Ijms Free Full Text Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis In Covid 19
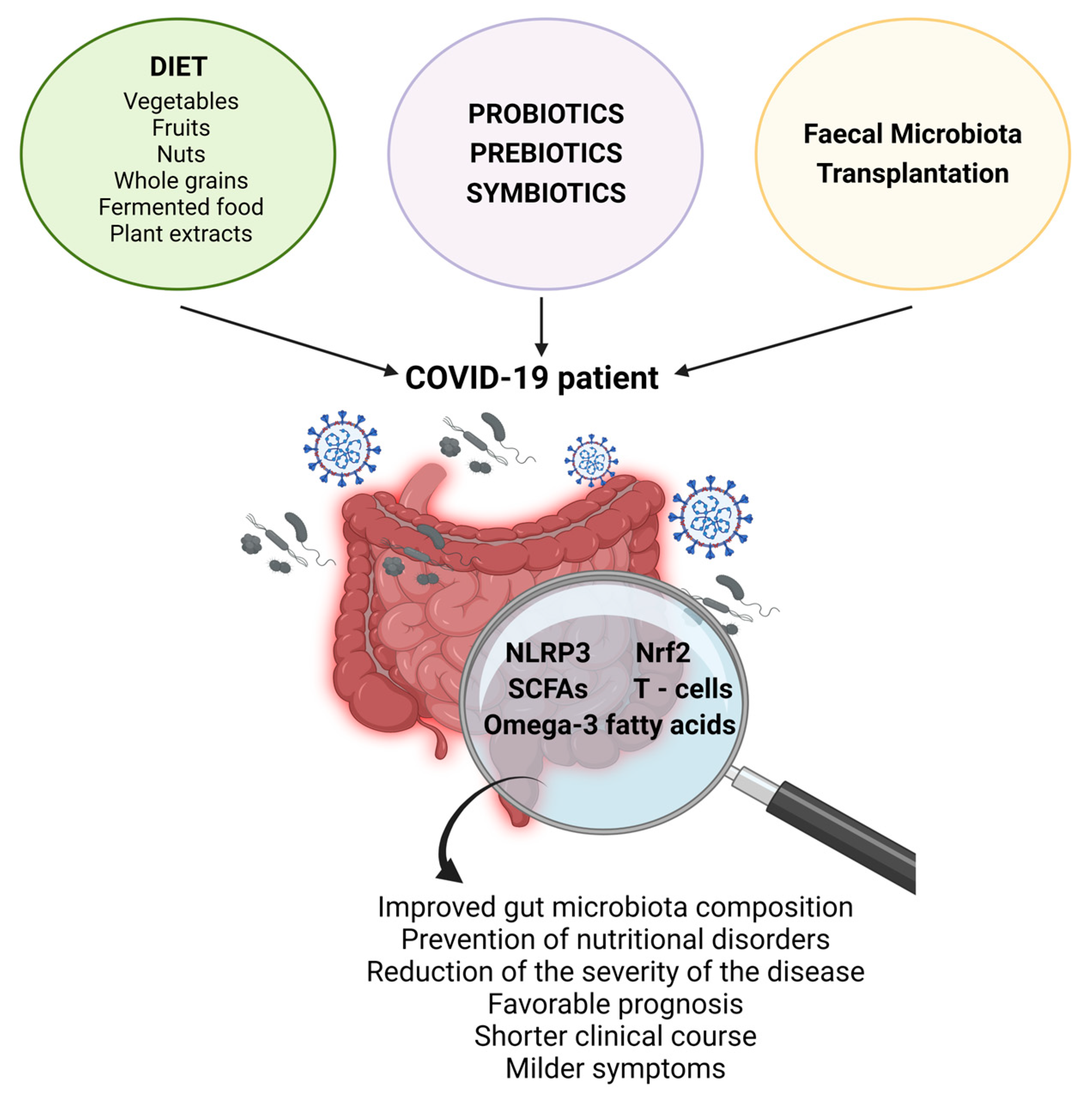
Ijms Free Full Text Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis In Covid 19 Inflammation and oxidative stress are critical underlying mechanisms associated with covid 19 that contribute to the complications and clinical deterioration of patients. additionally, covid 19 has the potential to alter the composition of patients’ gut microbiota, characterized by a decreased abundance of bacteria with probiotic effects. interestingly, certain strains of these bacteria. Many mechanisms may relate the gut microbiota dysbiosis to the development and clinical outcomes of covid 19. covid 19 patients show a diminution of lactobacillus species that may produce lactic acid because of carbohydrate fermentation, and the inactivation of viruses such as sars cov 2 by ph changes.
