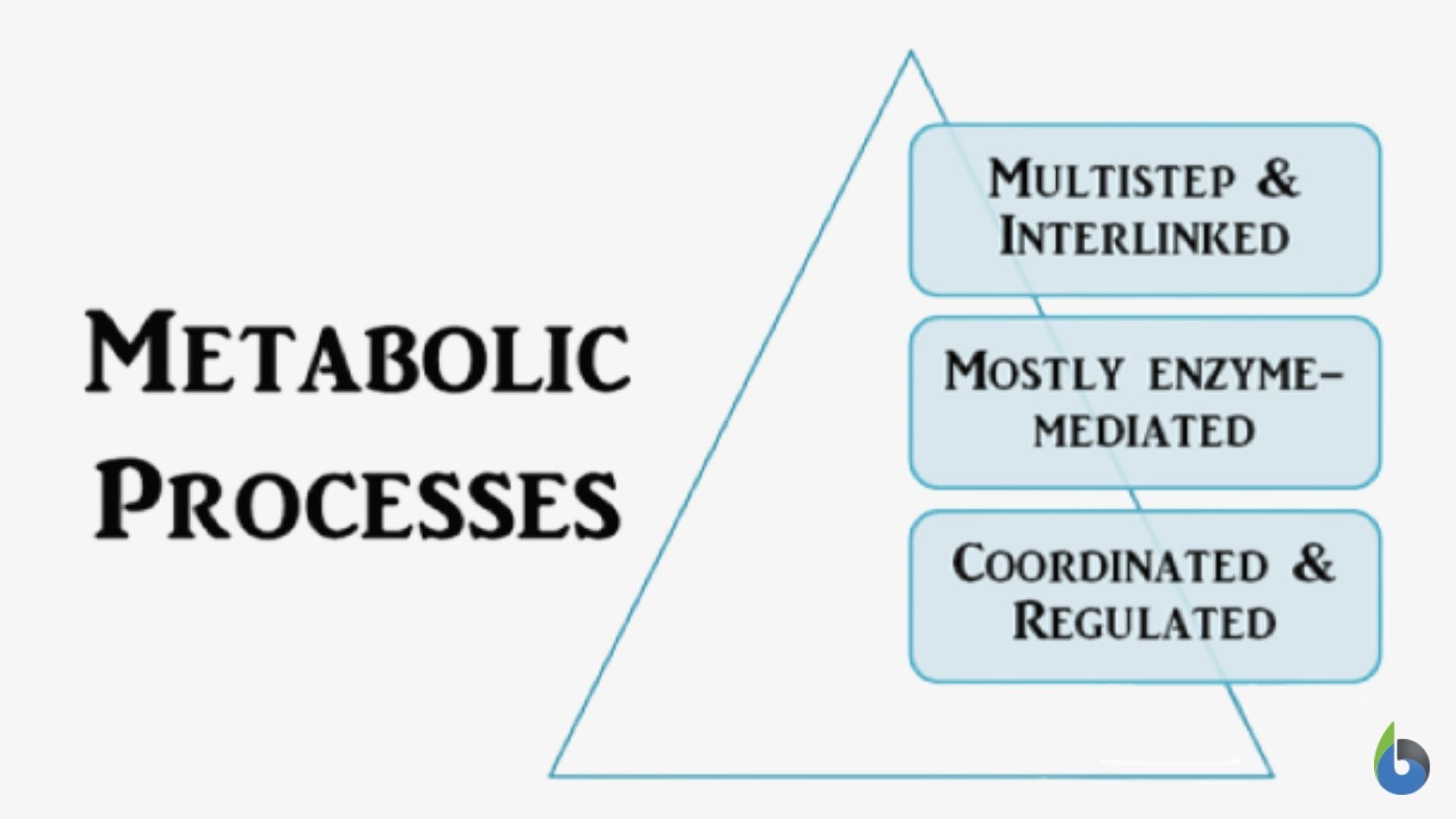
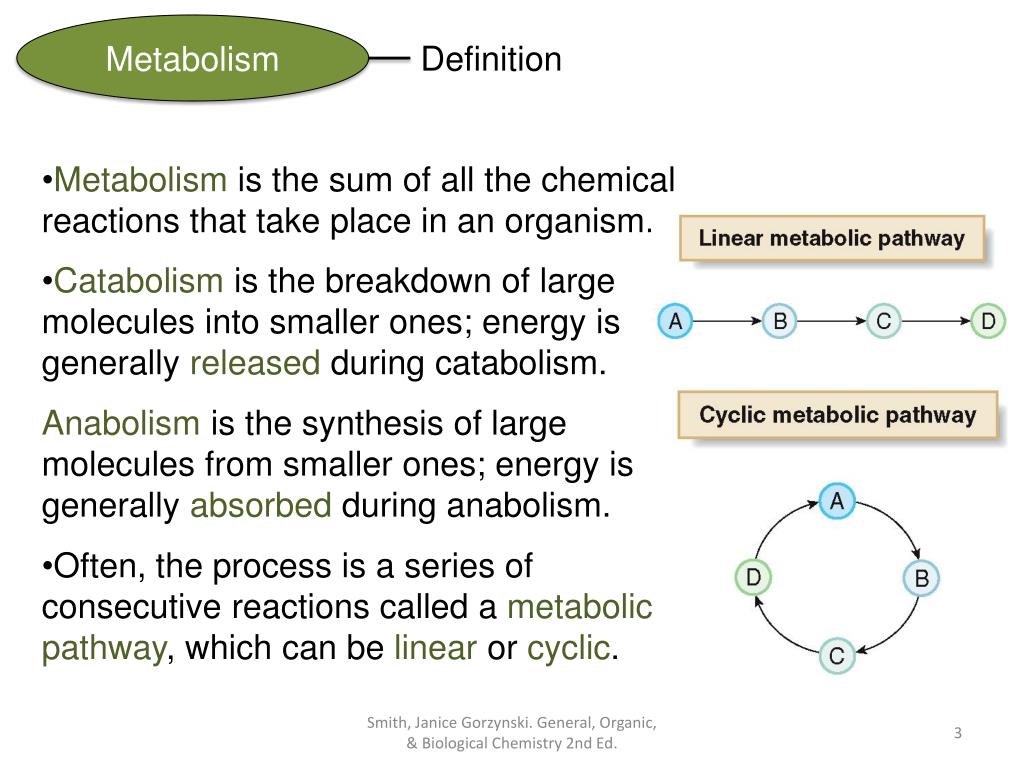
Metabolism Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Catabolism definition. catabolism is the part of the metabolism responsible for breaking complex molecules down into smaller molecules. the other part of the metabolism, anabolism, builds simple molecules into more complex ones. during the catabolism energy is released from the bonds of the large molecules being broken down. Calcium metabolism a set of biochemical processes which act to keep the level of calcium in the blood at a constant level, with enough around to build bones and teeth. calcium metabolism definition and examples biology online dictionary. Metabolism, the sum of chemical reactions that take place in living cells, providing energy for life processes and the synthesis of cellular material. living organisms are unique in that they extract energy from their environments via hundreds of coordinated, multistep, enzyme mediated reactions. The meaning of metabolism is the sum of the processes in the buildup and destruction of protoplasm; specifically : the chemical changes in living cells by which energy is provided for vital processes and activities and new material is assimilated.
Metabolism Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Metabolism, the sum of chemical reactions that take place in living cells, providing energy for life processes and the synthesis of cellular material. living organisms are unique in that they extract energy from their environments via hundreds of coordinated, multistep, enzyme mediated reactions. The meaning of metabolism is the sum of the processes in the buildup and destruction of protoplasm; specifically : the chemical changes in living cells by which energy is provided for vital processes and activities and new material is assimilated. Metabolism is the total amount of the biochemical reactions involved in maintaining the living condition of the cells in an organism. all living organisms require energy for different essential processes and for producing new organic substances. the metabolic processes help in growth and reproduction and help in maintaining the structures of. Metabolism definition: the sum of the physical and chemical processes in an organism by which its material substance is produced, maintained, and destroyed, and by which energy is made available.
Metabolism Definition And Examples Biology Online Dic Vrogue Co Metabolism is the total amount of the biochemical reactions involved in maintaining the living condition of the cells in an organism. all living organisms require energy for different essential processes and for producing new organic substances. the metabolic processes help in growth and reproduction and help in maintaining the structures of. Metabolism definition: the sum of the physical and chemical processes in an organism by which its material substance is produced, maintained, and destroyed, and by which energy is made available.

Comments are closed.