Limits Fits And Tolerances Basics And Terminology
Limits Fits And Tolerances Bartleby From the table, we can see that the tolerance grade applies to a range of basic sizes. so if we have a hole with a nominal size of 25 mm and a tolerance class of h7, we will fit into the 18…30 mm basic size group. looking at the it7 tolerance grade, the chart gives an allowed variance of 0.021 mm. Limits, fits and tolerances: definitions, types, and terminology. limits, fits, and tolerances are fundamental concepts in the field of engineering and manufacturing, serving as the anchor for ensuring the functionality and interchangeability of mechanical components. these principles define the acceptable variation in size and geometry of.

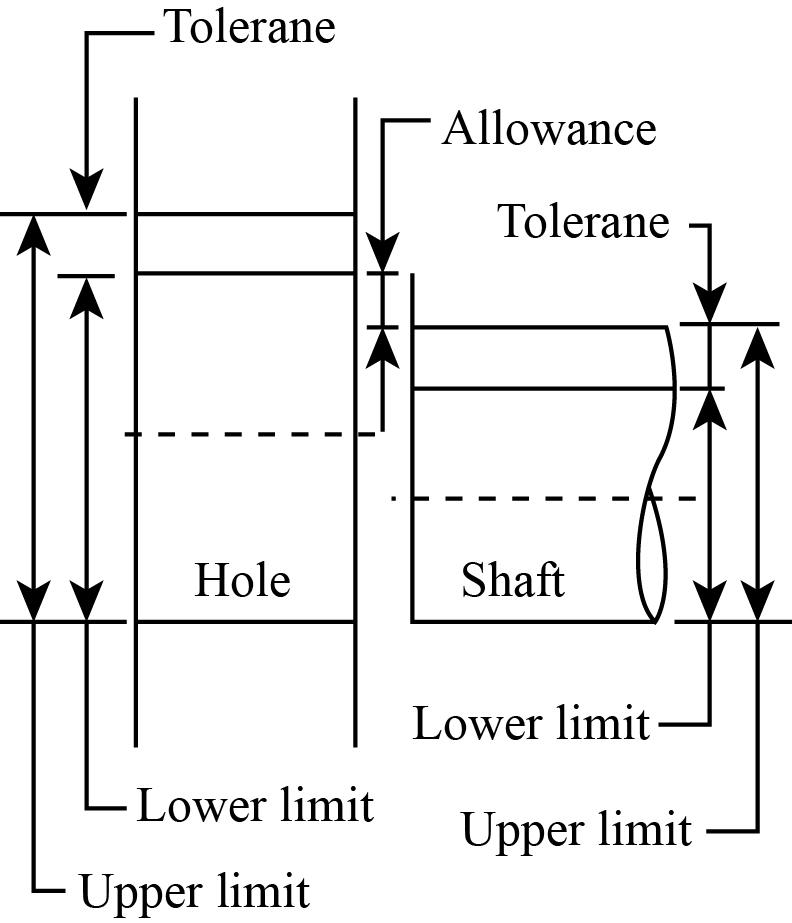
Limits Fits And Tolerances Types Explained With Diagram Engineering tolerance is the permissible variation in measurements deriving from the base measurement. tolerances can apply to many different units. for example, the working conditions may have tolerances for temperature (° c), humidity (g m 3), etc. in mechanical engineering, we are mainly talking about tolerances that apply to linear. The term 'limit' refers to the upper and lower tolerance a part can achieve, and 'fits' are the relationship resulting from a hole and a shaft's assembly. limits and fits standards, such as those by the international organization for standardization (iso), ensure uniformity and consistency in the production and assembly of mechanical parts. For example, an rc1 fit is a very loose clearance fit, while an fn9 fit is a very tight interference fit. the standard also uses capital letters for holes and lowercase letters for shafts. for example, a hole with an h7 tolerance means that its actual size can vary from 0 to 0.025 mm from its nominal size, while a shaft with an h6 tolerance. The effect is called tolerance stack up. metric limits and fits the standards used for metric measurements are recommended by the international organization for standardization (iso). the terms used in metric tolerancing are: basic size – the exact theoretical size to which limits of deviation are assigned and are the same for both parts.
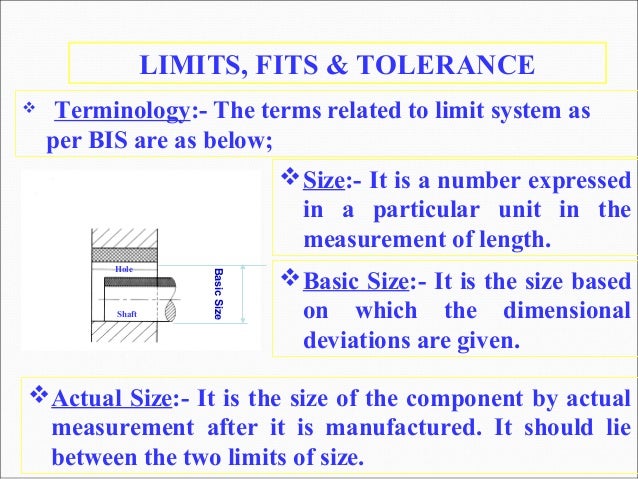
Limit Fit Tolerance For example, an rc1 fit is a very loose clearance fit, while an fn9 fit is a very tight interference fit. the standard also uses capital letters for holes and lowercase letters for shafts. for example, a hole with an h7 tolerance means that its actual size can vary from 0 to 0.025 mm from its nominal size, while a shaft with an h6 tolerance. The effect is called tolerance stack up. metric limits and fits the standards used for metric measurements are recommended by the international organization for standardization (iso). the terms used in metric tolerancing are: basic size – the exact theoretical size to which limits of deviation are assigned and are the same for both parts. Bilateral tolerance. bilateral tolerance is a type of tolerance in which both upper and lower deviation from the basic size is allowed. examples of bilateral tolerance are 200 ( 0.05 0.03) and 300 ( 0.08 0.02) fit; the relationship between the assembled parts due to the difference in their sizes before assembly, is known as a fit. types of fits. 1.unilateral tolerances: if the variation permitted is at only one side of the given dimension, called unilateral tolerance. when the variation permitted is at only one side of the given dimension, then it is slightly difficult to manufacture the components. hence the cost of manufacturing will be high. ex: mating parts.

Limits Fits Types Of Fits Explained Tolerance Charts Fractory Bilateral tolerance. bilateral tolerance is a type of tolerance in which both upper and lower deviation from the basic size is allowed. examples of bilateral tolerance are 200 ( 0.05 0.03) and 300 ( 0.08 0.02) fit; the relationship between the assembled parts due to the difference in their sizes before assembly, is known as a fit. types of fits. 1.unilateral tolerances: if the variation permitted is at only one side of the given dimension, called unilateral tolerance. when the variation permitted is at only one side of the given dimension, then it is slightly difficult to manufacture the components. hence the cost of manufacturing will be high. ex: mating parts.

Tolerance Limits And Fits Youtube

Comments are closed.