Introduction To Limits Fits And Tolerances _ Machine Drawing

Introduction To Limits Fits And Tolerances Machine Drawing Youtube Limits & fits. in engineering, we have to define the tolerances of parts to ensure a long lifespan and proper working of a machine. we can choose the fits according to the necessities and working conditions. the three main categories are: clearance fit. transition fit. interference fit. 1.unilateral tolerances: if the variation permitted is at only one side of the given dimension, called unilateral tolerance. when the variation permitted is at only one side of the given dimension, then it is slightly difficult to manufacture the components. hence the cost of manufacturing will be high. ex: mating parts.

Chapter 1 Limits Fits And Tolerances 1 Introduction For example, an rc1 fit is a very loose clearance fit, while an fn9 fit is a very tight interference fit. the standard also uses capital letters for holes and lowercase letters for shafts. for example, a hole with an h7 tolerance means that its actual size can vary from 0 to 0.025 mm from its nominal size, while a shaft with an h6 tolerance. Limit tolerances are typically employed when the precise magnitude of variation is not a critical factor; rather, adherence to the prescribed range is paramount. example: a dimension governed by limit tolerance, such as 10.0 mm to 10.2 mm, mandates that a component's dimensions must reside within this span to satisfy tolerance requirements. Bilateral tolerance. bilateral tolerance is a type of tolerance in which both upper and lower deviation from the basic size is allowed. examples of bilateral tolerance are 200 ( 0.05 0.03) and 300 ( 0.08 0.02) fit; the relationship between the assembled parts due to the difference in their sizes before assembly, is known as a fit. types of fits. Dimension tolerances. as machines can not perform to perfection, the final dimensions of a product will definitely vary from the stated measurements. for example, a 15 mm hole on a drawing may end up 15.1 mm for laser cut parts. so let’s see what you can do to make sure that the deviations are in the direction you would prefer them in.

Ppt Mechanical Drawing Chapter 10 Tolerances And Fits Powerpoint Bilateral tolerance. bilateral tolerance is a type of tolerance in which both upper and lower deviation from the basic size is allowed. examples of bilateral tolerance are 200 ( 0.05 0.03) and 300 ( 0.08 0.02) fit; the relationship between the assembled parts due to the difference in their sizes before assembly, is known as a fit. types of fits. Dimension tolerances. as machines can not perform to perfection, the final dimensions of a product will definitely vary from the stated measurements. for example, a 15 mm hole on a drawing may end up 15.1 mm for laser cut parts. so let’s see what you can do to make sure that the deviations are in the direction you would prefer them in. Tolerance is the total allowable variance in a dimension, i.e., the difference between the upper and lower limits. the tolerance of the slot in the example is 0.004" (0.502 0.498 = 0.004) and the tolerance of the mating part is 0.002" (0.497 0.495 = 0.002). fit types the degree of tightness between mating parts is called the fit. Tolerance class. usually, fit tolerances are marked with the use of the tolerance class. the tolerance class consists of the fundamental deviation identifier followed by the standard tolerance grade number. for example: toleranced size for a hole 80 h7 and a shaft 80 m6: 80 is the nominal size in millimeters; h is the fundamental deviation.
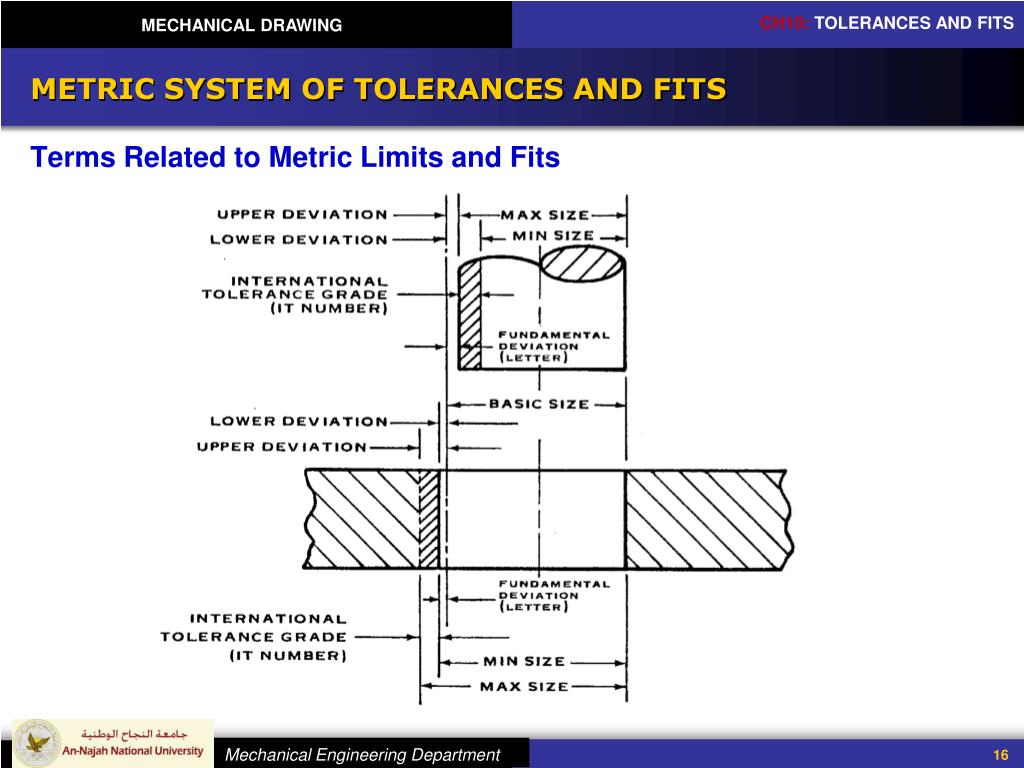
Ppt Mechanical Drawing Chapter 10 Tolerances And Fits Powerpoint Tolerance is the total allowable variance in a dimension, i.e., the difference between the upper and lower limits. the tolerance of the slot in the example is 0.004" (0.502 0.498 = 0.004) and the tolerance of the mating part is 0.002" (0.497 0.495 = 0.002). fit types the degree of tightness between mating parts is called the fit. Tolerance class. usually, fit tolerances are marked with the use of the tolerance class. the tolerance class consists of the fundamental deviation identifier followed by the standard tolerance grade number. for example: toleranced size for a hole 80 h7 and a shaft 80 m6: 80 is the nominal size in millimeters; h is the fundamental deviation.

Fit And Dimensional Tolerances Mechanical Engineering Drawing

Comments are closed.