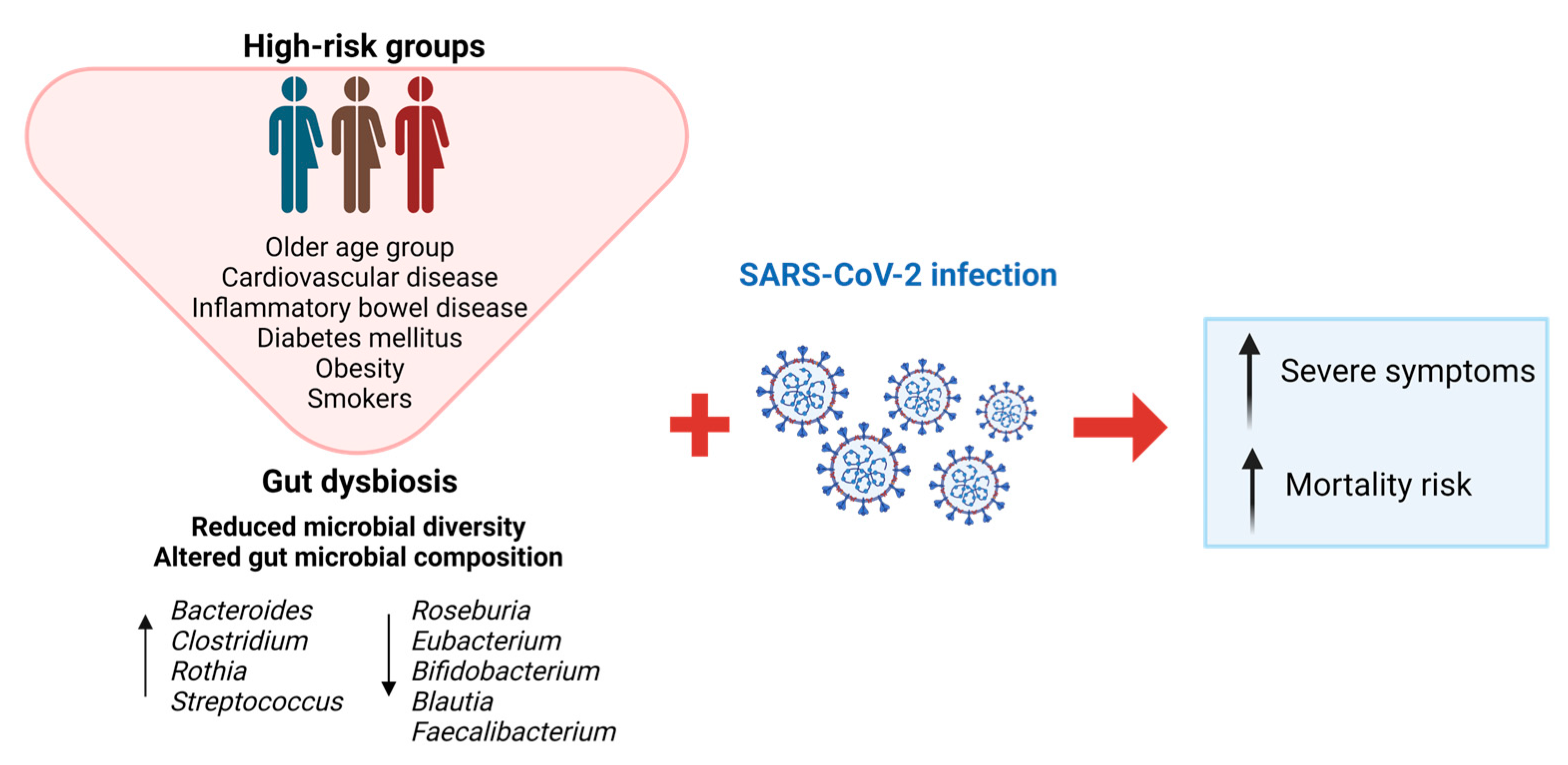
Ijms Free Full Text Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis In Covid 19 Efficient patient triage for covid 19 is vital to manage healthcare resources effectively. this study underscores the potential of gut microbiota (gm) composition as an early biomarker for covid 19 severity. by analyzing gm samples from 315 patients, significant correlations between microbial diversity and disease severity were observed. The gastrointestinal tract is involved in coronavirus disease 2019 (covid 19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (sars cov 2). the gut microbiota has important roles in. The gut microbiota of covid 19 patients exhibited significantly decreased alpha diversity compared to uninfected controls (kruskal wallis p < 0.001, see fig. 2a), in line with previous. Effect of gut dysbiosis in covid 19. current research highlights a notable link between the gut and covid 19. evidence suggests that the virus not only presents in the fecal mucosa but also infiltrates immune cells within the gastrointestinal tract, impacting the gut biome [[29], [30], [31]]. furthermore, the discovery of the angiotensin.

Comments are closed.